Choosing the wrong tile adhesive can lead to costly failures, cracked tiles, and complete reinstallation. I've seen beautiful tile work ruined simply because someone picked the wrong adhesive.
Tile adhesives1 are specialty bonding materials designed to secure tiles to various surfaces. The main types include organic mastics, thin-set mortars, dry-set mortars, latex-modified mortars, epoxy mortars, and medium-bed mortars, each suited for specific applications based on tile size, location, and substrate conditions.

When I first started supplying cellulose ethers2 to mortar manufacturers, I was surprised by how technical tile installation actually is. The right adhesive can make the difference between a lasting installation and a complete failure. Let me walk you through the key types and how our KEHAO additives enhance their performance.
What Are Organic Mastics and When Should You Use Them?
Organic mastics cause headaches for many contractors when used in wet areas. I've had customers call with tiles falling off shower walls because they used the wrong adhesive.
Organic mastics are premixed, ready-to-use adhesives made from organic resins that work best for small wall tiles in dry areas. They should never be used in showers, tub surrounds, or floors due to their poor water resistance and limited strength for heavy tiles.

Organic mastics offer convenience that many contractors appreciate, particularly for quick repairs or small wall installations. These adhesives come ready to use straight from the bucket with no mixing required. Their sticky consistency makes them excellent for vertical applications where tiles need to grip immediately without sliding down.
However, these products come with significant limitations. The organic components in mastics remain somewhat soft even after curing, which means they can't support heavy loads. Additionally, when exposed to moisture, they can reemulsify and lose their bonding properties. This makes them completely unsuitable for wet areas like bathrooms or exterior applications.
In our laboratory tests with clients, we've found that adding small amounts of our HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose) can improve the open time of organic mastics without affecting their grab properties. This gives installers more working time while maintaining the quick-grab properties that make mastics convenient for wall applications.
How Does Thin-Set Mortar Outperform Other Adhesives?
I once visited a factory in UAE where they switched from traditional thick mortar beds to thin-set, reducing their labor costs by 35% while improving bond strength significantly.
Thin-set mortar is a cement-based adhesive typically 3/16" to 1/4" thick that provides excellent bond strength for most tile installations. It contains cement, fine sand, water-retaining agents like HPMC, and often polymer additives for improved flexibility and adhesion.

Thin-set mortar represents one of the most versatile and widely used tile adhesives in modern construction. Unlike traditional thick mortar beds that required 1-2 inches of material, thin-set allows installers to work with a much thinner layer of adhesive, typically just 1/4 inch thick. This advancement has revolutionized tile installation by reducing weight, material costs, and installation time.
The key to thin-set's effectiveness lies in its composition. Portland cement provides the basic binding strength, while fine sand creates the proper texture and body. However, what truly transforms this mixture into an effective adhesive are water-retaining agents like our KEHAO HPMC. These cellulose derivatives prevent water from being absorbed too quickly by porous substrates or evaporating in dry conditions, giving installers adequate working time while ensuring proper cement hydration.
Modern thin-sets often include polymer modifiers that significantly enhance flexibility, adhesion, and water resistance. Our technical team has developed specific grades of Redispersible Polymer Powder (RDP) that, when added to thin-set formulations, improve bond strength by up to 40% and increase flexibility to accommodate substrate movement. This makes thin-set suitable for challenging installations like exterior facades, heated floors, and areas subject to thermal cycling.
What Makes Water-Mixed or Dry-Set Mortar Different?
During my visit to a job site in Saudi Arabia, I noticed contractors struggling with premature drying of their mortar in the intense heat, causing weak bonds and tile failures.
Water-mixed or dry-set mortar is a basic cement-based adhesive containing Portland cement, sand, and water-retentive additives like HPMC. It provides adequate bonding for standard tile installations in normal conditions but lacks the flexibility and strength of modified mortars.

Water-mixed mortar, often called dry-set mortar, forms the foundation of most modern tile installation systems. The distinguishing feature of these mortars is their water retention capability3, which addresses a critical challenge in cement-based adhesives. When cement mixtures lose water too quickly—either through evaporation or absorption into porous substrates—they fail to cure properly, resulting in weak bonds and installation failures.
Our KEHAO HPMC products are specifically engineered for this application, with viscosity profiles designed to maintain optimal water content throughout the curing process. This is particularly crucial in hot, dry climates like those found in many of our export markets including Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Iran, where rapid water loss presents a major challenge for installers.
These unmodified dry-set mortars work adequately for many basic installations on stable substrates with standard ceramic tiles. However, they do have limitations. Without polymer modification4, they lack flexibility to accommodate substrate movement and don't provide sufficient bond strength for challenging applications like large format tiles, exterior installations, or porcelain tiles with their low absorption rates.
For this reason, many of our mortar manufacturing clients have shifted toward incorporating additional additives into their formulations, transforming basic dry-set mortars into more versatile products with enhanced performance characteristics5.
Why Are Latex and Acrylic Mortars Preferred for Demanding Installations?
After a major hotel in Dubai experienced widespread tile failures in their pools, they switched to latex-modified mortars6 with our RDP additive and haven't reported a single failure since.
Latex and acrylic-modified mortars contain polymer additives that significantly enhance flexibility, adhesion strength, and water resistance. These mortars are ideal for demanding installations like exterior facades, large format tiles, porcelain tiles, and areas subject to moisture or movement.

Latex and acrylic-modified mortars represent a significant advancement in tile adhesive technology. By incorporating polymers into traditional cement-based formulations, these mortars achieve performance characteristics that were previously impossible with standard dry-set products. The polymer modification fundamentally changes how the mortar cures and performs over time.
Our KEHAO Redispersible Polymer Powder (RDP)7 plays a crucial role in these advanced formulations. Unlike liquid latex additives that require special handling and mixing on job sites, our powder form allows mortar manufacturers to create pre-blended, single-component products that only require water addition. This simplifies the installation process while ensuring consistent performance.
The polymer particles in these mortars form a flexible network within the cement matrix as the mortar cures. This network provides multiple benefits: it improves adhesion to difficult substrates like existing tile or smooth concrete; it enhances flexibility to accommodate substrate movement from thermal expansion or structural settling; and it creates a more water-resistant bond that performs well in wet areas.
These properties make latex-modified mortars8 particularly valuable for challenging installations. For large format tiles (those with any edge longer than 15 inches), the improved bond strength and flexibility help prevent cracking and lippage issues. For exterior installations, these mortars can withstand freeze-thaw cycles and thermal shock. And for low-absorption tiles like porcelain, the enhanced adhesive properties ensure secure bonding despite the non-porous surface.
When Should You Use Epoxy Mortar for Tile Installation?
I once consulted with a food processing plant that had tried three different adhesive systems before switching to epoxy mortar with our special additives, finally solving their chemical resistance problems.
Epoxy mortar is a high-performance, chemical-resistant adhesive made from epoxy resins and hardeners rather than cement. It provides exceptional bond strength, impermeability to water, and resistance to chemicals, making it ideal for industrial facilities, commercial kitchens, swimming pools, and other demanding environments.

Epoxy mortars represent the highest performance category in tile adhesives, offering exceptional strength and durability in the most demanding environments. Unlike cement-based products, epoxy mortars derive their bonding properties from chemical reactions between epoxy resins and hardeners, creating cross-linked polymer structures that provide remarkable adhesion and chemical resistance.
These specialized adhesives typically come as multi-component systems that must be mixed according to precise ratios. While traditional epoxies were notoriously difficult to work with due to their stiffness and quick setting properties, modern formulations incorporate our KEHAO additives to improve workability without compromising performance. Our specialized cellulose ethers can be incorporated to extend working time and improve trowelability, making these high-performance adhesives more installer-friendly.
The performance advantages of epoxy mortars are substantial, particularly in challenging environments:
| Feature | Benefit | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Withstands acids, alkalis, solvents | Food processing plants, laboratories |
| Water Impermeability | Zero water absorption | Swimming pools, steam rooms |
| High Bond Strength | Exceeds 1000 psi adhesion | Heavy traffic commercial areas |
| Stain Resistance | Prevents staining from foods, chemicals | Commercial kitchens, breweries |
These performance characteristics come at a premium price—epoxy mortars typically cost 4-5 times more than standard thin-set mortars. However, in applications where failure is not an option or where chemical exposure would quickly degrade cement-based adhesives, epoxy mortars provide exceptional value despite their higher initial cost.
What Makes Medium-Bed Mortar Essential for Large Format Tiles?
During a project in India last year, contractors were experiencing lippage with large marble tiles until we recommended medium-bed mortar with our specialized HPMC grade designed for thicker applications.
Medium-bed mortar is specially formulated to be applied in thicker layers (up to 3/4") without shrinking or losing bond strength. It's essential for large format tiles, natural stone, and installations with uneven substrates, allowing installers to compensate for variations while maintaining proper support.

Medium-bed mortars address a critical gap in tile installation systems that has become increasingly important with the growing popularity of large format tiles and natural stone materials. Traditional thin-set mortars are designed to be applied in layers typically not exceeding 1/4 inch, which proves inadequate when working with materials that have natural variations in thickness or when dealing with slightly uneven substrates.
These specialized mortars maintain their volume and strength even when applied in thicker layers—typically up to 3/4 inch—without the shrinkage, cracking, or extended curing times that would occur with standard thin-sets used at these thicknesses. This capability is particularly valuable when installing natural stone tiles like marble, granite, or limestone, which often vary significantly in thickness even within the same batch.
The formulation of medium-bed mortars requires careful engineering of both the aggregate composition and the binding system. Our KEHAO HPMC products play an essential role here, as they must provide water retention across a thicker mortar layer while still allowing proper curing throughout the entire thickness. We've developed specific grades with modified viscosity profiles that perform exceptionally well in these applications.
Additionally, medium-bed mortars typically incorporate our redispersible polymer powders to enhance flexibility and adhesion. This is crucial when working with large format tiles, as the larger the tile, the more critical proper bonding becomes. A 24" x 48" porcelain tile with even 10% bond coverage failure can lead to cracking under load, while the same percentage of failure on a small mosaic tile might never cause issues.
What Key Factors Should Guide Your Tile Adhesive Selection?
I remember a contractor in Pakistan who spent thousands on imported Italian tile but used the cheapest adhesive he could find—the entire installation failed within months, wasting both the beautiful tile and his reputation.
The key factors in choosing tile adhesive include the installation location (wet vs. dry, interior vs. exterior), tile type and size, substrate conditions, and performance requirements. Matching these factors to the appropriate adhesive type prevents costly failures and ensures long-lasting installations.
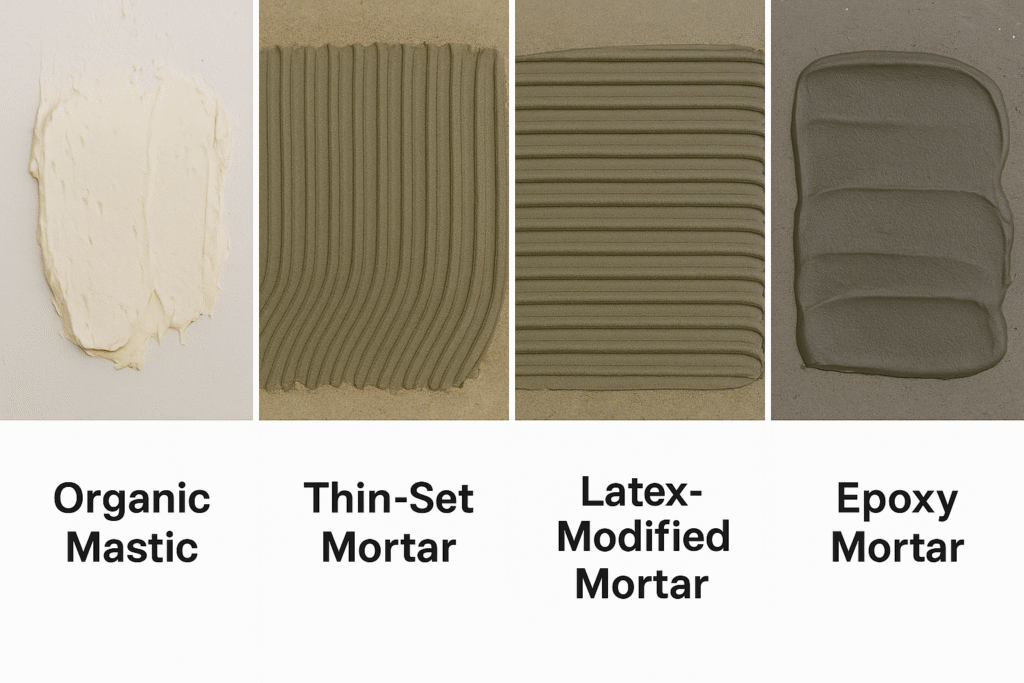
Selecting the appropriate tile adhesive requires careful consideration of multiple factors that influence installation success. This decision should never be based solely on price, as the adhesive typically represents only about 5-10% of the total installation cost but can determine whether a $50,000 tile job succeeds or fails completely.
The first consideration must be the installation environment. Exterior applications require adhesives with excellent freeze-thaw stability and water resistance, making polymer-modified mortars or epoxies the preferred choices. Wet interior areas like showers and tub surrounds similarly need water-resistant formulations, while dry wall areas might perform adequately with simpler adhesives.
Tile characteristics significantly impact adhesive selection:
| Tile Type | Special Requirements | Recommended Adhesive |
|---|---|---|
| Porcelain | Low absorption requires high adhesion | Polymer-modified thin-set |
| Natural Stone | Variable thickness, potential staining | Medium-bed mortar, non-staining |
| Glass Tile | Non-porous, translucent | White thin-set with high polymer content |
| Large Format (>15") | Requires excellent coverage | Medium-bed or specialized large tile mortar |
| Mosaic | Often in wet areas | Polymer-modified thin-set |
Substrate conditions present another critical variable. Concrete slabs with minor variations might require medium-bed mortars to achieve flat results. Wood subfloors need highly flexible adhesives to accommodate movement. Difficult surfaces like existing tile or smooth concrete demand adhesives with enhanced bonding properties.
At KEHAO, we work closely with mortar manufacturers to formulate products that address these specific challenges. Our technical team provides customized HPMC and RDP solutions that enable manufacturers to create adhesives optimized for their local markets and specific application requirements.
How Can KEHAO Additives Optimize Tile Adhesive Performance?
After one of my clients in Brazil incorporated our specialized HPMC grade into their tile mortar formula, they reported a 40% reduction in callback repairs and warranty claims.
KEHAO additives like HPMC and RDP significantly enhance tile adhesive performance by improving water retention, workability, open time, flexibility, and bond strength. Our customized solutions help manufacturers create high-performance adhesives optimized for specific applications and local conditions.
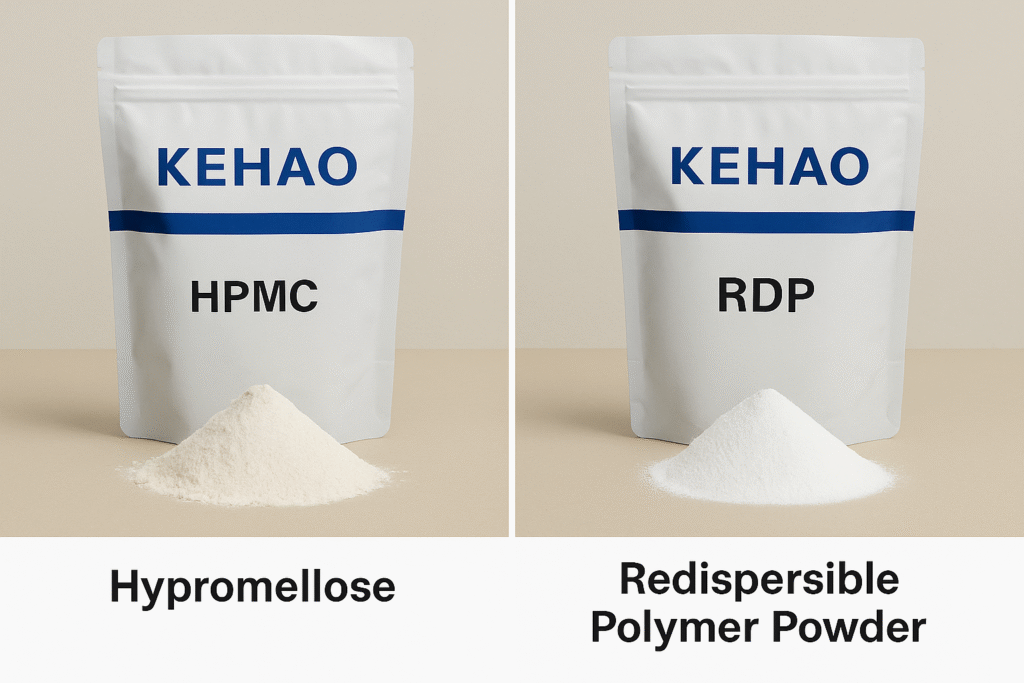
Our KEHAO additives play a crucial but often invisible role in tile adhesive performance. While end users may never know these components exist, they fundamentally determine how well an adhesive performs in real-world conditions. Through our six production lines and extensive R&D facilities, we've developed specialized grades of cellulose ethers and redispersible polymers that address the specific challenges faced in tile installation.
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) forms the foundation of most quality tile adhesives by providing essential water retention properties. This seemingly simple function actually solves multiple complex problems: it prevents water from being absorbed too quickly into porous substrates like concrete or gypsum board; it slows water evaporation in hot or windy conditions; and it ensures that cement has sufficient water for complete hydration and strength development.
Our KEHAO HPMC products are carefully engineered with specific viscosity profiles, particle sizes, and modification levels to optimize performance for different application requirements:
| HPMC Grade | Specialized Function | Benefit in Tile Adhesive |
|---|---|---|
| KH-P200 | High water retention | Extended open time in dry conditions |
| KH-P150 | Rapid dissolution | Fast mixing in production |
| KH-P100 | Medium viscosity | Excellent sag resistance for wall applications |
| KH-P50 | Low substitution | Compatible with specialty cements |
Beyond cellulose ethers, our redispersible polymer powders (RDP) transform basic mortars into high-performance adhesives. These spray-dried polymer emulsions redisperse when mixed with water, forming flexible polymer films within the cement matrix as the adhesive cures. This enhances adhesion to difficult substrates, improves deformability to accommodate movement, and increases tensile strength to prevent cracking.
Our technical team works directly with mortar manufacturers to develop customized formulations that address their specific challenges. Whether it's extreme climate conditions in Saudi Arabia, high-rise construction in Singapore, or large-format tile installations in Brazil, we provide tailored solutions that optimize performance for local requirements.
One area where our additives make a significant difference is in extending open time—the period during which tiles can be placed after adhesive application. In hot, dry climates like the Middle East, standard mortars may form a skin within minutes, making proper tile placement difficult. Our specialized HPMC grades can extend this working time by up to 30 minutes, preventing wasted material and ensuring proper bonding.
Similarly, our RDP products enhance adhesive strength on challenging surfaces. Modern construction often involves tiling over existing finishes or highly smooth concrete, where traditional mortars struggle to form adequate bonds. By incorporating our polymers at recommended dosages, manufacturers can create adhesives with bond strengths exceeding 250 psi, well above industry standards for even the most demanding applications.
Conclusion
Choosing the right tile adhesive requires understanding both the installation requirements and adhesive properties. With KEHAO additives, manufacturers can create high-performance products that ensure lasting installations, preventing costly failures and delivering superior results.
-
Understanding tile adhesives is crucial for successful installations. Explore this link to learn about their types and applications. ↩
-
Exploring cellulose ethers can provide insights into improving adhesive strength and durability in tile installations. ↩
-
Understanding water retention capability is crucial for ensuring strong tile installations, especially in challenging environments. ↩
-
Exploring polymer modification can reveal how it enhances flexibility and bond strength in tile installations. ↩
-
Learn about enhanced performance characteristics to improve the durability and effectiveness of your tile installations. ↩
-
Discover the advantages of latex-modified mortars, which can prevent failures in demanding tile applications. ↩
-
Discover how KEHAO RDP enhances tile adhesive performance and simplifies installation, making it a game-changer in the industry. ↩
-
Learn about the unique benefits of latex-modified mortars, including improved adhesion and flexibility for challenging installations. ↩







