Many contractors struggle with mortar workability1 and durability issues. Poor adhesion and rapid water loss lead to cracking, weak bonds, and project failures, costing you time and money.
HPMC2 (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) synergizes with redispersible polymer powder3 in mortars by creating a complementary system where HPMC provides water retention and improved workability, while RDP enhances adhesion, flexibility, and durability. Together, they create stronger, more reliable mortar systems with extended working time.

As a manufacturer with six production lines dedicated to construction chemicals4, I've seen countless projects transformed by the right combination of HPMC2 and redispersible polymer powder3. The synergy between these materials isn't just theoretical—it's a practical solution that addresses common challenges in modern construction. Let's explore how these two additives work together to create superior mortar formulations.
What is the Use of Redispersible Polymer Powder in Mortars?
Are you noticing poor adhesion and early cracking in your cement-based applications? Traditional mortars often fail when bonding to smooth surfaces or when subjected to movement, leading to costly repairs.
Redispersible polymer powder (RDP) improves mortar by forming flexible polymer films that enhance adhesion to difficult substrates, increase flexibility, reduce cracking, and improve water resistance. It transforms brittle cement-based materials into versatile compounds suitable for modern construction demands.

During my visits to construction sites across Saudi Arabia and the UAE, I've observed first-hand how RDP transforms ordinary mortars into high-performance building materials. The powder consists of polymer particles that redisperse in water during mixing, forming a latex similar to liquid polymers but with the convenience and stability of a dry powder.
Key Benefits of RDP in Mortar Formulations
RDP works by forming polymer films throughout the cement matrix as water evaporates. These films create bridges between cement particles and substrates, dramatically improving bond strength even on challenging surfaces like extruded polystyrene boards, old concrete, or glass.
| Property | Improvement with RDP | Real-world Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesion | +40-300% depending on substrate | Drastically reduced delamination and failure |
| Flexibility | Improved deformation capability | Better resistance to cracking from thermal cycles |
| Impact Resistance | Enhanced toughness | Reduced damage from physical impacts |
| Water Resistance | Decreased water absorption | Better durability5 in wet environments |
The dosage typically ranges from 1-5% for basic applications like rendering mortars, up to 5-10% for specialized applications like tile adhesives for non-porous tiles. I've found that our customers in hotter climates often benefit from slightly higher dosages to counteract the rapid drying conditions that can compromise proper film formation.
What is the Water Retention Mechanism of HPMC2 in Cement Mortar?
Have you ever applied mortar that dried too quickly, leaving a weak, dusty surface? Fast water loss can ruin mortar performance, especially in hot, dry environments where our customers often work.
HPMC retains water in cement mortar through formation of a reversible hydrogel network that physically traps water molecules and increases solution viscosity. This mechanism slows evaporation and cement hydration, ensuring optimal curing conditions and preventing premature drying.

I remember visiting a large construction project in Dubai where workers were struggling with rapid drying of render in 40°C heat. After recommending our high-viscosity HPMC6, the difference was remarkable—extended working time and proper hydration transformed their results.
How HPMC Creates Water Retention Effects
The water retention mechanism of HPMC in cement mortar is a fascinating process that combines chemical and physical principles. When HPMC dissolves in the mixing water, its molecular chains unfold and form a three-dimensional network throughout the mortar. This network functions through several mechanisms:
| Mechanism | How It Works | Impact on Mortar |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bonding | HPMC molecules form hydrogen bonds with water | Water becomes "bound" and less prone to evaporation |
| Viscosity Increase | Dissolved HPMC increases solution viscosity | Reduces water migration speed within the mortar |
| Gel Formation | HPMC creates a temporary gel structure | Physical barrier that slows water movement |
| Surface Film | Forms a microscopic film on exposed surfaces | Reduces evaporation rate at the air interface |
The effectiveness of HPMC for water retention increases with both molecular weight and concentration. Typically, a dosage of 0.2-0.5% by weight of dry mortar components provides effective water retention. This seemingly small amount makes a tremendous difference because each HPMC molecule can bind multiple water molecules.
In our laboratory tests, we've observed that cement mortars without HPMC can lose up to 40% of their mixing water in the first hour in hot conditions, while those with optimized HPMC formulations retain more than 90% during the same period—a critical difference for proper cement hydration.
What is the Difference Between RDP and HPMC2?
Confused about when to use RDP versus HPMC in your formulations? Many customers mix these additives without understanding their distinct functions, leading to expensive over-formulation or underperformance.
RDP and HPMC serve different primary functions: RDP improves adhesion, flexibility, and impact resistance by forming polymer films, while HPMC provides water retention, workability, and sag resistance through viscosity modification. They have different chemical compositions and complementary performance benefits.

During a technical seminar I conducted for our distributors in Pakistan last year, the most common question was about the interchangeability of these additives. The answer is clear: they cannot replace each other, but work best as partners in an optimized formulation.
Comparing Key Properties of RDP and HPMC
Understanding the fundamental differences between these two additives helps formulators achieve balanced mortar systems. While both are white powders added to dry mortar mixes, their chemical nature and functions differ significantly:
| Property | RDP | HPMC |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Basis | Polymer (often VAE, VA/VeoVa, or acrylics) | Cellulose derivative (modified plant material) |
| Primary Function | Adhesion enhancement | Water retention |
| Secondary Benefits | Flexibility, cohesion, water resistance | Workability, sag resistance, open time |
| Working Mechanism | Forms polymer films | Creates hydrogel network |
| Typical Dosage | 1-10% | 0.1-0.5% |
| Cost Impact | Higher (major cost contributor) | Lower (minor cost contributor) |
| Heat Sensitivity | More sensitive to extreme heat | Less sensitive to temperature |
I've found that explaining these differences to our customers helps them make more informed decisions about formulation optimization. For example, a customer making exterior insulation finishing systems (EIFS) needed to balance cost with performance. By understanding these differences, we optimized their formula with 3% RDP and 0.25% HPMC, achieving excellent adhesion and workability while saving them approximately 15% in raw material costs compared to their previous formulation.
The synergistic effect is particularly evident in applications requiring both good workability and strong adhesion, such as tile adhesives. In these cases, HPMC ensures proper hydration and extended open time, while RDP delivers the essential bond strength to non-porous tiles.
What is the Use of HPMC in Concrete?
Struggling with concrete workability, segregation, or pumping issues? Traditional concrete often presents challenges in special applications, leading to poor placement and reduced strength.
HPMC serves multiple functions in concrete by improving water retention, enhancing workability, reducing segregation, increasing pumpability, and controlling setting time. It's particularly valuable in shotcrete, self-leveling concrete7, and applications requiring extended workability.
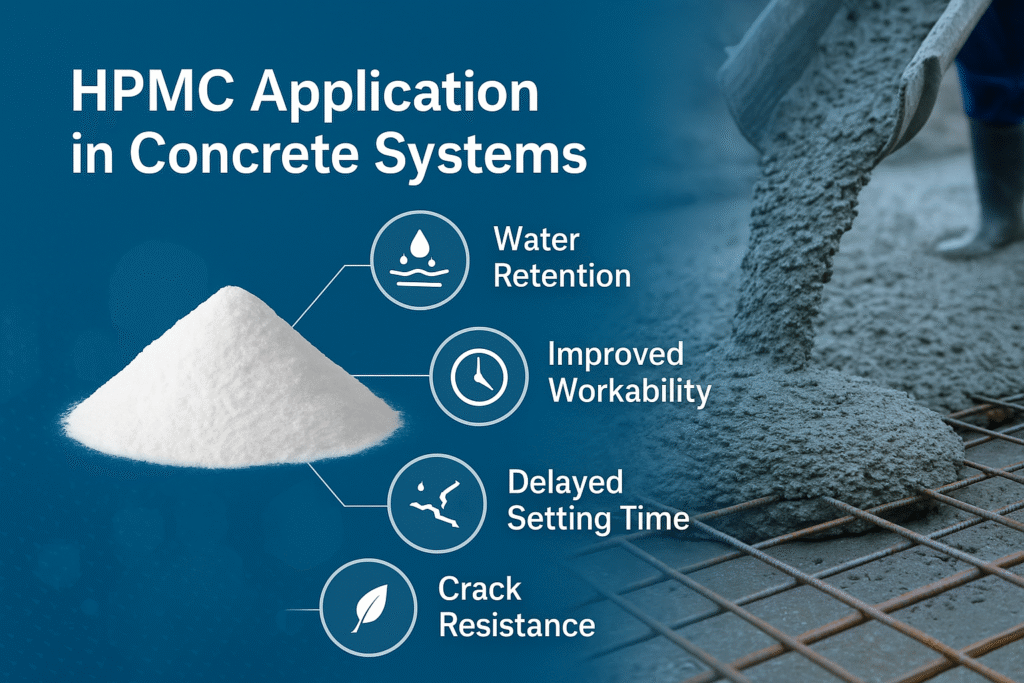
I've worked with several ready-mix concrete suppliers who faced challenges with concrete pumpability on high-rise buildings. Adding just 0.1% of our HPMC significantly improved pump performance and reduced segregation, saving them considerable time and resources.
How HPMC Transforms Concrete Performance
While HPMC is used at lower concentrations in concrete than in mortars, its impact remains substantial. The addition of HPMC affects concrete in several important ways:
| Benefit | Mechanism | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Bleeding | Increased viscosity prevents water separation | High-rise column casting where bleeding causes weakened zones |
| Improved Cohesion | Water-binding effect keeps mix together | Underwater concrete placement with reduced washout |
| Controlled Rheology | Viscosity modification | Pumped concrete with reduced pressure requirements |
| Air Entrainment | Surface activity stabilizes air bubbles | Freeze-thaw resistant concrete in cold climates |
| Extended Setting | Delayed cement hydration | Hot-weather concreting with difficult logistics |
The dosage of HPMC in concrete is typically lower than in mortars, ranging from 0.05% to 0.2% of cement weight. This small addition creates notable improvements in fresh concrete properties without significantly affecting final strength development.
In self-leveling concrete applications, HPMC works alongside superplasticizers to create a paradoxical effect: high flow combined with high cohesion. Without HPMC, highly fluid concretes would suffer from severe segregation and bleeding. I've demonstrated this effect to skeptical customers by showing comparative samples with and without HPMC—the difference in homogeneity is immediately apparent.
For shotcrete applications in tunneling and mining, HPMC reduces rebound (wasted material) by up to 30% while improving bond to irregular surfaces. A mining customer in South Africa reported savings of over $50,000 per month after implementing our recommended HPMC grade in their shotcrete mix.
Conclusion
HPMC2 and RDP create a powerful synergy in mortars—HPMC retains water and improves workability while RDP enhances adhesion and flexibility. Together, they solve common mortar problems and deliver superior performance across diverse construction applications.
-
Explore effective techniques to enhance mortar workability, ensuring better application and durability. ↩
-
Learn about HPMC's role in enhancing mortar properties and its benefits in construction. ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩
-
Discover how redispersible polymer powder transforms mortars and improves adhesion. ↩ ↩
-
Stay updated on the latest innovations and trends in construction chemicals for better performance. ↩
-
Learn about the essential elements that enhance the durability of mortar in construction. ↩
-
Learn about high-viscosity HPMC and its benefits in enhancing mortar performance. ↩
-
Explore the advantages of self-leveling concrete for achieving smooth surfaces. ↩







