Selecting the wrong HPMC for your paint formulation can lead to costly batch failures, customer complaints, and wasted resources. Most manufacturers focus solely on viscosity, missing critical parameters that ensure product stability.
The ideal HPMC1 for paints and coatings should balance viscosity grade with leveling properties while ensuring complete solubility, proper particle size, and enzyme resistance. These factors prevent sagging during application, eliminate brush marks, and maintain long-term stability throughout the product's shelf life.

I've worked with hundreds of paint manufacturers across developing markets, and I keep seeing the same costly mistakes. Whether you're producing interior wall paints in Saudi Arabia or exterior coatings in Vietnam, understanding these key parameters will save you money and reputation. Let me show you what really matters when selecting HPMC for your formulations.
What are the different grades of HPMC1 for coatings?
Paint manufacturers often get overwhelmed by the many HPMC grades2 available. Without proper guidance, they waste money on unnecessarily expensive grades or compromise quality with insufficient ones.
HPMC grades for coatings primarily differ in viscosity (ranging from 3,000 to 100,000 mPa·s), methoxyl content (E or K types), hydroxypropyl content, and particle size. E-type HPMCs with viscosities between 15,000-40,000 mPa·s are most common for standard interior paints.

Diving deeper into HPMC grades reveals important considerations beyond basic specifications. From my experience working with paint factories across the Middle East and Asia, the selection process should be systematic. Here's a breakdown of how these grades function in different coating applications:
HPMC1 Grade Selection by Application Type
| Paint Type | Recommended HPMC Grade | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Interior Flat | HPMC E15-E25 | Balanced sag resistance and leveling |
| Interior Semi-gloss | HPMC E5-E15 | Enhanced flow and leveling |
| Exterior Paints | HPMC K15-K35 | Better water resistance |
| Textured Coatings | HPMC E30-E50 | Superior thickening and pattern retention |
| Spray Applications | HPMC E3-E5 | Low viscosity for spray equipment |
I've found that many manufacturers in developing markets initially select solely based on price, but this approach often leads to reformulation costs that far exceed any initial savings. The key is matching the grade to your specific manufacturing process, application method, and expected environmental conditions. For instance, paints sold in high-humidity regions like Vietnam or the Philippines benefit significantly from K-type HPMC with its superior moisture resistance.
What is the role of HPMC1 in coating?
Many paint manufacturers add HPMC without fully understanding its function. This leads to formulation imbalances, application problems, and customer complaints about coverage and durability.
HPMC serves multiple crucial functions in coatings: it acts as a thickener to prevent sagging, provides water retention to extend working time, enhances suspension of pigments, improves film formation, and contributes to consistent application properties. Its pseudoplastic behavior allows paint to flow when applied but resist dripping.

Diving deeper into HPMC's role reveals how this versatile polymer transforms ordinary paint formulations into high-performance coatings. I've consulted with numerous factories throughout Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Pakistan where understanding these mechanisms has helped optimize their formulations.
HPMC's thixotropic properties create what formulators call "controlled rheology" – the paint thins under shear stress (during brushing or rolling) but quickly rebuilds viscosity when the stress stops. This behavior isn't just convenient; it's essential for preventing defects like sagging while ensuring smooth application.
The water retention capability of HPMC deserves special attention, especially for markets with hot, dry climates like Saudi Arabia and Iran. By forming a hydrophilic gel structure, HPMC slows water evaporation during the critical film formation period. Without sufficient water retention, premature drying leads to poor film integrity, reduced coverage, and adhesion failures – problems I've seen plague many manufacturers in these regions.
Beyond mechanical properties, HPMC contributes significantly to paint stability. Its protective colloid function prevents pigment agglomeration during storage, maintaining color consistency and preventing settling. The right HPMC grade can extend shelf life by months, a critical advantage in markets with challenging distribution channels like we see across developing Asian and Middle Eastern markets.
What is the difference between HPMC E3 and E5?
Manufacturers frequently misunderstand viscosity grades, thinking higher numbers automatically mean better performance. This misconception leads to unnecessary costs and potential application issues.
HPMC E3 and E5 differ primarily in viscosity - E3 creates a 3,000 mPa·s solution while E5 produces 5,000 mPa·s under standard testing conditions. E3 provides better leveling and is suitable for spray applications, while E5 offers improved sag resistance for brush applications. Both maintain similar chemical structures.

Diving deeper into these differences reveals practical implications that directly impact your coating performance and production costs. I've guided many manufacturers in countries like Pakistan and Mexico through this selection process to optimize their formulations for specific applications.
The viscosity difference may seem subtle on paper, but in practice, it dramatically influences application behavior. When formulating with HPMC E3, coatings exhibit superior flow characteristics that allow brush marks to level out more completely. This makes E3 the preferred choice for high-end interior finishes where surface perfection is paramount. In contrast, E5's higher viscosity provides enhanced anti-sag properties critical for ceiling applications or thick film builds.
This viscosity difference also affects the dosage required in your formulation. Typically, you'll need approximately 15-20% less HPMC E5 compared to E3 to achieve comparable viscosity in the final product. However, this doesn't automatically translate to cost savings - the true value depends on your specific application requirements and the end-user experience.
Beyond viscosity, there are subtle differences in dissolution rates that affect production efficiency. In my work with factories across India and Brazil, I've observed that E3 tends to hydrate slightly faster than E5 under identical conditions, potentially reducing production cycle times. However, this advantage diminishes if your facility uses heated water or high-shear mixing equipment.
For manufacturers dealing with export markets where products face varying application temperatures, the temperature stability profile becomes crucial. HPMC E3 typically shows less viscosity fluctuation across temperature ranges compared to E5, providing more consistent application properties in diverse climates - a significant advantage for exporters in Singapore serving various Southeast Asian markets.
What is the difference between HPMC E and K?
Many paint formulators make chemical substitutions without understanding how HPMC's molecular structure affects performance. This leads to incompatibility issues and reformulation costs.
HPMC E-type and K-type differ in their methoxyl content: E-type has 28-30% methoxyl groups while K-type has 19-24%. This makes E-type dissolve in cold water but gel in hot water, offering better workability. K-type provides superior water resistance and mechanical stability, making it ideal for exterior coatings.
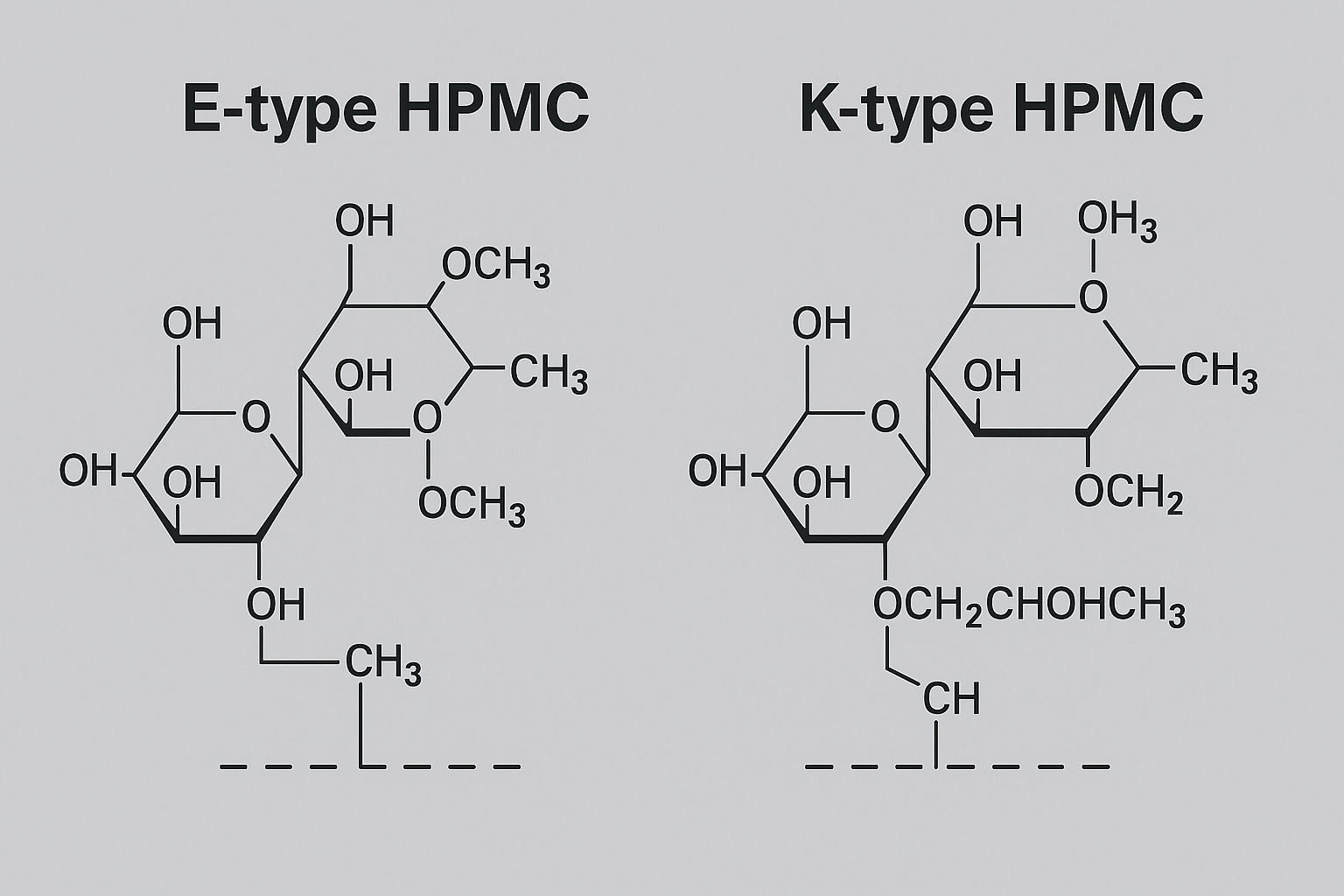
Diving deeper into this chemical distinction reveals practical implications for paint manufacturers across different climates and applications. Having worked with factories throughout regions like the Middle East and Southeast Asia, I've seen how this choice significantly impacts final product performance.
The methoxyl content difference creates distinctly different interactions with water molecules. E-type HPMC forms more hydrophobic interactions due to its higher methoxyl content, resulting in excellent water retention during the critical film formation phase. This makes it particularly valuable in hot, dry climates like Saudi Arabia and UAE, where premature drying is a common application challenge.
K-type, with its lower methoxyl content, forms stronger hydrogen bonds within the dried film, creating a more water-resistant matrix. This chemical behavior translates directly to improved washability and scrub resistance - critical properties for high-traffic areas and exterior applications. In high-humidity markets like Vietnam and the Philippines, K-type HPMC helps prevent moisture-related coating failures like blistering and peeling.
The temperature response also differs significantly between these types. E-type HPMC exhibits more pronounced thermal gelation (transitioning from solution to gel at elevated temperatures), which can be advantageous for controlling application properties but may present challenges during hot-weather application. K-type shows more stability across temperature ranges, an important consideration for products used in regions with extreme seasonal variations.
When formulating multi-component systems, the compatibility profile becomes critical. Through my work with manufacturers in countries like Iran and Pakistan, I've observed that E-type HPMC generally offers better compatibility with acrylic emulsions and certain surfactants, while K-type excels in systems containing higher PVC (Pigment Volume Concentration) and certain inorganic fillers.
Compatibility Chart: HPMC Types with Common Paint Components
| Component | Compatibility with E-Type | Compatibility with K-Type |
|---|---|---|
| Acrylic Emulsions | Excellent | Good |
| Calcium Carbonate | Good | Excellent |
| TiO₂ Pigments | Excellent | Excellent |
| Silicone Additives | Good | Very Good |
| Surfactants | Very Good | Good |
Conclusion
Selecting the right HPMC1 for your paint formulation requires balancing viscosity grade with leveling properties while ensuring complete solubility, proper particle size, and enzyme resistance. These factors directly impact your product quality, production efficiency, and customer satisfaction.






