Self-leveling mortar faces a tough challenge: it needs to flow like water while avoiding separation of components. Without proper additives, you'll end up with water rising and sand sinking, ruining your floor project completely.
HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose)1 solves this fundamental contradiction by creating an invisible 3D gel network that gently suspends all particles, preventing separation while allowing flow when force is applied. It's the essential ingredient that makes true self-leveling possible.

When I first started helping customers with self-leveling mortar2 formulations, I saw many failed attempts - either too stiff to level or too runny with materials separating. The key problem was always finding the right balance between flowability and stability. Let me share why HPMC has become indispensable for solving this problem.
What is the Purpose of HPMC in Self-Leveling Mortar?
Self-leveling floors often fail because standard additives can't maintain suspension while allowing proper flow. Without the right cellulose ether, you'll face constant frustration with uneven surfaces and weak final strength.
HPMC forms a temporary three-dimensional network within the mortar that suspends cement and sand particles while still allowing the mixture to flow when pressure is applied. This thixotropic behavior is essential for achieving true self-leveling properties while preventing component separation.

The magic of HPMC lies in its unique molecular structure that creates what I call a "smart suspension system." When I explain this to customers, I often use this analogy: imagine a crowd of people (the sand and cement particles) standing in a hall. Without HPMC, when the floor tilts (when you pour the mortar), everyone rushes to the bottom in a disorganized way. With HPMC, it's like everyone is connected by elastic bands - they still move toward the lower side but in a controlled, unified motion.
HPMC's hydroxypropyl and methyl groups give it this remarkable dual functionality. The hydrophobic parts interact with cement particles while hydrophilic sections bind water, creating a balanced matrix. This property makes it vastly superior to basic methylcellulose for self-leveling applications.
HPMC Performance Comparison in Self-Leveling Mortar
| Property | Without HPMC | With HPMC |
|---|---|---|
| Flowability | Poor or excessive | Controlled and consistent |
| Component stability | Separation occurs | Particles remain suspended |
| Water retention | Low | High (80-95%) |
| Setting time | Irregular | Controlled |
| Final surface | Uneven, weak spots | Smooth, consistent strength |
What is the Purpose of Methylcellulose in Compounding?
Many mortar manufacturers struggle with material compatibility in complex formulations. Poor compounding leads to lumps, inconsistent performance, and wasted materials that cost you time and money.
Methylcellulose serves as a compatibility agent in mortar compounding, helping diverse ingredients blend harmoniously. It prevents premature reactions between components, improves mixing efficiency, and ensures uniform distribution of additives throughout the mixture.

When developing formulations for our clients across various regions, I've found that the compounding phase is often overlooked but critically important. In self-leveling mortars particularly, we're typically combining cement, various aggregates, accelerators, retarders, superplasticizers, and anti-foaming agents - each with potential incompatibilities.
Methylcellulose creates what I call a "molecular buffer zone" between reactive components. Its polymer chains physically position themselves between potentially reactive particles, preventing premature cement hydration and unwanted chemical interactions during the dry-mixing and early wet-mixing phases.
The compounding benefits extend beyond just preventing incompatibilities. I've observed that properly incorporated methylcellulose significantly improves the homogeneity of the final product. This translates to consistent performance across batches and reduced quality control issues. For industrial producers, this means fewer customer complaints and more reliable performance even when mortar is mixed in various conditions on job sites.
Impact of Methylcellulose on Component Interaction
| Component Pair | Without Methylcellulose | With Methylcellulose |
|---|---|---|
| Cement + Superplasticizer | Risk of rapid slump loss | Maintained workability |
| Accelerator + Retarder | Unpredictable setting | Controlled, predictable setting |
| Cement + Air Entrainers | Irregular air void structure | Uniform micro-air distribution |
| Fine + Coarse Aggregates | Segregation during mixing | Maintained particle distribution |
What is HPMC Used For in Construction?
Construction projects often suffer from material failures caused by environmental challenges. Without proper additives, your mortars and concretes may crack, lose strength, or fail to adhere properly in varying conditions.
HPMC enhances construction materials by improving water retention, workability, adhesion strength, and sag resistance. It extends open time for better application, prevents rapid drying in hot environments, and ensures proper cement hydration for maximum strength development.
Throughout my years working with construction material manufacturers across diverse climates - from the scorching heat of Saudi Arabia to the humid conditions in Southeast Asia - I've seen HPMC consistently solve problems that other additives simply cannot address.
The water retention capability of HPMC is particularly valuable in construction applications. When applying mortars in hot, dry environments or on highly absorbent substrates like old concrete or brick, water can be drawn out before cement properly hydrates. HPMC creates a moisture barrier that slows this process down, essentially forming a microscopic water reservoir within the material. I've measured up to 95% water retention in our laboratory tests with properly formulated HPMC mixtures.
Beyond water retention, HPMC significantly improves the adhesion of mortars to difficult substrates. This is crucial for rendering, tiling, and repair applications. The polymer forms physical bridges between the mortar and substrate while also improving wetting of the surface. I've recorded adhesion strength improvements of 30-60% when optimal HPMC grades are incorporated into mortars.
HPMC Benefits Across Construction Applications
| Application | HPMC Benefit | Practical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Tile Adhesives | Extended open time | More tiles placed before skinning occurs |
| Renders/Plasters | Improved workability | Easier application, reduced applicator fatigue |
| Repair Mortars | Enhanced adhesion | Better bonding to old substrates, fewer failures |
| Joint Compounds | Better sag resistance | Clean installations without material slumping |
| Self-leveling Compounds | Controlled flow | Perfect leveling without material separation |
What is Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Used For in Construction?
Working with unskilled labor or in extreme weather conditions makes proper material application nearly impossible. Traditional formulations fail when faced with real-world job site variables, causing project delays and costly rework.
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) modifies construction materials to be more forgiving during application, resist weather extremes, and maintain performance despite variable mixing and application techniques. It creates more consistent results across different environmental conditions and worker skill levels.

When I visit construction sites where our HPMC is being used, I'm always struck by the variability of real-world conditions. Laboratory formulations must translate to practical performance in unpredictable environments. HPMC helps bridge this gap by making materials more robust against application variables.
The hydroxypropyl group modification gives this cellulose derivative enhanced temperature stability compared to regular methylcellulose. This chemical distinction is crucial for performance in extreme environments. I've tested formulations in climate chambers simulating desert heat (45°C/113°F) and found that HPMC-modified mortars maintained workable consistency 40-60% longer than those with standard cellulose ethers.
Water quality is another real-world variable that HPMC helps overcome. In developing markets where my customers operate, water can contain various impurities that interfere with cement hydration and additive performance. HPMC's molecular structure makes it more tolerant of dissolved minerals and slight alkalinity in mixing water. This translates to more consistent performance regardless of water source - a critical advantage when working across various regions with different water quality standards.
HPMC Performance in Variable Construction Conditions
| Condition Variable | Impact Without HPMC | Impact With HPMC |
|---|---|---|
| High Temperature (35°C+) | Rapid drying, incomplete hydration | Maintained workability, proper strength development |
| Variable Water Quality | Inconsistent setting, strength issues | Consistent performance despite impurities |
| Unskilled Application | Uneven thickness, poor finish | More forgiving application window, better finish |
| Highly Absorbent Substrates | Rapid moisture loss, weak bond | Maintained moisture, strong adhesion |
| Low Humidity Environments | Surface cracking, dusting | Proper curing, intact surface |
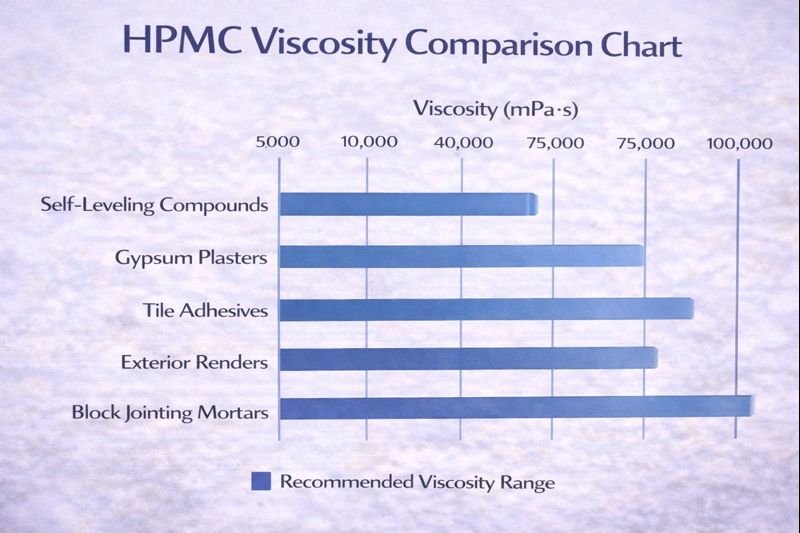
HPMC Viscosity Selection Guide
Choosing the wrong HPMC viscosity destroys your mortar performance. Too low, and you get separation and bleeding; too high, and your product becomes unworkable, wasting time and materials on formulations that simply won't perform.
Select HPMC viscosity based on your specific application requirements: 15,000-30,000 mPa·s for self-leveling compounds, 100,000+ mPa·s for vertical applications like renders, and 40,000-80,000 mPa·s for general-purpose mortars. Match viscosity to your application method and desired flow characteristics.
Throughout my years helping customers optimize formulations, I've found that viscosity selection is often misunderstood. Many formulators initially believe that higher viscosity always means better performance, but this oversimplification leads to problems.
Viscosity in HPMC is fundamentally about molecular chain length - higher viscosity grades have longer polymer chains that create stronger networks in water. For self-leveling applications specifically, we need to balance the network strength with the need for flow. I typically recommend 15,000-30,000 mPa·s for self-leveling compounds because this range creates sufficient particle suspension while still allowing proper flow under gravity.
The relationship between viscosity and concentration is also crucial to understand. You can achieve similar rheological effects with different combinations of viscosity and dosage. For example, 0.3% of a 100,000 mPa·s HPMC might create similar flow characteristics to 0.5% of a 60,000 mPa·s grade. However, these will behave differently under varying shear conditions and provide different water retention levels.
HPMC Viscosity Application Guide
| Viscosity Range (mPa·s) | Best Applications | Typical Dosage | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5,000-15,000 | Grouts, fluid mortars | 0.2-0.3% | Maximum flow, minimal thickening |
| 15,000-30,000 | Self-leveling compounds | 0.3-0.4% | Balanced flow and stability |
| 40,000-80,000 | General mortars, adhesives | 0.25-0.5% | Good workability, moderate sag resistance |
| 100,000+ | Renders, thick-bed adhesives | 0.2-0.4% | Strong sag resistance, high water retention |
Instructions for Compatibility with Latex Powder
Poor compatibility between HPMC and redispersible latex powder3 causes serious quality issues. Many contractors struggle with film formation defects, uneven performance, and reduced adhesion strength when these key ingredients don't work together properly.
For optimal compatibility between HPMC and redispersible latex powder, add them separately during the dry mixing process, use HPMC with medium substitution degrees (MS 1.4-1.9), maintain pH between 7-9 in the final mix, and ensure complete dispersion of both polymers during mixing.

I've spent considerable time investigating compatibility issues between these critical additives in our research laboratory. The molecular interaction between cellulose ethers and redispersible polymer powders is complex but understanding it is essential for quality formulations.
The first compatibility factor is dispersion sequence. I always advise our customers to add HPMC and redispersible polymer powder at different stages of the dry mixing process. This prevents the formation of agglomerates that can lead to "fish eyes" (undispersed gel lumps) in the wet mix. Typically, HPMC should be pre-blended with a portion of the fine aggregates before introducing the latex powder.
The substitution degree of HPMC significantly affects its interaction with latex polymers. From our testing, medium substitution degrees (MS 1.4-1.9) offer the best compatibility with most VAE and VeoVa-based redispersible powders. Lower substitution can lead to precipitation in alkaline environments, while higher substitution may interfere with latex film formation.
Temperature sensitivity is another important consideration. Most redispersible powders have minimum film formation temperatures (MFFT) that must be considered alongside HPMC gel temperature. I recommend selecting HPMC with gel points at least 5-10°C higher than the expected application temperature to prevent premature thickening that could inhibit proper latex dispersion.
Optimization Parameters for HPMC-Latex Powder Compatibility
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Potential Issues Outside Range |
|---|---|---|
| HPMC Substitution Degree | MS 1.4-1.9 | Poor dispersion, reduced film integrity |
| System pH | 7-9 | Precipitation, reduced effectiveness |
| Mixing Sequence | Separate addition | Agglomeration, uneven distribution |
| Mixing Time After Water Addition | 3-5 minutes minimum | Incomplete dispersion, performance loss |
| Storage Conditions | Below 30°C, <60% humidity | Premature reaction, reduced shelf life |
Construction Environment Requirements and Other Precautions
Even perfectly formulated self-leveling mortars fail when environmental conditions aren't controlled. Temperature fluctuations, improper substrate preparation, and poor curing practices lead to expensive failures and damaged reputation.
Successful HPMC-containing self-leveling applications require controlled environments (10-30°C), properly prepared substrates (clean, primed, sealed), adequate water quality, and proper curing protocols. Protect freshly applied materials from direct sunlight, strong airflow, and foot traffic during the critical first 24 hours.

In my site consultations across different countries, I've seen how environmental factors can make or break project success. The interaction between HPMC, other mortar components, and the environment is delicate and demands careful management.
Temperature control is paramount. HPMC has a critical dissolution temperature - below this point, it dissolves properly in water, but above it, it forms lumps with dry centers. I always advise contractors to maintain both material and ambient temperatures below 30°C during mixing and application. In hot climates like Saudi Arabia and UAE, this often means scheduling pours for early morning or evening and using chilled mixing water.
Substrate preparation interacts significantly with HPMC performance. The polymer's water retention benefits are undermined by excessively absorbent substrates. I recommend always using appropriate primers that seal porosity while enhancing adhesion. Particularly for self-leveling applications, any substrate leakage points must be sealed completely, as HPMC increases flow time and gives more opportunity for material loss through cracks.
The relationship between humidity, temperature, and curing deserves special attention. HPMC slows water evaporation, which is generally beneficial for cement hydration, but in very high humidity environments (>80% RH), this can extend setting times excessively. In such conditions, I've found that reducing HPMC dosage slightly while ensuring adequate ventilation provides better results.
Environmental Control Checklist for HPMC-Modified Mortars
| Environmental Factor | Recommended Condition | Mitigation If Unachievable |
|---|---|---|
| Ambient Temperature | 10-30°C (50-86°F) | Use warm/cold water to compensate |
| Substrate Temperature | 10-25°C (50-77°F) | Apply during cooler periods, shade area |
| Relative Humidity | 40-70% | Use dehumidifiers or provide ventilation as needed |
| Air Movement | Minimal during application | Wind breaks, close windows and doors |
| Substrate Moisture | <4% moisture content | Use moisture barriers or wait for drying |
| Direct Sunlight | Avoid during application and early curing | Use shading or apply during overcast days |
Beyond environmental controls, there are several handling precautions specific to HPMC-modified self-leveling mortars that I've learned through experience:
First, mixing sequence matters tremendously. Always add HPMC-containing dry mixture to water (not water to powder) and allow 30-60 seconds of pre-wetting before intensive mixing. This prevents the formation of difficult-to-dissolve lumps which can compromise the entire batch.
Water quality and temperature significantly impact HPMC performance. Hard water with high mineral content can interfere with dissolution and effectiveness. When working in areas with questionable water quality, I recommend testing formulations with the actual site water before full-scale application begins.
Finally, the interaction between HPMC and cement chemistry deserves attention. Modern cements with high C3A (tricalcium aluminate) content can react differently with HPMC than traditional formulations. High-alumina cements particularly may require specific HPMC grades with modified substitution patterns to prevent unwanted acceleration or retardation of setting.
Conclusion
HPMC is truly the secret weapon for high-quality self-leveling mortar, creating an invisible 3D network that suspends particles while allowing flow. It solves the fundamental flowability-stability contradiction while providing essential water retention for proper curing and strength development.







