Selecting the wrong HPMC viscosity1 can ruin your entire construction project. I've seen countless customers waste thousands of dollars on inappropriate hydroxypropyl methylcellulose2 that failed during application or compromised structural integrity.
The optimal HPMC viscosity depends on your specific application requirements, temperature conditions, and desired water retention. For exterior renders, choose 100,000-150,000 mPa·s at 20°C while ensuring at least 50% viscosity retention at 40°C and water retention above 88% after 24 hours.

When I started supplying HPMC to construction material manufacturers twenty years ago, I noticed even experienced professionals making critical mistakes when selecting viscosity grades. These errors often resulted in product failures, customer complaints, and costly rework. Let me share what I've learned so you can avoid these common pitfalls.
What Are the Grades of HPMC Viscosity?
Many buyers get overwhelmed by the vast range of HPMC viscosity options. Should you choose 100,000 mPa·s or 200,000 mPa·s? The numbers alone can be confusing without understanding what they truly represent.
HPMC viscosity grades typically range from 5 to 200,000 mPa·s (measured at 2% solution, 20°C), with common construction grades including 15,000, 40,000, 60,000, 100,000, and 150,000 mPa·s. Each grade serves specific applications - lower viscosities (5,000-20,000) for tile adhesives, medium grades (40,000-80,000) for self-leveling compounds3, and higher grades (100,000+) for renders and plasters.

Dive deeper into HPMC viscosity grades requires understanding how molecular structure impacts performance. The viscosity of HPMC directly correlates with molecular weight - higher molecular weight polymers create stronger intermolecular forces in solution, resulting in higher viscosity. However, this relationship isn't purely linear.
The degree of substitution (DS) and molar substitution (MS) significantly affect how HPMC behaves across temperature ranges. For instance, HPMC with higher methoxyl content typically displays stronger thermal gelation properties, which is crucial for applications where temperature stability matters.
Consider these key factors when selecting HPMC grade:
| Application | Recommended Viscosity Range | Key Property Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Tile Adhesives | 5,000-20,000 mPa·s | Good sag resistance, moderate water retention |
| Self-leveling Compounds | 40,000-80,000 mPa·s | Balanced flow and stability, good water retention |
| Renders/Plasters | 100,000-200,000 mPa·s | High water retention, excellent workability |
| Joint Compounds | 30,000-60,000 mPa·s | Good adhesion, moderate water retention |
The most dangerous mistake is selecting viscosity based solely on numerical values without considering the application environment. A 100,000 mPa·s HPMC might perform perfectly in moderate conditions but fail completely when ambient temperatures rise above 35°C.
How to Thicken HPMC?
Many clients ask me how to increase viscosity when their HPMC solution seems too thin. They often make hasty decisions like simply adding more powder without understanding the science behind proper thickening.
To increase HPMC viscosity, you can use three primary methods: increase concentration (from 2% to 2.5-3%), reduce water temperature during mixing (use cool water around 10-15°C), or incorporate compatible rheology modifiers like silica or bentonite clay at 0.1-0.5% dosage.

Dive deeper into HPMC thickening involves understanding the dissolution mechanism and factors that affect final viscosity development. When HPMC powder contacts water, it first forms a gel layer around each particle before slowly dissolving into solution. This process is temperature-dependent and can be manipulated to achieve desired viscosity profiles.
Improper dispersion is a common issue I encounter with customers. When HPMC is added directly to water without proper dispersion, it forms "fish eyes" - clumps with wet exteriors but dry cores that never fully dissolve. To prevent this, I always recommend a specific mixing procedure: first disperse HPMC in hot water (80-90°C) where it remains insoluble, then add cold water to bring the temperature down, allowing proper dissolution.
The dissolution temperature (thermal gelation point) varies between HPMC grades and can be leveraged for specific applications. For example:
| HPMC Type | Thermal Gelation Temperature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Standard HPMC | 58-64°C | General construction applications |
| Low-substituted HPMC | 62-68°C | High-temperature stability applications |
| Highly-substituted HPMC | 54-60°C | Cold-weather applications |
Beyond simple concentration increases, consider these advanced thickening strategies:
- pH adjustment - HPMC viscosity peaks slightly in alkaline environments (pH 7-9)
- Synergistic thickening - combining HPMC with complementary cellulose ethers like HEC
- Cross-linking agents - specialized additives that create bonds between HPMC chains
Each approach has specific benefits and limitations depending on your formulation requirements and production capabilities.
Which HPMC is Best?
I often hear clients asking which HPMC brand or grade is "the best." This question misses an important point - there's no universally superior HPMC, only the right HPMC for your specific application requirements.
The best HPMC for your application depends on multiple factors: required viscosity stability across temperature ranges (choose thermally stable grades for hot climates), water retention needs (select grades with >88% water retention for cement-based materials), and workability duration (look for grades with delayed dissolution profiles).

Dive deeper into selecting the optimal HPMC involves evaluating several critical performance parameters beyond just the viscosity number. During my 20 years supplying HPMC to construction companies across developing markets, I've developed a comprehensive evaluation framework that considers application-specific requirements.
For cement-based applications4, water retention becomes the make-or-break property. Some manufacturers modify HPMC to improve initial workability but sacrifice water retention, creating a dangerous situation where cement hydration remains incomplete. This results in weak structures prone to cracking and failure. I always recommend testing water retention according to standard methods (like EN 459-2) and insisting on minimum values above 88% for 24-hour performance.
Temperature stability represents another critical factor often overlooked. While standard specifications list viscosity at 20°C, real-world construction sites in places like Saudi Arabia or the UAE frequently experience temperatures exceeding 40°C. Consider these viscosity retention guidelines:
| Application Climate | Recommended Viscosity Retention at 40°C | Example Grade Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Temperate (15-25°C) | >60% retention | Standard HPMC 100,000 mPa·s |
| Hot (25-35°C) | >70% retention | Thermally-enhanced HPMC 80,000 mPa·s |
| Extreme (>35°C) | >80% retention | Specialty thermally-stable HPMC 60,000 mPa·s |
Beyond viscosity and water retention, consider these additional selection criteria:
- Particle size distribution - affects dissolution rate and incorporation ease
- Surface treatment - influences anti-lumping properties and dispersion behavior
- Substitution pattern - impacts thermal gelation properties and compatibility with additives
The most successful projects result from matching these properties precisely to application requirements rather than simply choosing the highest viscosity or most expensive product.
How Does CMC Affect Viscosity?
Some suppliers secretly blend CMC (carboxymethyl cellulose5) with HPMC to artificially boost viscosity numbers. This practice creates serious problems that many buyers discover too late.
CMC can increase initial viscosity measurements by 20-50%, but creates unstable solutions that break down rapidly under heat or shear stress. When purchasing HPMC, request thermal stability tests showing viscosity retention after storage at 40°C for 14 days (quality products maintain >80% original viscosity).
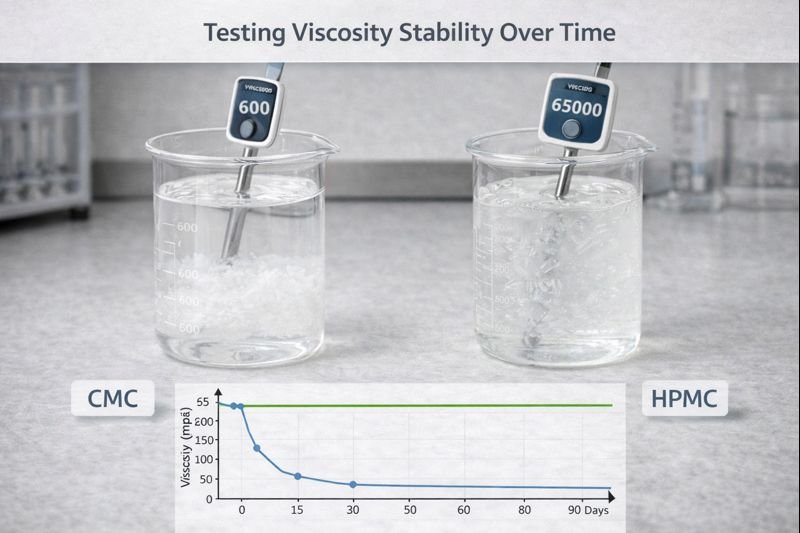
Dive deeper into the CMC/HPMC relationship reveals complex chemical interactions that significantly impact performance. While both are cellulose ethers, they function through different mechanisms. HPMC creates viscosity through hydrophobic associations between polymer chains, while CMC works through ionic interactions. This fundamental difference explains why CMC-adulterated HPMC performs poorly in real-world applications.
During my factory visits across China, I've observed some manufacturers deliberately adding 5-10% CMC to boost apparent viscosity readings without disclosing this practice. This saves them production costs while presenting artificially high viscosity specifications. However, these blended products typically show three revealing weaknesses:
- Accelerated viscosity breakdown under mechanical shear (critical for spray applications)
- Poor performance in hard water environments due to CMC's sensitivity to calcium ions
- Significantly reduced thermal stability, with viscosity losses exceeding 50% after 7 days at elevated temperatures
To protect yourself from this deceptive practice, implement these verification strategies:
| Test Method | What It Reveals | Red Flag Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Infrared Spectroscopy | Chemical composition | Unusual carboxyl peaks indicating CMC presence |
| Heat Stability Testing | Viscosity retention under thermal stress | Rapid viscosity decline (>30% within 7 days) |
| Salt Tolerance Test | Response to electrolytes | Excessive viscosity drop in hard water |
| pH Sensitivity | Behavior across pH range | Abnormal viscosity increase in alkaline conditions |
Additionally, be suspicious of suppliers offering unusually high viscosity specifications at significantly lower prices than market standards. The economics of HPMC production create a relatively consistent price-to-viscosity relationship across the industry.
Conclusion
Avoiding HPMC viscosity selection mistakes requires understanding temperature effects, prioritizing water retention alongside viscosity, and testing for viscosity stability. Select suppliers who provide comprehensive technical data rather than just impressive viscosity numbers.
FAQ
What happens if I choose too high HPMC viscosity?
Excessively high viscosity can cause mixing difficulties, air entrainment, reduced workability, and increased material costs without proportional performance benefits.
Can I blend different HPMC viscosities?
Yes, blending is an effective strategy for customizing performance, but requires understanding the non-linear relationship between concentration and viscosity.
How do I test HPMC quality before bulk purchase?
Request samples for in-house testing including viscosity measurement at application temperature, water retention testing, and 14-day thermal stability assessment.
Does HPMC viscosity affect setting time?
Higher viscosity typically extends setting time slightly by reducing water mobility within the matrix, which can be advantageous for complex applications requiring longer workability.
How does particle size affect HPMC performance?
Finer particles dissolve more quickly but may require special handling to prevent lumping; coarser grades offer easier incorporation but slower dissolution.
-
Understanding HPMC viscosity is crucial for ensuring the right application and preventing costly mistakes in construction projects. ↩
-
Explore the diverse applications of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose to enhance your construction materials and techniques. ↩
-
Learn about self-leveling compounds and how they can improve the quality and efficiency of your construction projects. ↩
-
Explore the challenges faced in cement-based applications and how to overcome them with the right HPMC. ↩
-
Learn about carboxymethyl cellulose and its impact on HPMC performance in construction materials. ↩







