Are you confused about which mortar to use for your construction project? With so many options available, selecting the wrong type can lead to structural failures and expensive repairs.
Mortar is a workable paste used to bind building materials like stones, bricks, and concrete blocks. The most common types include cement mortar, lime mortar, polymer-modified mortar, and refractory mortar, each designed for specific applications based on strength requirements, environmental exposure, and durability needs.
Choosing the right mortar isn't just about picking any mix off the shelf. It requires understanding how different formulations perform under various conditions. Let me walk you through everything you need to know about mortar types and their applications.
What Are The Different Types Of Mortar And Their Uses?
Have you ever wondered why some mortars crack easily while others last for centuries? The secret lies in their composition and how well they're matched to the application.
Mortar is primarily classified into five main types: cement mortar, lime mortar, polymer-modified mortar, refractory mortar, and mud mortar. Each type has a specific strength, setting time, and durability profile that makes it suitable for particular construction applications.

Cement Mortar1
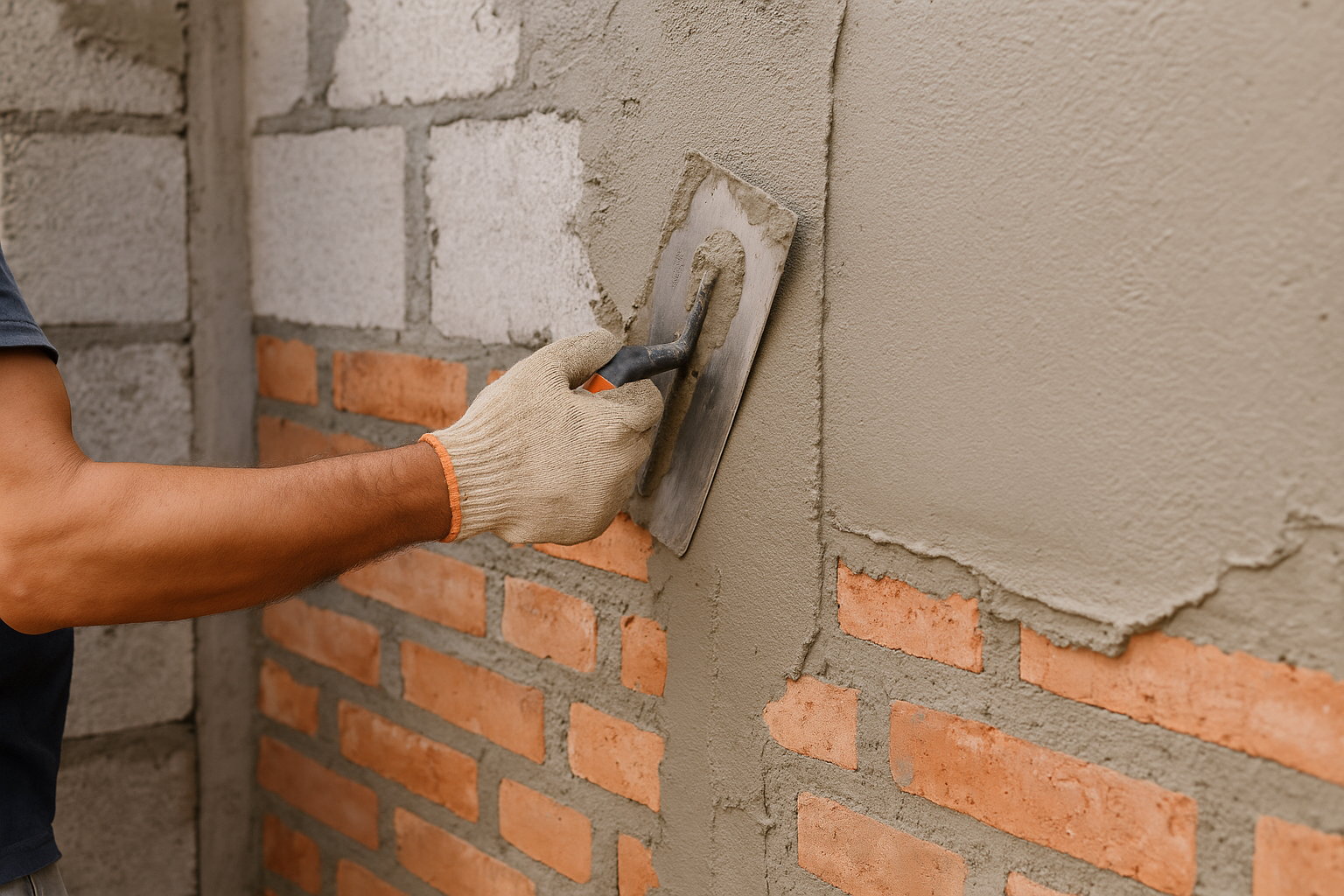
Cement mortar is the most widely used type in modern construction. It's made by mixing cement, sand, and water, sometimes with additives like hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) to improve workability and water retention. The strength of cement mortar depends on the cement-to-sand ratio, typically ranging from 1:3 to 1:6.
For high-strength applications, a 1:3 ratio is common, while general masonry work often uses a 1:4 or 1:5 mix. Our factory produces high-quality HPMC that significantly improves cement mortar performance by enhancing its water retention capacity, which is crucial for proper cement hydration.
One interesting property of cement mortar is its excellent compressive strength but relatively poor tensile strength. This is why it's frequently reinforced with materials like polypropylene fibers, another product we manufacture. These fibers help prevent shrinkage cracks and improve the mortar's overall durability.
Cement Mortar1 Applications:
| Application | Cement:Sand Ratio | Additives Recommended2 |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation work | 1:3 | Water reducers, HPMC |
| Brick masonry | 1:4 | HPMC, air entrainers |
| Plastering | 1:5 | HPMC, fibers |
| Floor screeding | 1:3 | Redispersible latex powder |
Lime Mortar3
Did you know that many ancient structures still standing today were built using lime mortar? This traditional material offers flexibility that modern mortars can't match.
Lime mortar is made by combining lime (calcium oxide), sand, and water. Unlike cement mortar, it cures through carbonation—a process where it absorbs carbon dioxide from the air—rather than hydration. This results in a more breathable and flexible material.
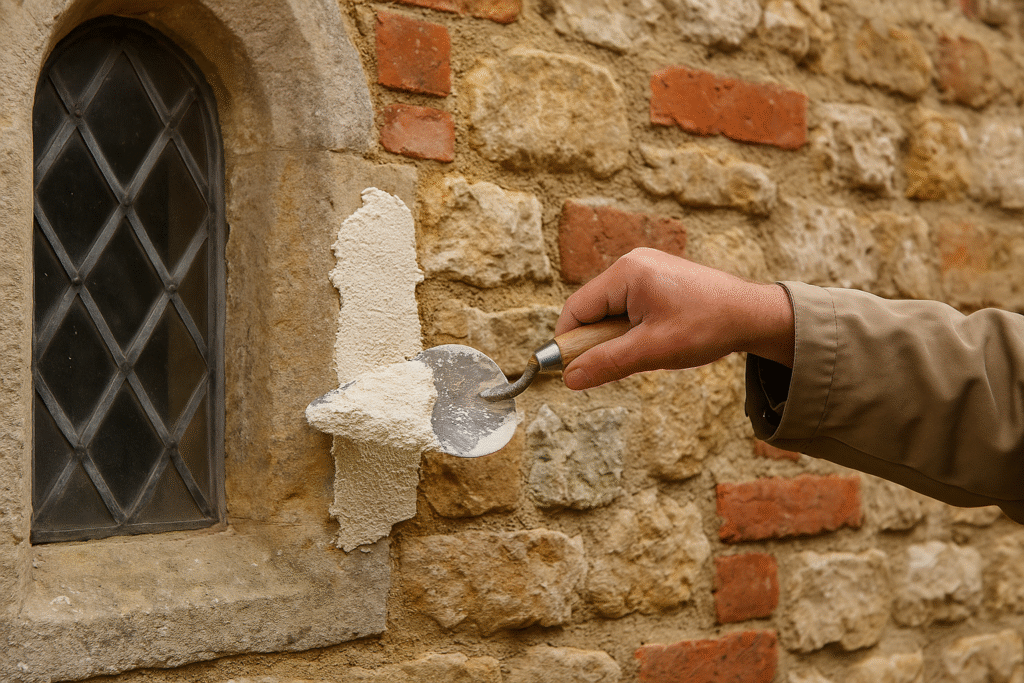

Lime mortar comes in two main varieties: non-hydraulic (air lime) and hydraulic lime. Non-hydraulic lime sets only through contact with air, making it slower to harden but more flexible. Hydraulic lime contains clay impurities that allow it to set partially through reaction with water, providing a middle ground between pure lime and cement mortars.
The flexibility of lime mortar makes it ideal for historic building restoration where structures need to accommodate movement. It's also environmentally friendly, as the carbonation process actually absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere, partially offsetting the emissions produced during limestone calcination.
In our experience working with international clients, particularly those in Saudi Arabia and UAE, lime mortar is increasingly being specified for heritage conservation projects. We often recommend adding small amounts of our hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) to improve workability and water retention without compromising the breathable nature of lime mortar.
Lime Mortar3 Properties:
| Type | Setting Time | Strength | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-hydraulic | Very slow (weeks) | Low | Historic restoration, interior work |
| Moderately hydraulic | Medium (days) | Medium | General masonry in damp conditions |
| Eminently hydraulic | Fast (similar to cement) | High | Structural work, exposed conditions |
Polymer-Modified Mortar4
Have you ever applied mortar to a smooth surface only to watch it slide right off? Polymer-modified mortars solve this problem through dramatically improved adhesion.
Polymer-modified mortar contains polymers (usually in the form of redispersible powder) that significantly enhance adhesion, flexibility, and water resistance. This type of mortar bridges the gap between traditional mortars and modern construction requirements.
Our factory specializes in producing redispersible latex powder, a key component in polymer-modified mortars. When water is added, these powders redisperse into polymer particles that form films as the mortar dries. These polymer films create bridges between cement particles and the substrate, drastically improving bond strength.
Polymer-modified mortars are particularly valuable in areas with temperature fluctuations or vibration. The polymers provide elasticity that helps the mortar accommodate movement without cracking. This makes them ideal for external wall insulation systems, tile adhesives, and repair mortars.
In countries with extreme temperature variations like Saudi Arabia—where temperatures can range from near freezing at night to over 50°C during the day—polymer-modified mortars have become essential for long-lasting installations. Our clients in these regions particularly value our customizable formulations that can be adjusted for specific climate conditions.
Benefits of Polymer Modification:
| Property | Improvement | Application Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesion | 3-5× higher | Better bond to difficult substrates |
| Flexibility | 2-3× more elastic | Reduced cracking in temperature changes |
| Water resistance | Significantly reduced permeability | Better durability in wet environments |
| Freeze-thaw resistance | Improved durability | Longer lifespan in cold climates |
Refractory Mortar5
Have you ever noticed that fireplaces and furnaces require special mortars? Regular mortar would quickly deteriorate under high temperatures.
Refractory mortar is specially designed to withstand extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C. It's primarily used in applications involving fire or extreme heat, such as furnaces, fireplaces, chimneys, and pizza ovens.
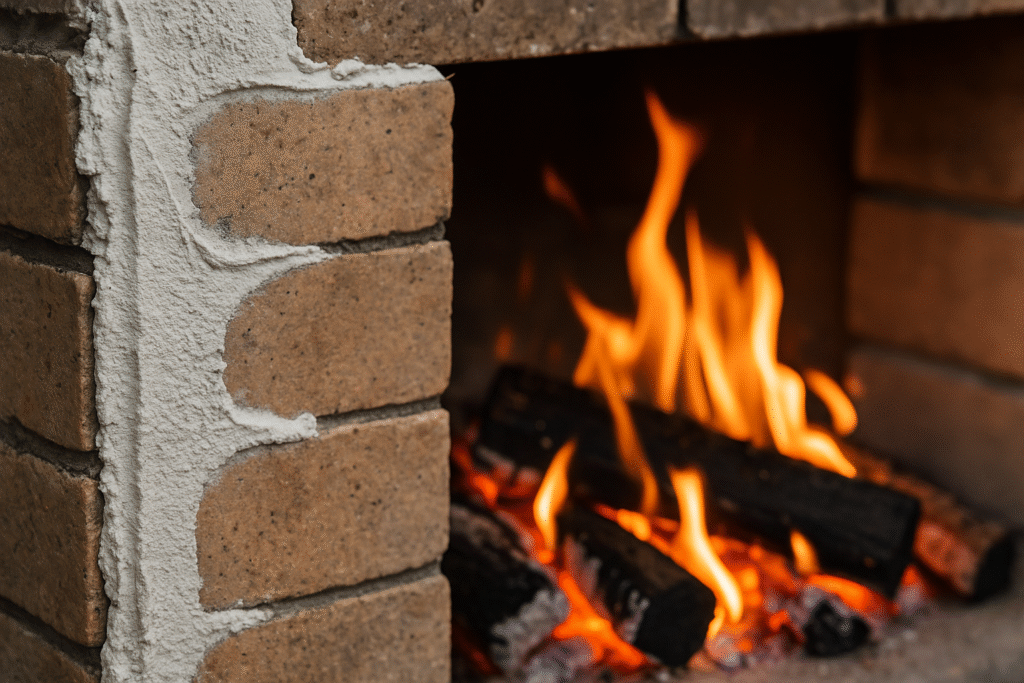

Unlike standard mortars, refractory varieties are formulated with heat-resistant materials like fire clay, calcium aluminate cement, and various aggregates that maintain stability at high temperatures. These specialized ingredients prevent the mortar from breaking down or emitting toxic substances when heated.
The performance of refractory mortar depends heavily on its formulation. Some are designed for intermittent heating (like home fireplaces), while others are engineered for continuous high-temperature industrial applications. The choice of binder and aggregates determines the temperature rating and thermal shock resistance.
Our experience with industrial clients in India and Pakistan has shown that additive selection is crucial for refractory mortar performance. We supply specialized grades of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) that improve workability without compromising heat resistance. This has proven particularly valuable in the metallurgical and cement kiln industries where precise mortar application around complex shapes is necessary.
Refractory Mortar5 Classifications:
| Class | Temperature Rating | Typical Applications | Key Components |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-duty | Up to 870°C | Residential fireplaces | Fire clay, HPMC |
| Medium-duty | Up to 1260°C | Commercial ovens | Calcium aluminate, special CMC |
| High-duty | Up to 1650°C | Industrial furnaces | High-alumina cement, silica |
| Super-duty | Above 1650°C | Specialty kilns | Silicon carbide, zirconia |
Mud Mortar6
Did you know that one of the oldest and most environmentally friendly mortars is still used today in many parts of the world?
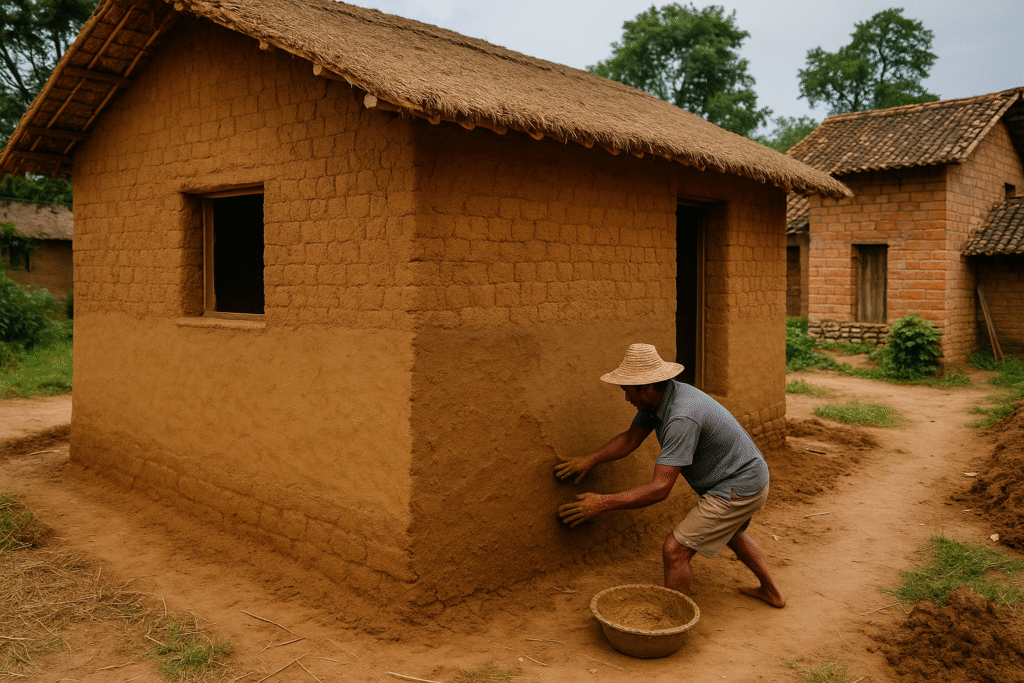
Mud mortar, made from a mixture of clay soil, sand, and sometimes organic fibers like straw or animal dung, has been used for thousands of years and remains common in many developing regions. It's incredibly eco-friendly, requiring no energy-intensive manufacturing processes.
 "Sustainable building using mud mortar techniques")
"Sustainable building using mud mortar techniques")
While lacking the strength of cement-based mortars, mud mortar offers excellent thermal insulation properties, helping maintain comfortable interior temperatures in both hot and cold weather. This makes it particularly suitable for residential construction in regions with extreme temperature variations.
In our work with clients in rural regions of India, Pakistan, and parts of the Middle East, we've seen increasing interest in enhancing traditional mud mortars with modern additives. Small amounts of our HPMC or CMC products can significantly improve water resistance and durability without sacrificing the ecological benefits of mud construction.
The sustainability aspect of mud mortar cannot be overstated. It has virtually zero embodied energy, can be sourced locally (reducing transportation emissions), and is completely biodegradable at the end of its life cycle. As green building practices gain momentum worldwide, improved mud mortars represent an important area of development for sustainable construction.
Mud Mortar6 Enhancement Options:
| Challenge | Traditional Solution | Modern Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Water erosion | Lime addition, frequent maintenance | HPMC water-repellent additives |
| Cracking | Straw fibers | Polypropylene microfibers |
| Durability | Thick walls, wide eaves | Surface sealants, stabilizers |
| Strength | Limited applications | Partial cement hybridization |
Conclusion
Choosing the right mortar is crucial for construction success. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each type—cement, lime, polymer-modified, refractory, and mud—you can ensure your projects have the proper balance of strength, flexibility, and durability.
-
Explore this link to understand the versatility and strength of Cement Mortar in construction. ↩ ↩
-
Find out which additives enhance the performance of Cement Mortar in various applications. ↩
-
Discover how Lime Mortar's flexibility and breathability make it ideal for historic restorations. ↩ ↩
-
Learn how Polymer-Modified Mortar enhances adhesion and flexibility for modern construction needs. ↩
-
Find out why Refractory Mortar is essential for high-temperature applications like fireplaces and kilns. ↩ ↩
-
Understand the eco-friendly benefits of Mud Mortar and its applications in sustainable building. ↩ ↩







