Cracking concrete structures drain budgets and frustrate building owners everywhere. The repair costs climb higher each year, turning minor issues into major financial headaches.
PP fibers1 work by preventing microscopic plastic shrinkage cracks during concrete's early curing stage. These tiny fibers create a three-dimensional reinforcement network throughout the mix, distributing stress and blocking pathways that would otherwise allow water and chloride ions to reach and corrode steel reinforcement.

I remember visiting a client's 15-year-old warehouse that had used PP fiber-reinforced concrete2. While neighboring structures showed extensive repairs, his floors remained solid with minimal maintenance. This stark contrast showed me the true long-term value these small fibers deliver.
How Do PP Fibers Stop Concrete Cracks Before They Start?
Concrete structures often fail from the inside out, beginning with tiny cracks too small to see. These invisible weaknesses let moisture and chemicals attack the reinforcing steel inside.
PP fibers1 prevent micro-cracks by absorbing internal stresses during the critical first 24 hours when concrete is most vulnerable. By distributing these forces throughout the concrete matrix, the fibers intercept cracks at the microscopic level before they can develop into larger structural problems.
 https://placehold.co/600x400 "PP fibers preventing micro-cracks")
https://placehold.co/600x400 "PP fibers preventing micro-cracks")
The key concept here is "prevention rather than cure." I've spent years analyzing concrete failures, and the pattern is clear - most expensive repairs stem from problems that begin in the concrete's first day of life. PP fibers act during this crucial period when concrete is transitioning from plastic to solid state.
Understanding the Cost Impact of Early Protection
The economics of using PP fibers becomes clear when we examine the lifecycle costs of concrete structures:
| Without PP Fibers | With PP Fibers |
|---|---|
| Initial micro-cracks form | Micro-crack formation prevented |
| Water/chloride penetration accelerates | Waterproofing properties enhanced |
| Steel corrosion begins within 5-10 years | Steel remains protected for decades |
| Repair costs escalate over time | Maintenance remains minimal |
| Structure lifespan shortened | Structure lifespan extended |
When concrete cracks, even microscopically, it creates entry points for moisture and chemicals. These substances eventually reach the steel reinforcement, causing corrosion. When steel corrodes, it expands up to 4-6 times its original volume, creating internal pressure that further damages the concrete from within.
This creates a destructive cycle: small cracks allow water entry → water causes steel corrosion → corroding steel expands → expansion causes larger cracks → more water enters → accelerated deterioration occurs. PP fibers break this cycle at its first link by preventing those initial micro-cracks.
How Does PP Fiber Prevention Translate to Cost Savings?
Maintaining concrete structures without fiber-reinforcement often means accepting a cycle of increasingly expensive repairs. The costs spiral upward as simple surface treatments give way to more invasive structural repairs.
PP fibers reduce maintenance costs by preventing the initial plastic shrinkage cracks that eventually lead to steel corrosion and concrete spalling. This protection mechanism keeps the reinforcing steel in a dry, alkaline environment where corrosion cannot occur, eliminating the need for costly repairs to damaged concrete and compromised structural elements.
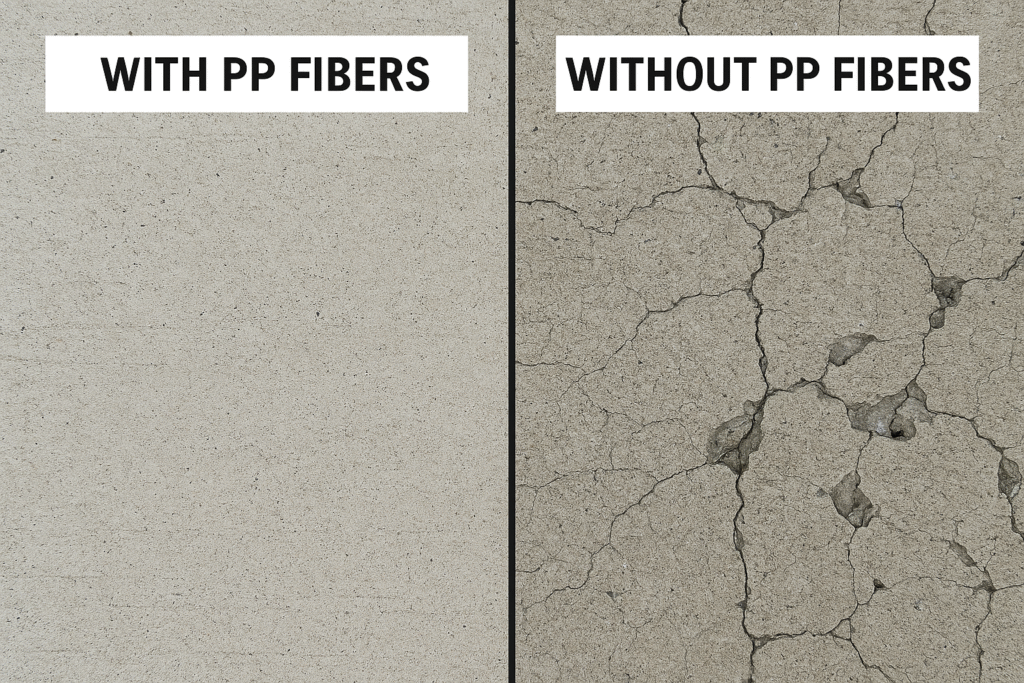
I've worked with several projects where we analyzed the lifecycle costs of concrete structures. The data consistently shows that the small upfront investment in PP fibers pays tremendous dividends over the structure's lifetime.
The Long-Term Financial Advantage of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
The economic benefits of PP fiber reinforcement extend far beyond simple repair cost avoidance:
| Cost Category | Without PP Fibers | With PP Fibers |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection frequency | Every 1-2 years | Every 3-5 years |
| Repair complexity | Often requires structural intervention | Typically limited to surface maintenance |
| Downtime during repairs | Weeks to months | Days to weeks |
| Equipment/tenant relocation | Often necessary | Rarely required |
| Property value impact | Decreases with visible deterioration | Maintains value longer |
The math becomes especially compelling when considering operational impacts. When a concrete structure requires major repairs, the true costs extend far beyond the repair itself. Business interruption, tenant relocation, equipment protection, and potential revenue loss can easily multiply the direct repair costs.
For instance, repairing a significantly damaged concrete floor in an industrial facility might cost $100,000 directly, but the associated downtime could cost millions in lost production. PP fibers essentially trade a small material cost today (typically $5-15 per cubic meter of concrete) for massive savings decades later.
How Do PP Fibers Compare to Other Concrete Reinforcement Methods?
Traditional concrete reinforcement focuses on adding tensile strength, but often overlooks the microscopic behavior that leads to long-term durability problems. This creates a fundamental maintenance cost gap.
PP fibers1 complement rather than replace traditional reinforcement by addressing different failure mechanisms. While steel reinforcement handles structural loads, PP fibers control microcracking during curing. This dual protection system creates concrete with both immediate strength and long-term durability, reducing total maintenance costs compared to concrete with steel reinforcement alone.
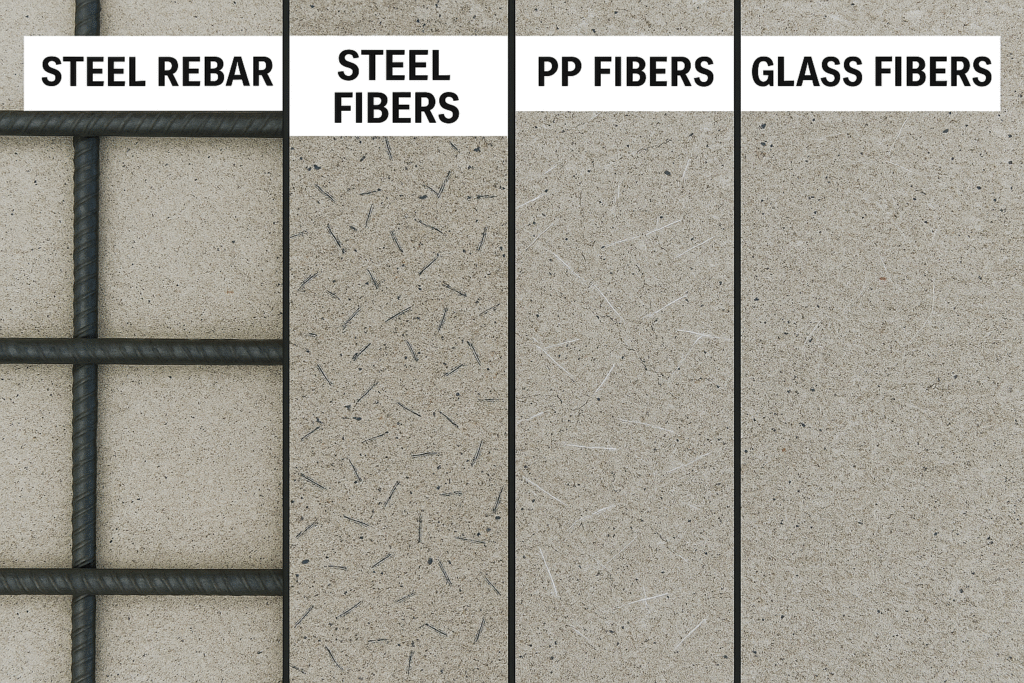

I've consulted on projects where developers initially resisted adding PP fibers due to upfront costs. Years later, those same property owners showed me maintenance records displaying the stark difference between fiber-reinforced and non-fiber-reinforced sections of their facilities.
Comparative Analysis of Reinforcement Approaches
Different reinforcement strategies offer varying degrees of protection against specific types of concrete deterioration:
| Reinforcement Method | Protection Against Plastic Shrinkage | Protection Against Structural Loads | Corrosion Resistance | Maintenance Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Steel Rebar | None | Excellent | Poor | High long-term costs |
| Steel Mesh | Limited | Good | Poor | Moderate to high costs |
| PP Fibers | Excellent | Limited | Excellent | Low long-term costs |
| PP Fibers + Steel Rebar | Excellent | Excellent | Good to Excellent | Lowest total lifecycle costs |
The complementary nature of PP fibers with traditional reinforcement creates an optimal combination. Steel provides the necessary tensile strength for structural performance, while PP fibers protect that steel investment by maintaining the concrete's integrity around it.
This combination transforms the maintenance equation from reactive (fixing problems after they occur) to proactive (preventing problems from developing). The cost differential becomes particularly apparent after 7-10 years, when non-fiber-reinforced structures typically begin showing signs of deterioration requiring intervention.
Conclusion
PP fibers1 in concrete structures prevent micro-cracking that leads to corrosion and expensive repairs. This small upfront investment protects reinforcing steel and dramatically reduces lifetime maintenance costs, making it a smart financial decision for any long-term property owner.







