I've seen countless construction projects fail because of excessive foam in mortar mixtures. Bubbles might seem harmless, but they can drastically reduce mortar strength and durability, costing thousands in repairs.
Defoamers are chemical additives1 that eliminate air bubbles in mortar mixtures by reducing surface tension. They improve mortar density, enhance fluidity, and extend workability time, resulting in stronger, more durable construction materials with fewer surface defects.
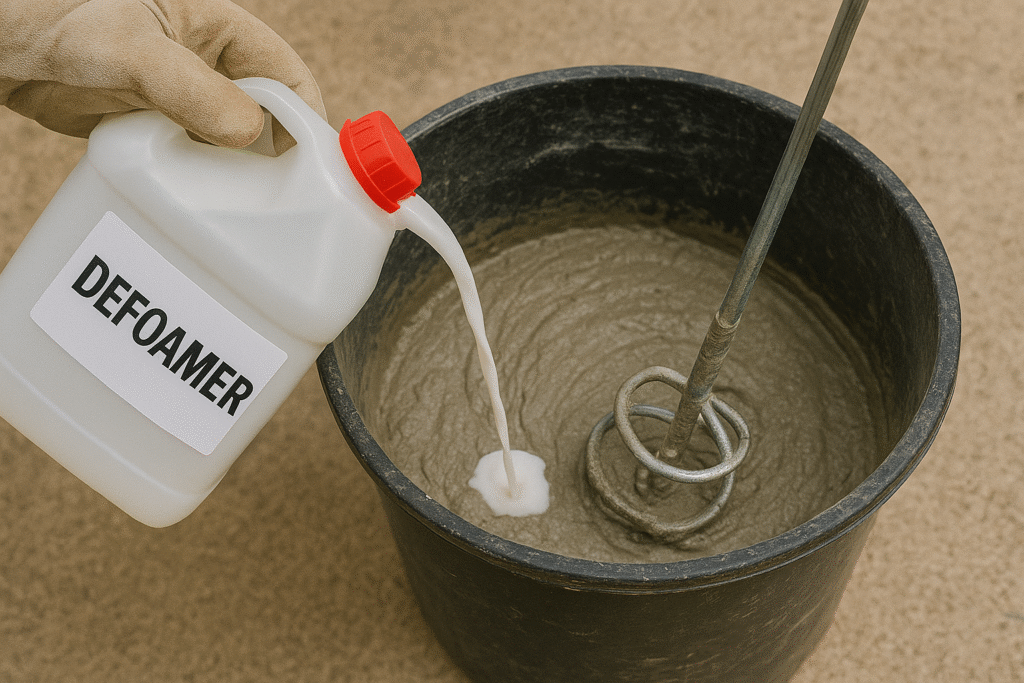

As a manufacturer with six production lines of construction chemicals2, I've tested thousands of mortar formulations. The right defoamer can make the difference between a solid structure and one that crumbles prematurely. Let me share what I've learned about how defoamers truly impact your mortar's performance.
How Does Defoamer Affect the Wet Density of Mortar?
Every time I test a mortar mix without defoamer, I'm amazed at how much air gets trapped. These tiny bubbles create weak points that can compromise the entire structure, making density control crucial.
Defoamers increase wet mortar density by eliminating entrapped air bubbles that form during mixing. This results in more compact material with fewer voids, improving compressive strength by 15-30% and enhancing the mortar's water resistance and overall durability.
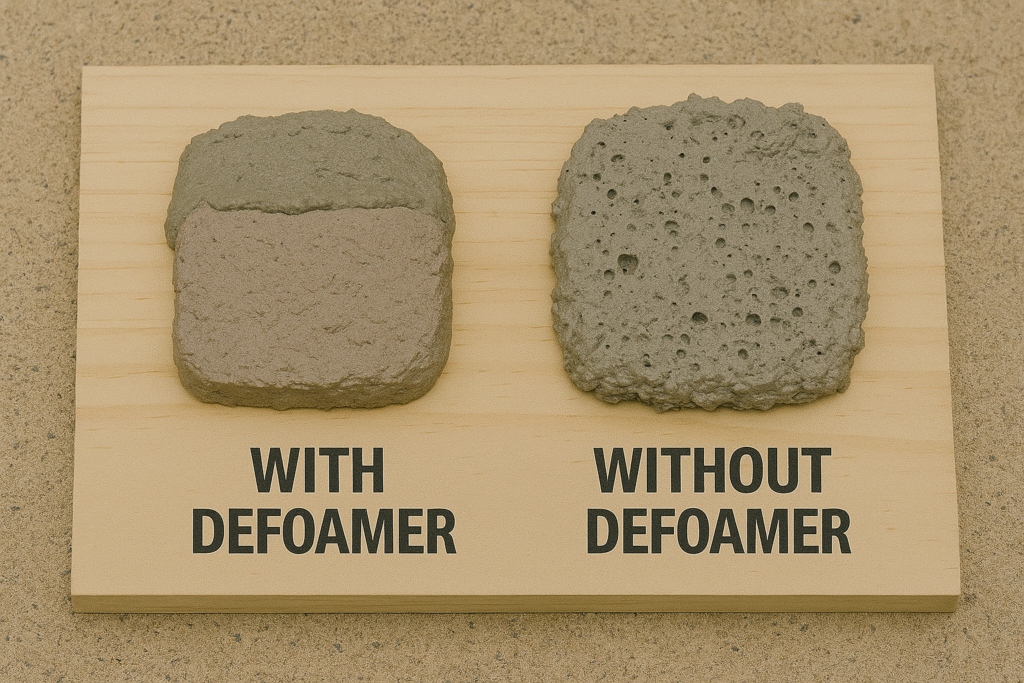
Density is key to mortar performance, and defoamers play a vital role in optimizing this property. During mortar mixing, mechanical agitation and surfactants from other additives naturally create foam. This foam consists of tiny air bubbles that, if left untreated, become permanently trapped in the hardened material.
When we add an effective defoamer to the mixture, it works by breaking these bubble films. The mechanism involves spreading across bubble surfaces and creating a localized imbalance in surface tension, which causes the bubbles to collapse. In my factory testing, we've found that properly defoamed mortar can increase in density by 5-10% compared to untreated samples.
This density improvement directly impacts several performance metrics:
| Property | Without Defoamer | With Defoamer | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | Base value | +15-30% | Higher load-bearing capacity |
| Water Penetration | Higher | Lower | Better waterproofing |
| Freeze-Thaw Resistance | Lower | Higher | Extended durability |
| Shrinkage Cracking | More likely | Less likely | Fewer defects |
I once supplied a customer in Saudi Arabia who was experiencing mysterious strength issues despite following all other formulation guidelines. When we tested his mixture, we discovered excessive air entrainment was the culprit. After incorporating our specialized defoamer, his mortar density increased by 8%, and compressive strength improved by 22%.
How Does Defoamer Impact Mortar Fluidity?
I remember working with a customer whose mortar was so stiff it was nearly impossible to apply. Adding water would weaken it, but a defoamer solved the problem perfectly by removing the air that was restricting flow.
Defoamers improve mortar fluidity by eliminating air bubbles that create flow resistance. With reduced internal friction, the mortar requires less water for proper consistency, resulting in better particle dispersion, improved flow properties, and easier application without compromising strength.
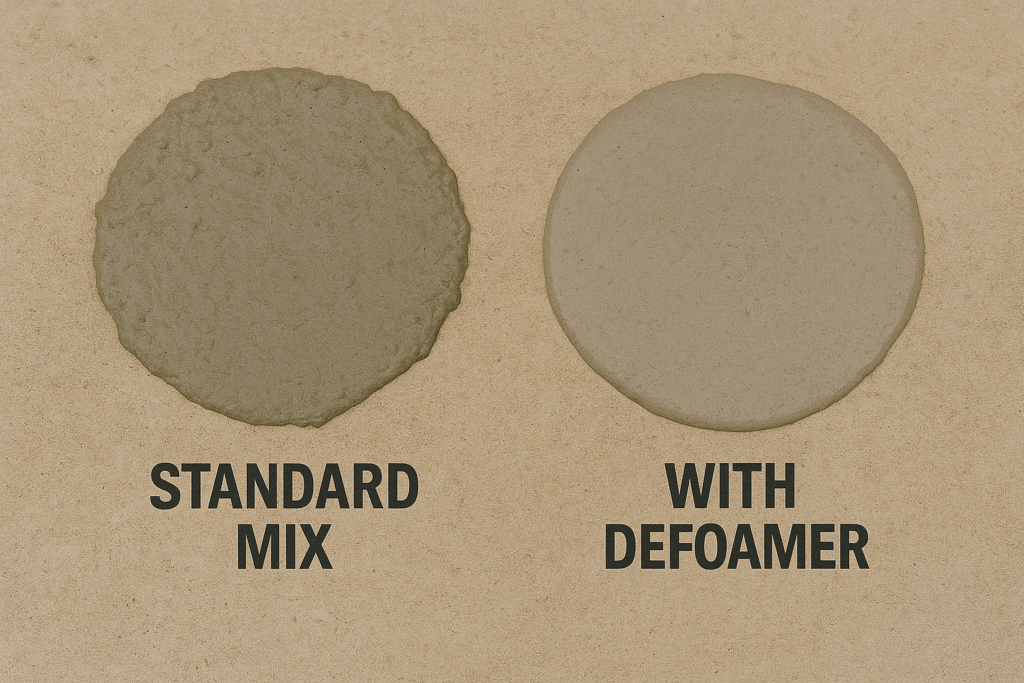
Fluidity might seem separate from foaming issues, but they're closely connected. When mortar contains numerous air bubbles, these bubbles act like ball bearings between solid particles, creating discontinuities in the flow pattern. This disruption makes the mortar behave unpredictably and often stiffly, despite appearing to have adequate water content.
A quality defoamer addresses this problem by eliminating these air interfaces, allowing particles to move more freely against each other. My testing shows that defoamed mortars typically achieve the same flow characteristics with 3-5% less water than untreated mixes. This water reduction brings additional benefits:
| Aspect | Impact of Defoamer on Fluidity |
|---|---|
| Water Demand | Decreased by 3-5% for same workability |
| Particle Packing | More efficient particle arrangement |
| Pumping Pressure | Reduced by up to 15% in mechanical applications |
| Bleeding/Segregation | Decreased risk of component separation |
| Application Range | Wider temperature tolerance |
During one particularly challenging project for a high-rise building in Dubai, our customer needed mortar that could be pumped to extreme heights while maintaining consistent properties. By fine-tuning the defoamer dosage, we helped them achieve optimal fluidity that reduced pumping pressure by 18%, while actually improving the final strength of the cured mortar.
The relationship between defoamers and fluidity additives can be complex. We've found that certain defoamer chemistries interact synergistically with superplasticizers, enhancing their effectiveness, while others may compete for adsorption sites on cement particles. This is why we always recommend compatibility testing when using multiple admixtures.
How Does Defoamer Affect the Workability of Mortar?
Last month, a customer complained that their mortar was setting too quickly on hot days. By adjusting the defoamer type, we extended their working time by 45 minutes without changing any other ingredients.
Defoamers extend mortar workability by improving moisture retention and preventing premature stiffening caused by excess air. They maintain consistent handling properties longer, reduce the need for retempering, and allow for smoother finishing with fewer defects.

Workability is perhaps the most underappreciated aspect of defoamer performance. When I visit construction sites, I often hear complaints about mortar becoming unworkable too quickly. Many don't realize that foam can significantly contribute to this problem, as air bubbles accelerate water evaporation and create false stiffening.
The right defoamer keeps mortar workable longer through several mechanisms. First, by eliminating air channels that accelerate moisture loss. Second, by ensuring better dispersion of cellulose ethers (like our HPMC products) that control water retention. In extensive field testing across different climate conditions, we've documented these improvements:
| Workability Factor | Without Defoamer | With Optimized Defoamer |
|---|---|---|
| Open Time | Base duration | Extended by 25-40% |
| Edge Slumping | More likely | Reduced occurrence |
| Finishing Quality | More effort required | Smoother with less effort |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Highly variable | More consistent across temperatures |
| Retemper Requirements | More frequent | Significantly reduced |
The workability extension is particularly valuable in hot, dry climates like those in Saudi Arabia and the UAE, where many of our customers operate. In these challenging conditions, even small amounts of air entrainment can dramatically shorten working time. One customer in Riyadh was able to extend their mortar's practical working time from 30 minutes to over an hour by optimizing their defoamer usage.
Different types of construction require different workability profiles. For thin-set tile adhesives, we recommend defoamers that maintain fluidity without slumping. For renders and plasters, defoamers that allow longer smoothing time are preferable. By understanding these specific needs, we can customize defoamer recommendations for each application.
Conclusion
The right defoamer is essential for achieving optimal mortar performance, affecting density, fluidity, and workability. By selecting the appropriate defoamer for your specific application, you'll create stronger, more durable mortar with improved handling properties.







