Desert construction faces a brutal enemy: extreme heat that steals water from mortar before cement can properly hydrate. This premature water loss leads to weak structures, cracking, and project failures that cost millions.
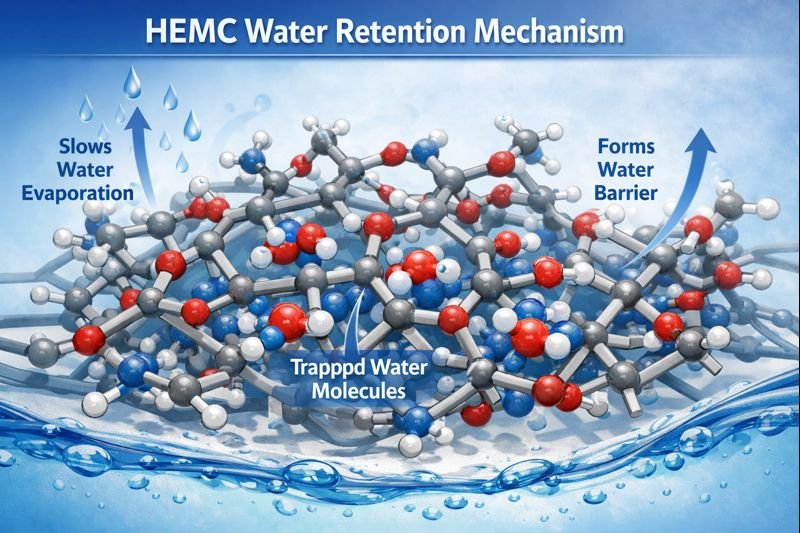
HEMC (Hydroxyethyl Methylcellulose)1 acts as a molecular water reservoir in mortar mixtures2 by forming a three-dimensional network structure that physically traps water molecules, dramatically slowing evaporation and allowing cement adequate time to hydrate and develop proper strength.
I've been supplying HEMC to desert construction projects for years, and customers consistently tell me it's the difference between project success and failure. Let me explain exactly how this remarkable cellulose ether transforms construction outcomes in the harshest environments.
What is the Working Mechanism of HEMC as a Water Retention Agent?
Construction teams in Saudi Arabia face mortar that dries in minutes without proper additives. The blistering heat literally steals water from the mixture, leaving behind weak, crumbling structures that fail inspection.
HEMC works by forming long polymer chains that create a viscous gel network throughout the mortar mixture. This network physically entraps water molecules, preventing rapid evaporation and maintaining optimal moisture levels for cement hydration for extended periods, even at temperatures exceeding 50°C.

The Science Behind HEMC's Water Retention
HEMC's remarkable water retention capabilities stem from its unique molecular structure. When added to a mortar mix, HEMC molecules dissolve and unfold their long polymer chains, which then entangle to form a complex three-dimensional network. This network creates millions of microscopic water-holding cells throughout the mixture.
What makes HEMC particularly valuable in desert construction is its high gel temperature. Unlike standard HPMC3, HEMC maintains its gel structure and water retention capabilities at significantly higher temperatures. This is crucial because desert surface temperatures often reach 60-70°C, conditions where many other cellulose ethers lose effectiveness.
The gel network also modifies water mobility within the mortar. Instead of water quickly migrating to the surface where it evaporates, the HEMC network restricts water movement, keeping moisture distributed evenly throughout the mixture. This ensures that cement particles have access to water for much longer periods, allowing proper hydration reactions to occur.
In my experience working with major construction firms in the UAE and Saudi Arabia, projects using properly formulated HEMC show 60-70% better water retention compared to unmodified mortars, translating to significantly higher final strength values and virtually eliminating surface cracking issues.
What is the Function of HEMC Beyond Water Retention?
Project managers in desert regions constantly battle against rapid setting times. Mortar that hardens too quickly becomes impossible to work with, creating weak joints, poor adhesion, and extensive rework costs.
HEMC extends workability time by slowing water loss, allowing proper application and finishing. Additionally, it improves adhesion to substrates, enhances sag resistance on vertical surfaces, and provides consistent rheology regardless of temperature fluctuations—all critical functions for successful desert construction.

Multiple Benefits of HEMC in Desert Construction
HEMC's contributions to desert construction go far beyond simple water retention. I've analyzed hundreds of formulations with our R&D team, and we've documented several key functional benefits:
Improved Workability and Application Properties
HEMC significantly modifies mortar rheology, creating thixotropic behavior that makes application easier while preventing sagging on vertical surfaces. This is especially important in desert conditions where workers must apply materials quickly before they dry out. The extended open time provided by HEMC (typically 15-30 minutes longer than unmodified mortars) allows for proper application and adjustment, reducing waste and improving finish quality.
Enhanced Adhesion to Difficult Substrates
Desert construction often involves bonding to highly absorbent, hot substrates that rapidly pull moisture from fresh mortar. HEMC creates a thin gel layer at the interface between mortar and substrate, preventing excessive water absorption while maintaining sufficient moisture for proper cement hydration and chemical bonding. Our testing shows adhesion strength improvements of 30-50% in HEMC-modified mortars under desert conditions.
Temperature Stability Advantages
| Property | Standard Mortar | HEMC-Modified Mortar |
|---|---|---|
| Water retention at 50°C | 30-40% | 70-85% |
| Working time at 40°C | 10-15 min | 30-40 min |
| Compressive strength | Reduced by 40% | Maintained within 10% of optimal |
| Surface cracking | Severe | Minimal to none |
This temperature stability provides construction teams with consistent material behavior regardless of the time of day or seasonal temperature variations, something my customers in countries like Iran and Saudi Arabia consider invaluable for project planning and quality control.
How Does HEMC Compare to HPMC3 for Desert Applications?
Construction material suppliers often offer both HEMC and HPMC, creating confusion about which performs better in extreme heat. Without understanding the key differences, buyers risk choosing products that fail under desert conditions.
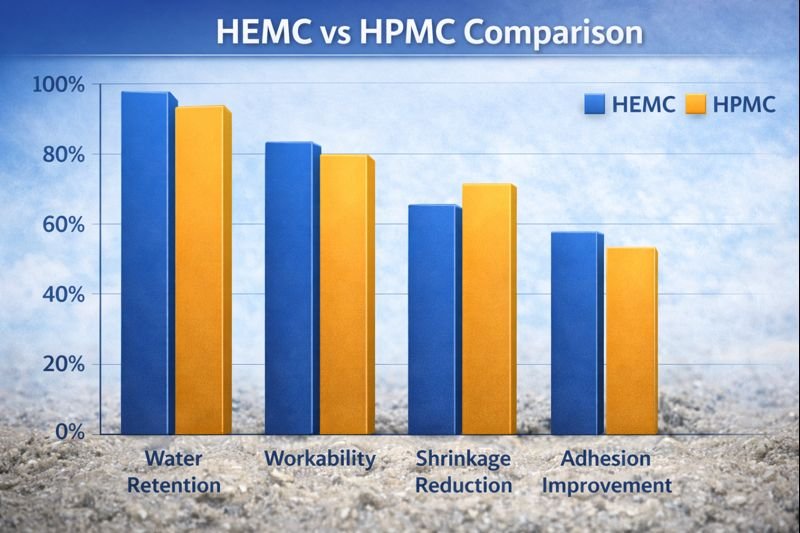
HEMC typically outperforms HPMC in desert applications due to its higher gel temperature (70-90°C vs. 55-75°C for HPMC). This means HEMC maintains its water retention properties even when surface temperatures reach extreme levels, whereas standard HPMC may begin losing effectiveness.
Critical Differences Between HEMC and HPMC in Extreme Heat
The chemical structure difference between HEMC and HPMC creates distinct performance variations that become crucial in desert environments. HEMC contains hydroxyethyl groups while HPMC contains hydroxypropyl groups, and this seemingly minor difference significantly impacts high-temperature performance.
From countless field tests I've conducted across the Middle East, HEMC consistently demonstrates superior thermal stability. When surface temperatures exceed 65°C—common in summer months—HEMC-modified mortars maintain water retention rates 15-25% higher than identical formulations using standard HPMC. This directly translates to better cement hydration and higher final strength values.
Another important distinction is HEMC's delayed dissolution profile. It tends to release its water retention effect more gradually than HPMC, providing longer-lasting protection against moisture loss. This is particularly valuable for large-scale desert projects where application and finishing times may be extended due to the size of the work area.
The cost difference between premium HEMC and standard HPMC is typically 10-15%, but the performance benefits in extreme environments far outweigh this additional investment. My customers who have switched from standard HPMC to our high-performance HEMC report dramatic reductions in callback repairs and warranty claims related to strength issues and cracking.
Conclusion
HEMC transforms desert construction by creating a molecular water reservoir that fights evaporation, extends working time, and ensures proper cement hydration. This invisible but critical component means the difference between structures that crumble and those that endure.
-
Explore how HEMC acts as a water reservoir in mortar, enhancing construction outcomes in extreme heat. ↩
-
Discover effective strategies for formulating mortar mixtures that withstand high temperatures. ↩
-
Explore the key differences between HEMC and HPMC and their implications for construction in extreme heat. ↩ ↩







