Building material manufacturers constantly struggle to find additives that improve product performance without compromising quality. Many face costly failures and production delays when using inferior cellulose ethers.
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)1 is a non-ionic cellulose ether2 derived from cellulose through chemical modification processes. It functions as a binding agent, thickener, film former, and water retention agent in various formulations, particularly in construction materials and pharmaceutical products.
 https://placehold.co/600x400 "Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Powder")
https://placehold.co/600x400 "Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Powder")
I've been in the cellulose ether manufacturing industry for over 15 years, and during this time, I've seen how HPMC has revolutionized the construction materials industry. Our factory produces premium HPMC that meets stringent quality standards across six production lines. Let me share what makes this versatile additive so valuable to industries worldwide.
What Is Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose?
Many construction material manufacturers struggle with product consistency and performance issues. Poor water retention and workability can lead to failed applications and damaged reputation.
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)1 is a semi-synthetic, non-ionic cellulose ether produced by modifying cellulose with propylene oxide and methyl chloride. This white to off-white powder dissolves in cold water to form clear, viscous solutions with unique thickening, binding, film-forming, and water-retention properties.
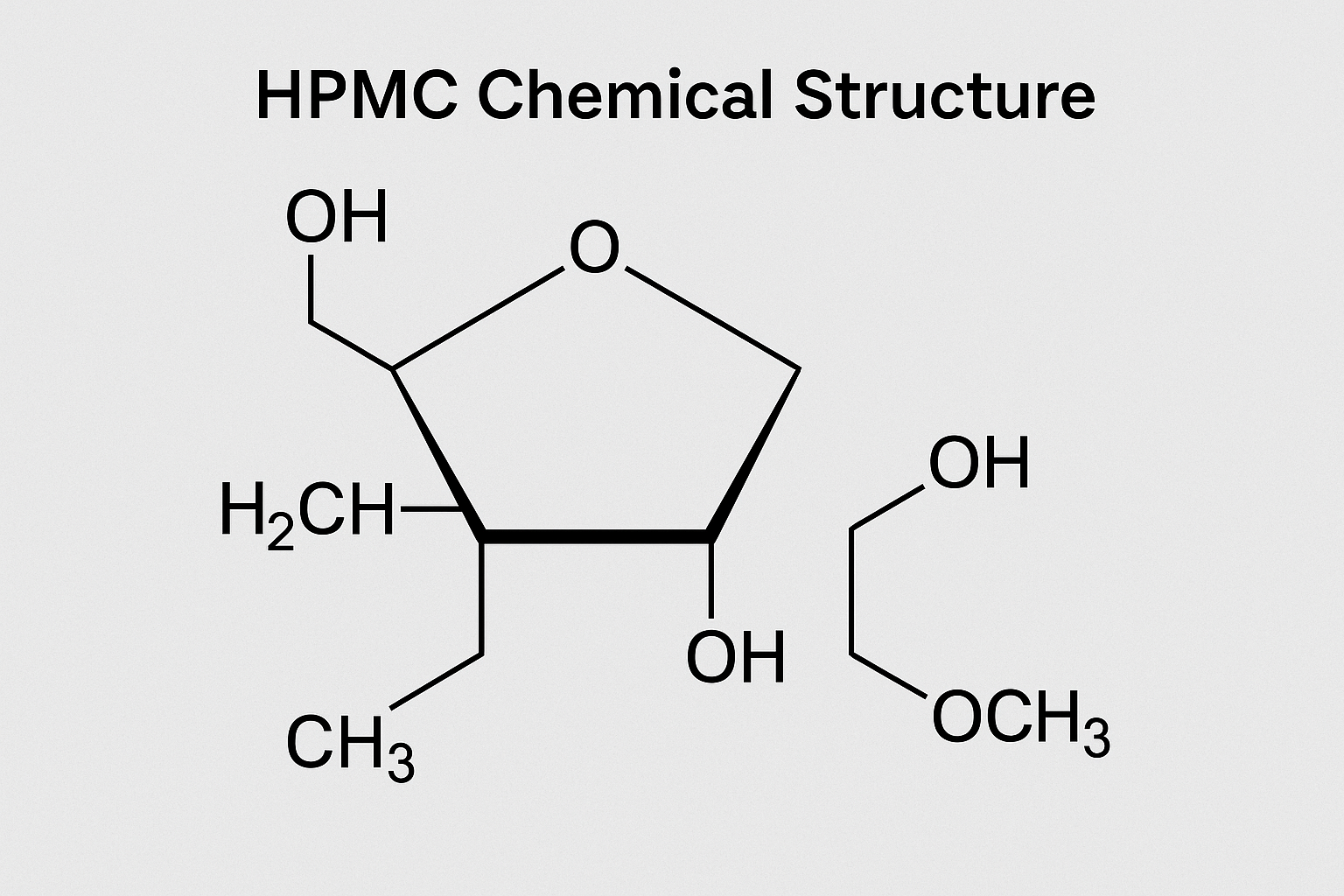
Chemical Composition and Structure
HPMC's performance stems directly from its unique chemical structure, which is worth understanding if you want to select the right grade for your application. The base cellulose molecule undergoes a two-step modification process in our manufacturing facilities.
First, alkali cellulose reacts with methyl chloride to substitute some hydroxyl groups with methoxyl groups. Then, propylene oxide reacts with the remaining hydroxyl groups to introduce hydroxypropyl groups. The ratio between methoxyl (OCH₃) and hydroxypropyl (OCH₂CH(OH)CH₃) substituents determines the final properties of the HPMC.
We can precisely control these substitution levels during production. Typical commercial HPMC grades have methoxyl content between 19-30% and hydroxypropyl content between 7-12%. These percentages directly affect solubility, thermal gelation temperature, and surface activity.
| Parameter | Typical Range | Effect on Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Methoxyl Content | 19-30% | Higher content increases organic solubility |
| Hydroxypropyl Content | 7-12% | Higher content improves water solubility |
| Viscosity | 5-200,000 mPa·s | Controls thickening effect and workability |
| Particle Size | 80-100 mesh | Affects dissolution rate |
In my experience working with clients across Saudi Arabia, UAE, and India, understanding these structural parameters is crucial for selecting the appropriate HPMC grade for specific applications.
HPMC Properties
Construction professionals often face material failures due to poor water retention, inadequate workability, or insufficient adhesion. These issues can lead to cracking, poor bonding, and reduced durability.
HPMC exhibits key properties that make it invaluable in construction applications3, including water retention, thickening, temperature-dependent gelation, surface activity, and film formation. These properties control workability in mortars, enhance adhesion in tile adhesives, and improve consistency in gypsum products.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Understanding the detailed physical and chemical properties of HPMC helps my clients select the perfect grade for their specific applications. When I consult with large mortar factories in markets like Pakistan or Brazil, I emphasize these critical characteristics that determine performance.
HPMC's viscosity is perhaps its most essential property, ranging from 5 to 200,000 mPa·s depending on molecular weight and concentration. This directly controls the thickness and workability of mortars and other construction materials. Our production facilities can precisely control this parameter to meet customer specifications.
The thermal gelation property of HPMC is particularly valuable in construction applications3. When an HPMC solution is heated to a specific temperature (typically 65-90°C depending on the grade), it forms a reversible gel. This property creates a "water barrier" that prevents rapid water loss during cement hydration, crucial for proper curing in hot climates like the Middle East.
| Property | Characteristic | Benefit in Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | White or off-white powder | Easy to incorporate into dry mixes |
| Solubility | Cold water soluble, forms clear solution | Convenient processing in construction applications |
| pH (2% solution) | 5.5-8.0 | Compatible with cement chemistry |
| Thermal Gelation | 65-90°C | Controls water release during curing |
| Surface Activity | Moderate | Enhances air entrainment and stability |
| Ash Content | <5% | Minimal interference with cement chemistry |
I've worked with clients in Vietnam and the Philippines who initially struggled with premature water loss in hot climates. By recommending HPMC grades with specific thermal gelation points, we were able to solve their curing problems and significantly improve their products' performance.
Conclusion
HPMC's unique combination of water retention, thickening, and binding properties makes it essential for modern construction materials, ensuring consistent quality and performance across diverse applications and conditions.
-
Explore how HPMC enhances construction materials with its unique properties, ensuring better performance and durability. ↩ ↩
-
Learn about cellulose ethers and their critical role in improving the quality of construction materials. ↩
-
Explore the diverse applications of HPMC in construction and how it improves material performance. ↩ ↩







