Many customers ask me if HPMC is a natural product when looking for eco-friendly building materials. The confusion is understandable - with "cellulose" in the name, it seems like it might come straight from plants.
HPMC (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose)1 is semi-synthetic, not fully natural. It starts with natural cellulose from wood or cotton, which is then chemically modified with synthetic compounds to create the final product with its special properties for construction applications.
At Kehao, we often explain this distinction to our clients who need to understand exactly what they're buying. The semi-synthetic nature of HPMC gives it advantages over both purely natural and purely synthetic materials. Let me break down what this really means and why it matters for your construction projects.
Is HPMC semi-synthetic?
When customers visit our factory in China, they're often surprised to learn that HPMC isn't completely natural. The raw materials come from trees, but the final product requires significant processing.
Yes, HPMC is definitively semi-synthetic. It begins with natural cellulose extracted from plant sources (usually wood pulp or cotton linters), which is then chemically modified through reactions with propylene oxide and methyl chloride to create the final HPMC product with its valuable properties.
The semi-synthetic nature of HPMC is actually its biggest advantage for construction applications. Pure natural cellulose2 dissolves poorly in water and doesn't provide the workability needed in mortars and paints. Through chemical modification, we transform this natural material into something with remarkable properties.
The Semi-Synthetic Manufacturing Process
The production of HPMC follows several critical stages:
- Raw Material Preparation: Natural cellulose fibers are extracted from wood pulp or cotton
- Alkalization: The cellulose is treated with sodium hydroxide (caustic soda)
- Etherification: Chemical reactions with propylene oxide and methyl chloride
- Purification: Removing byproducts and unreacted materials
- Drying and Milling: Creating the final powder product
This semi-synthetic nature allows us to carefully control the degree of substitution and viscosity of our HPMC products. For our customers in Saudi Arabia, UAE, and other hot climates, we can adjust these properties to provide better water retention in mortars despite the challenging environmental conditions.
Is HPMC healthy?
Construction workers and end-users sometimes worry about using chemical-sounding materials like HPMC, especially in residential buildings where health is a priority.
HPMC is generally recognized as safe for human contact and even food contact applications. It has low toxicity, is non-irritating to skin, and creates minimal dust hazards when properly handled. In construction applications, cured HPMC poses virtually no health risks to building occupants.

When I visit construction sites in places like India and Pakistan, I often observe workers handling various additives with minimal protection. HPMC3 stands out as one of the safer materials on the jobsite.
Unlike some other construction chemicals, it doesn't release harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during application or after curing.
HPMC Safety Considerations
| The health profile of HPMC can be examined across several dimensions: | Exposure Type | Risk Level | Precautions Needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skin Contact | Very Low | Basic gloves for prolonged exposure | |
| Inhalation | Low | Dust mask during mixing | |
| Ingestion | Low | Basic hygiene practices | |
| Long-term Exposure | Minimal | Standard ventilation | |
| Environmental Impact | Low | Biodegradable over time |
In my 15 years working with construction chemicals, I've found that HPMC presents fewer health concerns than most alternatives. Even the most safety-conscious clients in Singapore and Vietnam have been satisfied with its health profile after reviewing the material safety data sheets we provide.
Are HPMC capsules natural?
Many of our clients who know HPMC from pharmaceutical applications often ask if the capsules made from it are natural, especially when they're looking for vegetarian alternatives to gelatin capsules.
HPMC capsules4 are not fully natural but vegetarian-friendly. They're made from the same semi-synthetic hydroxypropyl methylcellulose used in construction applications, but with pharmaceutical-grade purity. They provide a plant-based alternative to animal-derived gelatin capsules.
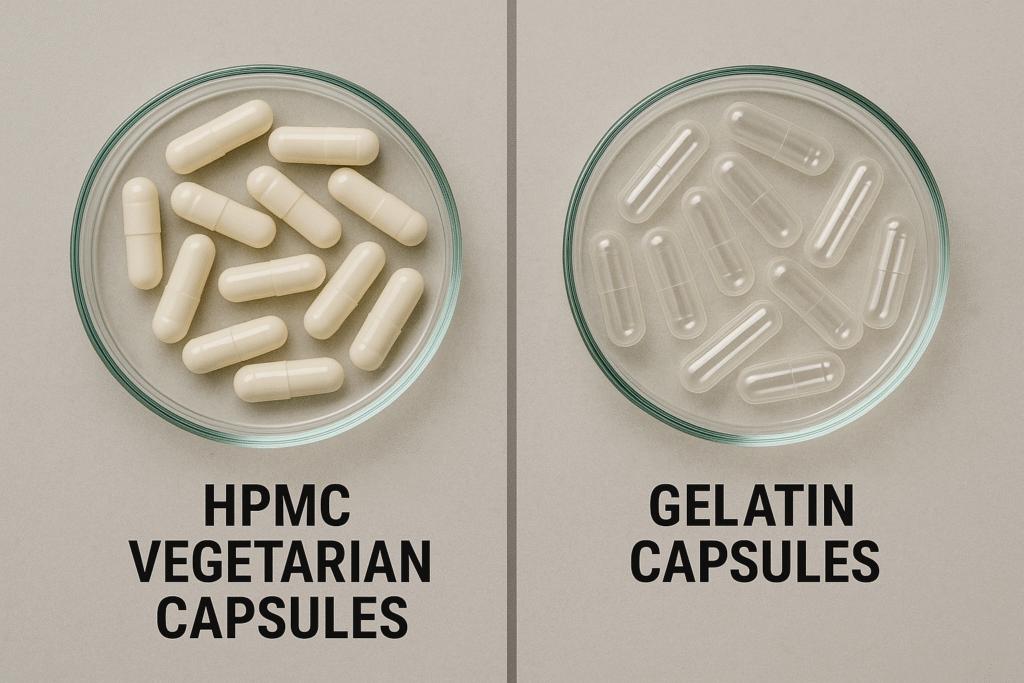
While our company Kehao focuses on HPMC for construction rather than pharmaceuticals, I find the crossover applications fascinating. The same core material that makes our mortars water-retentive also creates capsules that dissolve reliably in the human digestive system.
Pharmaceutical vs. Construction Grade HPMC
The difference between pharmaceutical and construction grade HPMC is significant:
- Purity Requirements: Pharmaceutical HPMC undergoes additional purification steps to remove nearly all contaminants, while construction grade has acceptable trace elements that don't affect performance.
- Particle Size Control: Capsule-grade HPMC requires extremely consistent particle size distribution for smooth capsule formation, whereas construction applications can tolerate more variation.
- Regulatory Oversight: Pharmaceutical HPMC must meet strict pharmacopeia standards (USP, EP, JP) with extensive documentation. Construction HPMC focuses more on performance specifications than regulatory compliance.
- Testing Protocols: Capsule HPMC undergoes biological testing for safety that construction grade doesn't require.
Although we manufacture for the construction sector, we maintain strict quality controls that approach pharmaceutical standards. This is particularly important for our clients in markets like Georgia and Brazil, where regulatory frameworks are increasingly demanding about chemical compositions in building materials.
What is the natural source of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose?
New clients often ask me where the natural component of HPMC comes from, especially when they're comparing different suppliers' environmental credentials.
The natural source of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose5 is cellulose from wood pulp (primarily from pine, spruce, or eucalyptus trees) or cotton linters. This natural cellulose provides the backbone structure that is then chemically modified to create HPMC.
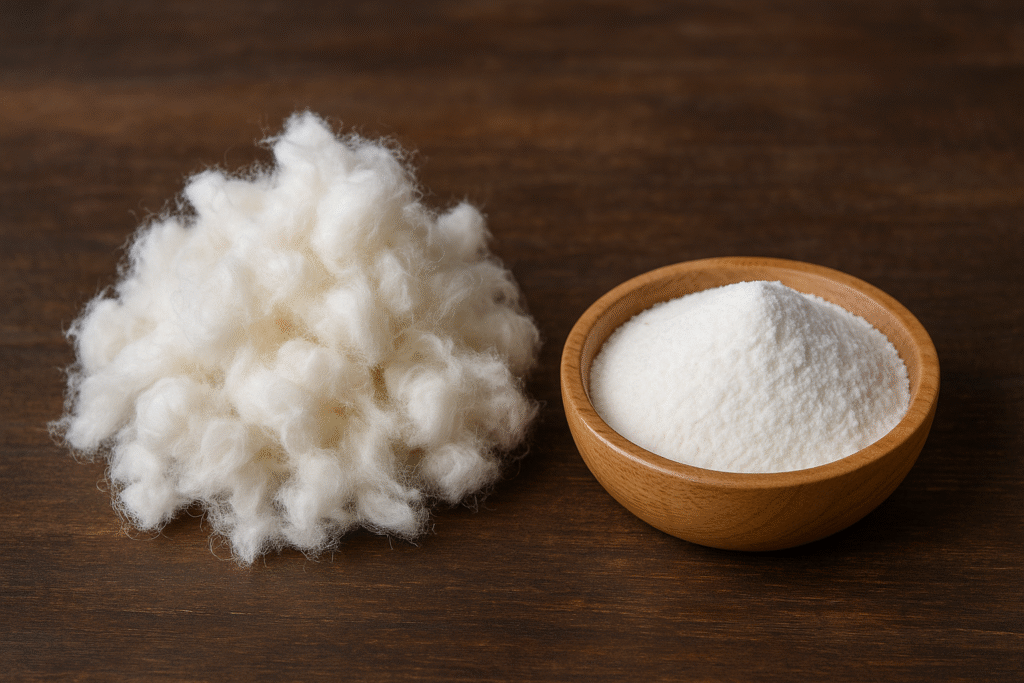

At our production facility in China, we primarily use wood pulp as our cellulose source6. I've personally visited our suppliers' forestry operations to ensure sustainable harvesting practices, something that matters increasingly to our customers in environmentally conscious markets.
The Journey from Tree to HPMC
The transformation from natural material to finished HPMC product7 involves several fascinating stages:
- Sustainable Forestry: Trees are harvested according to responsible forestry practices
- Pulping Process: Wood chips are processed to separate cellulose fibers from lignin and other wood components
- Purification: The cellulose undergoes multiple washing and bleaching steps
- Alkalization: The purified cellulose is treated with sodium hydroxide
- Chemical Modification: The alkali cellulose reacts with methyl chloride and propylene oxide
- Neutralization: The pH is adjusted to create a stable product
- Refinement: The material is purified, dried, and milled to specification
Through this process, approximately 30-40% of the final HPMC molecule remains from the original natural cellulose structure. The rest consists of the synthetic hydroxypropyl and methyl groups that give HPMC its unique properties.
For environmentally conscious customers in markets like Mexico and Philippines, we emphasize that our production process maximizes the efficiency of natural resource use, with minimal waste and energy consumption compared to fully synthetic alternatives.
Conclusion
HPMC sits at the intersection of natural and synthetic - starting with wood or cotton cellulose but chemically modified for performance. This semi-synthetic nature gives it the best of both worlds for construction applications while maintaining a favorable safety profile.
-
Explore this link to understand the properties and applications of HPMC in eco-friendly building materials. ↩
-
Discover how natural cellulose is transformed into valuable construction materials and its significance in eco-friendly practices. ↩
-
Explore the safety benefits of HPMC in construction to understand its advantages over other materials and its minimal health risks. ↩
-
Discover if HPMC capsules are a natural alternative to gelatin, especially for those seeking vegetarian options in pharmaceuticals. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the diverse applications of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in various industries, including construction and pharmaceuticals. ↩
-
Learn about various cellulose sources and their impact on sustainability and product quality, crucial for informed decision-making. ↩
-
Discover the diverse applications of HPMC and how it can be utilized in different sectors, enhancing your knowledge of this versatile compound. ↩







