Are you confused about which cellulose ether to choose for your construction projects? Many mortar manufacturers struggle with selecting between HPMC and MHEC, often paying more than necessary due to unclear understanding of their differences.
Both HPMC and MHEC are cellulose ethers used in construction materials, but they have distinct chemical structures and performance characteristics. HPMC contains hydroxypropyl groups while MHEC has hydroxyethyl groups, resulting in different water retention capabilities, workability, and cost effectiveness for specific applications.
 https://placehold.co/600x400 "HPMC vs MHEC cellulose ethers")
https://placehold.co/600x400 "HPMC vs MHEC cellulose ethers")
I've been supplying both these products to construction chemical manufacturers for over 15 years. Many customers come to me confused about which product would work best for their specific application. Let me break down the key differences to help you make an informed decision for your projects.
Introduction: What Are These Cellulose Ethers?
Do you know what these white powders actually do in your construction formulations? Many manufacturers use them without fully understanding their chemical nature and specific benefits.
HPMC and MHEC are both modified cellulose ethers derived from natural cellulose. They function as water-retaining agents, thickeners, binders, and film-formers in various building materials like tile adhesives, renders, and self-leveling compounds.

These additives might look similar as white powdery substances, but their chemical structures differ significantly. Both start as cellulose extracted from plants, typically wood pulp or cotton fibers. The production process involves treating cellulose with sodium hydroxide to create alkali cellulose. Then, specific etherification agents are introduced to create either hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) or methyl hydroxyethyl cellulose (MHEC).
The etherification process is where they diverge: HPMC is produced using propylene oxide and methyl chloride, while MHEC uses ethylene oxide and methyl chloride. This difference in chemical composition leads to the distinct performance characteristics we'll discuss in the following sections.
Chemical Structure Comparison
| Property | HPMC | MHEC |
|---|---|---|
| Etherifying Agents | Propylene oxide + Methyl chloride | Ethylene oxide + Methyl chloride |
| Functional Groups | Hydroxypropyl + Methyl | Hydroxyethyl + Methyl |
| Molecular Structure | Longer side chains | Shorter side chains |
| Typical DS (Degree of Substitution) | 1.4-2.0 | 1.3-1.9 |
| Typical MS (Molar Substitution) | 0.1-1.0 | 0.05-0.9 |
Similarities Between HPMC & MHEC in Construction Chemicals?
Are you wondering why these two products often appear interchangeable in many applications? Their shared properties explain why switching between them seems possible in some cases.
Both HPMC and MHEC provide essential functions like water retention, improved workability, and adhesion enhancement in cement-based formulations. They create a gel-like layer that slows water evaporation and improves open time for applications like tile adhesives.
When I visit construction sites across Saudi Arabia and UAE, I notice both HPMC and MHEC performing admirably in high-temperature environments. These cellulose ethers share several important characteristics that make them valuable in construction applications. Both create a protective colloid effect that stabilizes the cement hydration process, ensuring proper curing even in challenging conditions.
From a practical standpoint, they both improve the consistency and workability of mortars, reducing the amount of water required while maintaining proper consistency. This results in stronger final products with fewer cracks and improved durability. Additionally, both HPMC and MHEC enhance the sag resistance of vertical applications, allowing for thicker application of materials like tile adhesives without slippage.
Shared Benefits in Construction Applications
| Function | Benefit in Construction |
|---|---|
| Water Retention | Prevents rapid water loss, improves cement hydration |
| Workability | Makes mortar smoother and easier to apply |
| Open Time | Extends working time for better application |
| Anti-sagging | Improves vertical stability of applied materials |
| Anti-bleeding | Prevents water separation in fresh mixtures |
| Film Formation | Creates protective films in paint applications |
Key Differences Between HPMC & MHEC?
Have you noticed that some manufacturers insist on MHEC for specific applications while others use only HPMC? The distinct performance characteristics explain these preferences.
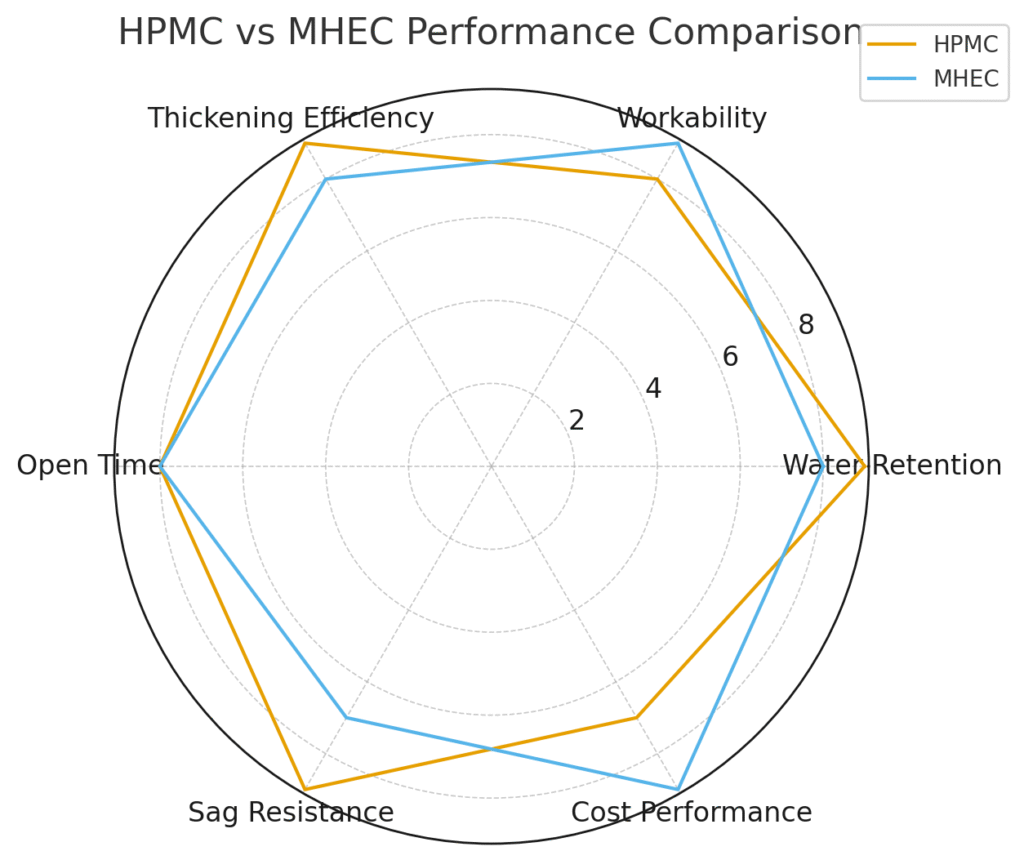
HPMC provides stronger water retention and higher viscosity at the same dosage compared to MHEC. Meanwhile, MHEC offers better workability at lower temperatures and dissolves more easily in cold water than HPMC, which requires hot water for optimal dissolution.
In my experience working with hundreds of mortar manufacturers, I've observed these differences firsthand. HPMC's hydroxypropyl groups create a more robust gel structure that excels in extreme conditions, particularly in hot climates like the Middle East. During summer months in Saudi Arabia, when temperatures regularly exceed 40°C, HPMC maintains its water retention properties more effectively than MHEC.
The dissolution behavior between these products becomes particularly important in production environments. MHEC dissolves more rapidly in cold water, which can streamline production processes in facilities without hot water systems. HPMC, by contrast, often requires hot water or special dissolution equipment to achieve optimal performance. I've helped customers implement both approaches depending on their specific plant capabilities.
Another key difference lies in their compatibility with other additives. MHEC typically shows better compatibility with redispersible polymer powders, creating more stable formulations. HPMC, on the other hand, offers stronger anti-sagging properties in high-build applications like thick-bed tile adhesives. The selection between these products often comes down to which performance characteristic is most critical for the specific application.
Performance Differences Table
| Property | HPMC | MHEC |
|---|---|---|
| Water Retention | Higher | Good but less than HPMC |
| Dissolution | Requires hot water (>70°C) | Dissolves well in cold water |
| Viscosity Development | Slower | Faster |
| Temperature Stability | Better in high temperatures | Better in low temperatures |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Typically higher cost |
| Sustainability | Lower energy production | Higher energy production |
Choosing Between HPMC & MHEC for Construction Applications?
Are you struggling to decide which cellulose ether is right for your specific application? Different construction materials have different requirements that may favor one product over the other.
For tile adhesives and renders in hot climates, HPMC's superior water retention makes it the preferred choice. For self-leveling compounds and applications in colder regions, MHEC's better flowability and cold-water dissolution may be more advantageous.
Through my years of working with construction chemical manufacturers across developing markets, I've developed some practical guidelines for material selection. The decision should be based on multiple factors beyond just price. Climate conditions at the application site play a crucial role - for projects in hot, dry areas like the Middle East, HPMC's superior water retention becomes essential to prevent premature drying and ensure proper cement hydration.
Production capabilities also factor into the decision. If your factory has limited hot water capacity, MHEC may be more practical despite its higher cost, as it can be incorporated more easily into existing production lines. I've helped several customers in Vietnam and the Philippines switch to MHEC for this specific reason, resulting in fewer production issues despite the higher raw material cost.
The specific application is perhaps the most important consideration. For tile adhesives, especially those designed for large-format tiles, HPMC's stronger anti-sagging properties make it ideal. For self-leveling compounds where flow characteristics are paramount, MHEC often performs better. Joint fillers and grouts can use either product, with the choice often coming down to cost considerations.
Application-Specific Recommendations
| Application | Recommended Product | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Tile Adhesives (hot climate) | HPMC | Better water retention |
| Tile Adhesives (cold climate) | Either (MHEC preferred) | Better workability at low temperatures |
| Self-leveling Compounds | MHEC | Better flowability |
| Renders/Plasters | HPMC | Cost-effective water retention |
| Joint Fillers | Either | Depends on specific requirements |
| Exterior Insulation Systems | HPMC | Better outdoor durability |
| Gypsum Products | MHEC | Better compatibility |
Conclusion
Both HPMC and MHEC offer valuable benefits in construction applications, but their different chemical structures create distinct performance advantages. Your specific application, climate conditions, and production capabilities should guide your choice between these cellulose ethers.







