Are you struggling to understand the full potential of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) in today's markets? Many manufacturers are missing opportunities because they don't grasp the diverse applications of this versatile polymer.
Carboxymethyl cellulose1 is a water-soluble cellulose derivative used across food, pharmaceuticals, detergents, oil drilling, paper, textiles, and construction industries. Its thickening, binding, stabilizing, and film-forming properties make it essential in products ranging from ice cream to construction mortars.
As a manufacturer with six production lines dedicated to cellulose derivatives, I've witnessed the remarkable growth of CMC demand across multiple sectors. Let me share what makes this versatile polymer so valuable and why understanding its applications matters for your business.
What Is The Structural Composition of Carboxymethyl Cellulose?
Have you ever wondered why CMC works so well in so many different applications? The secret lies in its unique molecular structure, which puzzles many first-time users who struggle to select the right grade for their products.
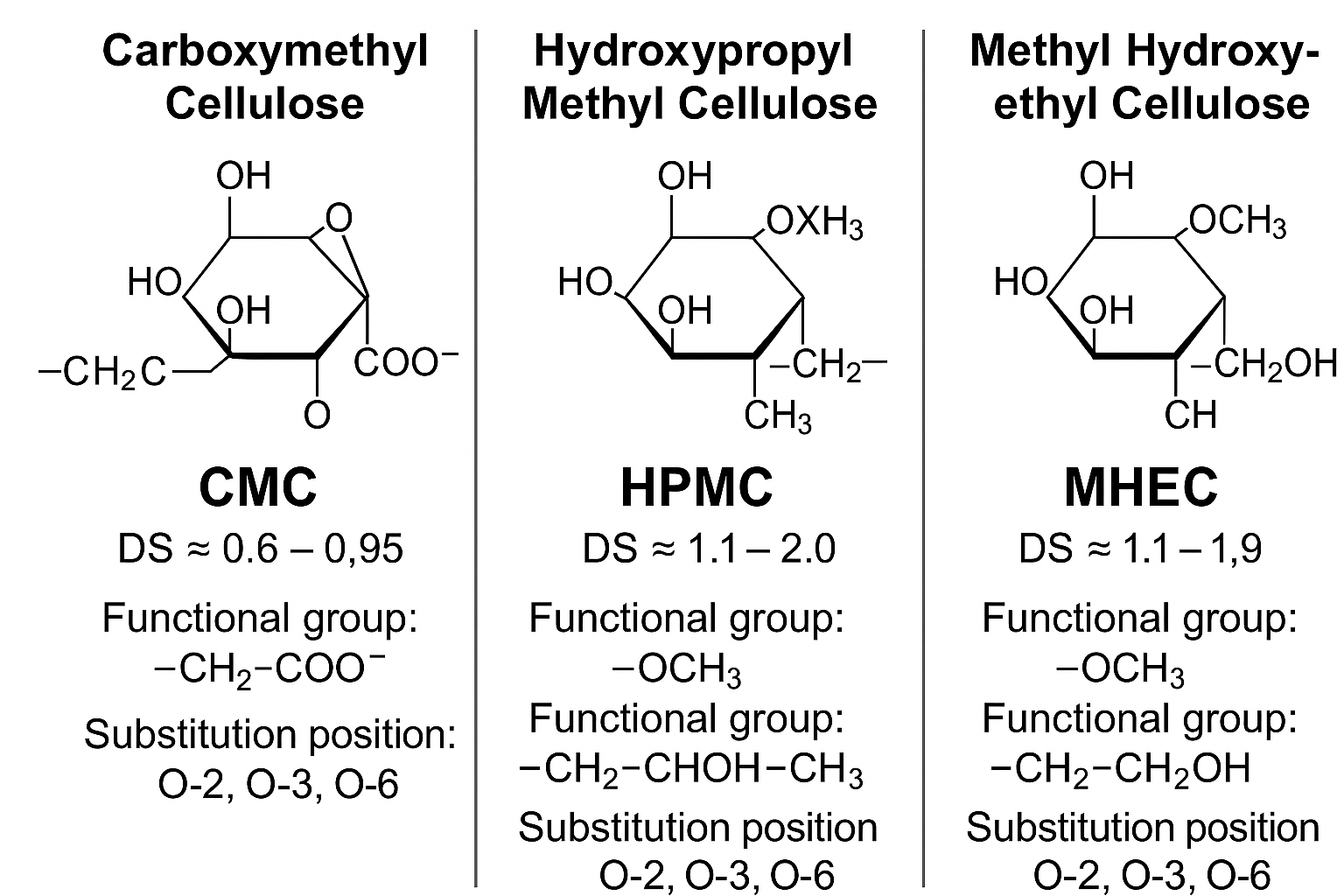
Carboxymethyl cellulose1 is formed by replacing hydroxyl groups in cellulose with carboxymethyl groups, creating a water-soluble polymer with anionic character. Its structure consists of β-(1→4)-D-glucopyranose units with varying degrees of substitution (DS), typically between 0.4-1.5, determining its solubility and functionality.
 https://placehold.co/600x400 "Molecular structure of carboxymethyl cellulose showing substitution")
https://placehold.co/600x400 "Molecular structure of carboxymethyl cellulose showing substitution")
The molecular structure of CMC gives it remarkable versatility across applications. When I first started producing CMC, I realized that controlling the degree of substitution was critical for meeting different industry requirements. A higher DS increases water solubility but also affects viscosity behavior.
Key Structural Parameters That Impact Performance
Different applications require specific CMC properties. The most important structural parameters include:
| Parameter | Description | Impact on Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Degree of Substitution (DS) | Number of hydroxyl groups replaced by carboxymethyl groups | Determines solubility, viscosity, and ionic character |
| Molecular Weight | Size of the polymer chain | Affects solution viscosity and film-forming properties |
| Purity | Level of unwanted by-products | Critical for food and pharmaceutical applications |
| Particle Size | Physical dimensions of CMC powder | Impacts dissolution rate and handling characteristics |
From my experience working with various customers, I've found that food-grade CMC typically requires a DS of 0.7-0.9 with high purity standards, while technical applications like drilling fluids can use CMC with DS values around 0.4-0.7. Understanding these structural differences helps me recommend the right CMC type for each customer's specific needs.
How Is Carboxymethyl Cellulose Produced Commercially?
Are you concerned about consistency and quality in your CMC supply? Many buyers I've spoken with worry about batch-to-batch variations that can disrupt their production processes and product performance.
Carboxymethyl cellulose1 is manufactured through alkaline treatment of cellulose (typically wood pulp or cotton linters) with sodium monochloroacetate. The process involves alkalizing cellulose with sodium hydroxide, followed by etherification, neutralization, purification, drying, and grinding to produce the final powder form.

In our factory, we've perfected this process across our six production lines. Each step requires precise control to ensure consistent quality. The raw material selection is particularly critical—we've found that using high-grade cellulose sources directly impacts the final product's purity and performance.
Production Challenges and Quality Control
Manufacturing CMC with consistent properties presents several technical challenges. At our facility, we implement rigorous quality control measures throughout the production process:
- Raw Material Screening: We test each cellulose batch for moisture content, DP (degree of polymerization), and purity
- Reaction Control: Maintaining precise temperature, time, and reagent ratios during alkalization and etherification
- Purification Efficiency: Removing by-products like sodium glycolate and salt to achieve desired purity levels
- Particle Size Management: Controlling grinding and classification to meet customer specifications
I remember when we first began exporting to Saudi Arabia and UAE—customers were particularly concerned about batch consistency as they used our CMC in paint formulations where any variation could affect the final product performance. We implemented additional in-process testing points and statistical process control, which reduced variation and improved customer satisfaction significantly.
The production method directly influences the CMC's properties. For example, the solvent used during the reaction (whether water-based or alcohol-based) affects the uniformity of substitution along the cellulose chain, which in turn impacts solution clarity and stability—properties particularly important for food and pharmaceutical applications.
Which Industries Rely on Carboxymethyl Cellulose Applications?
Do you know the full range of industries where CMC creates value? Many of our new customers are surprised to learn how this versatile polymer solves problems across diverse applications they hadn't considered before.
Carboxymethyl cellulose1 serves as a thickener, stabilizer, binder, and film-former across multiple industries. In food, it prevents ice crystal formation and improves texture; in pharmaceuticals, it controls drug release; in detergents, it prevents soil redeposition; while in construction, it enhances workability and water retention in mortars.

Over my years working with customers across continents, I've seen CMC solve unique challenges in practically every industry. Let me share some insights from our most significant market segments.
Food Industry Applications
The food industry represents one of the largest markets for high-purity CMC. Here's how it functions in different food categories:
| Food Category | CMC Function | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Dairy Products | Stabilizer, texture modifier | Prevents whey separation in yogurt; improves mouthfeel in ice cream |
| Bakery Products | Water binding agent | Extends shelf life; improves dough stability |
| Beverages | Stabilizer | Prevents sedimentation in fruit juices and milk drinks |
| Sauces & Dressings | Thickener, emulsion stabilizer | Creates smooth texture; prevents oil separation |
One of our clients in Saudi Arabia produces a popular traditional dairy drink. They were struggling with phase separation during summer storage. By recommending a specific grade of CMC with the right DS and viscosity profile, we helped them solve this problem without altering the flavor—resulting in expanded distribution and reduced returns.
Construction Industry Applications
In construction materials—particularly in dry-mix mortars, tile adhesives, and renders—CMC plays several crucial roles:
- Water retention: Prevents rapid water loss, ensuring proper cement hydration
- Workability enhancer: Improves application properties and reduces sagging
- Open time extension: Gives applicators more time to adjust tiles before setting
- Enhances adhesion: Improves bonding to various substrates
Our experience with construction customers in developing markets like India and Pakistan has shown that the right grade of CMC can compensate for challenging application conditions like extreme heat or variable substrate quality. For instance, we developed a specialized CMC grade with enhanced water retention for a customer in Dubai, where rapid evaporation was causing premature mortar drying and poor adhesion.
What Are The Current Market Trends and Future Outlook For CMC?
Are you wondering how the CMC market will evolve in the coming years? Many of our partners are concerned about sustainability requirements and regulatory changes that might affect their supply chain and product formulations.
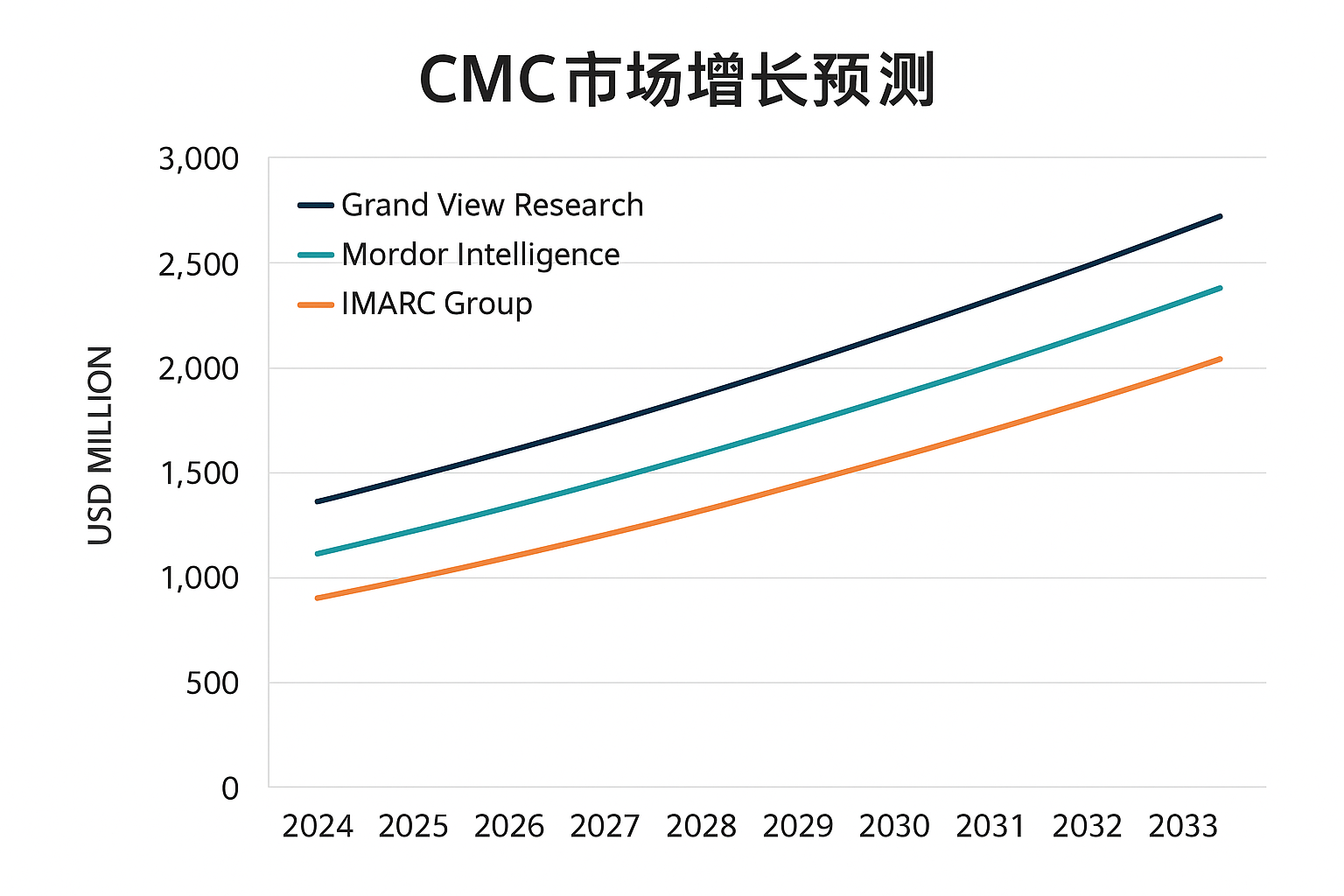
The global CMC market is trending toward sustainable production methods, higher purity grades, and specialized functional properties. Growth is driven by increasing demand in convenience foods, pharmaceutical delivery systems, and eco-friendly detergents, with projections showing 4-5% annual growth through 2028.
 https://placehold.co/600x400 "CMC market growth projection chart")
https://placehold.co/600x400 "CMC market growth projection chart")
As I meet with customers at international exhibitions and during factory visits, I've noticed several clear market directions emerging. These trends present both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers and end-users alike.
Sustainability and Bio-Based Alternatives
The push for greener chemistry and sustainable materials is reshaping the CMC market. Key developments include:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: New production methods that use less water and energy
- Alternative Cellulose Sources: Exploration of agricultural waste streams instead of wood pulp
- Biodegradability Focus: Enhanced formulations that ensure complete biodegradation
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Supply chain optimizations and local sourcing initiatives
Just last year, we invested in new equipment that reduced our water consumption by 30% and energy usage by 25% per ton of CMC produced. These improvements weren't just environmentally beneficial—they also reduced our production costs, allowing us to stay competitive while meeting the sustainability requirements of our European customers.
Regional Market Dynamics
Different regions show varied growth patterns and application preferences:
| Region | Key Growth Drivers | Dominant Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Asia Pacific | Food industry expansion, construction boom | Food, detergents, construction |
| Middle East | Oil industry recovery, processed food growth | Drilling fluids, food |
| North America | Pharmaceutical innovation, premium food products | Pharmaceuticals, specialty food |
| Europe | Eco-friendly products, technical textiles | Detergents, textiles, paper |
In our export business, we've seen particularly strong growth in the Middle East and Southeast Asian markets. In Saudi Arabia, the combination of oil industry activity and expanding food processing has created dual demand streams for our CMC products. Meanwhile, in markets like Vietnam and the Philippines, the rapid construction sector growth has driven demand for our construction-grade CMC.
Conclusion
Carboxymethyl cellulose1's versatility across food, pharmaceuticals, construction, and numerous other industries makes it an essential ingredient in countless products we use daily. By understanding its structure, production, and application potential, manufacturers can leverage CMC to improve product performance and meet evolving market demands.







