Puzzled by inconsistent product performance? Many mortar manufacturers struggle with quality issues without realizing it often traces back to improper CMC degree of substitution selection.
The degree of substitution (DS) in CMC refers to the average number of hydroxyl groups substituted per glucose unit, ranging from 0 to 3. Higher DS values (0.7-1.2) generally indicate better water solubility, improved thickening capability, and enhanced stability in your final construction products.
I've been manufacturing cellulose ethers for over 15 years at our Kehao factory, and I've seen firsthand how choosing the wrong DS value can sabotage an otherwise perfect formulation. Let me guide you through this critical parameter that many buyers overlook.
What is the Degree of Substitution of CMC and Why Does It Matter?
Pain point: Using CMC with improper DS values can lead to product failures, wasted materials, and unhappy customers - problems I frequently help clients solve.
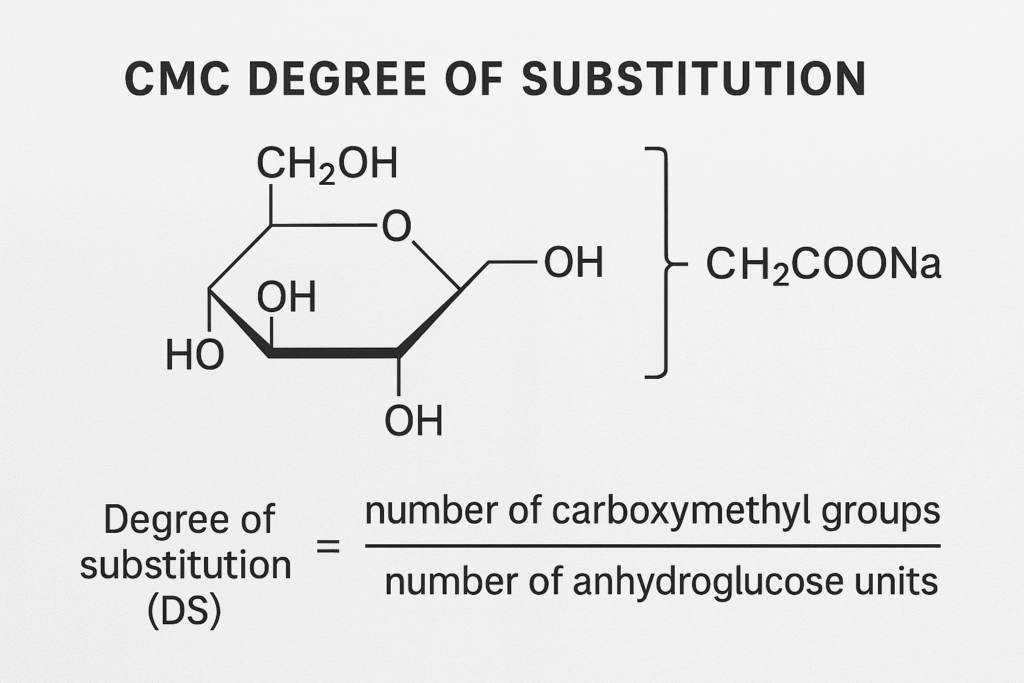
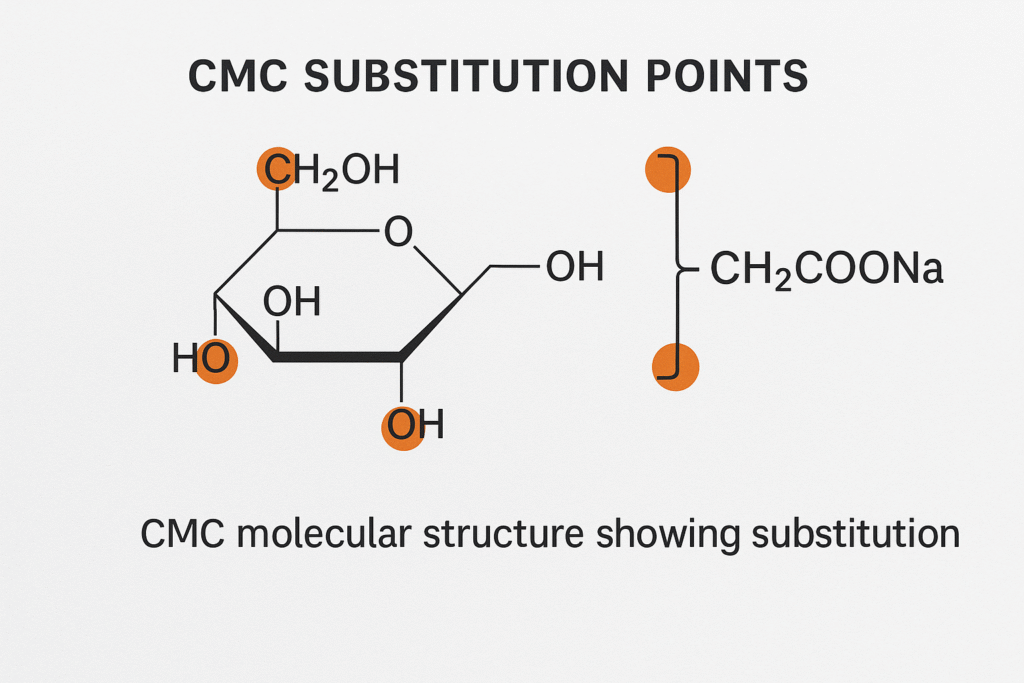
The degree of substitution1 (DS) in carboxymethyl cellulose2 represents the average number of hydroxyl groups replaced by carboxymethyl groups in each glucose unit of the cellulose chain. With each unit offering three replaceable hydroxyl groups, DS theoretically ranges from 0-3, though commercial CMC typically falls between 0.4-1.4.
The DS value directly impacts how your CMC will perform in your formulations. Through years of testing at our Kehao laboratories, I've observed that DS affects several critical properties:
How DS Affects CMC Properties
| DS Range | Solubility | Viscosity Behavior | Salt Tolerance | Acid Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4-0.6 | Water-swellable but not fully soluble | Lower viscosity | Poor | Poor |
| 0.7-0.9 | Good water solubility | Medium viscosity | Moderate | Moderate |
| 0.9-1.2 | Excellent water solubility | Higher viscosity | Good | Better |
| 1.2-1.4 | Excellent water solubility | Highest viscosity | Excellent | Best |
For building materials, the DS value determines key application properties. In tile adhesives3, for example, a CMC with DS 0.9-1.2 provides optimal water retention without excessive stickiness. For rendering mortars, DS values of 0.7-0.9 often balance cost and performance better.
Last year, one of our Saudi Arabian clients was experiencing inconsistent open time in their tile adhesives. Through careful analysis, we discovered their previous supplier was providing CMC with fluctuating DS values. After switching to our consistent DS 0.95 product, their quality issues disappeared completely.
What is the Degree of Substitution DS in Chemical Terms?
Struggling with technical specifications? Many customers I work with find the chemical aspects of CMC confusing, leading to costly formulation mistakes.
DS represents the average number of hydroxyl groups (OH) in the cellulose molecule that have been substituted with carboxymethyl groups (-CH₂COOH) through an etherification process. Mathematically, it's calculated by dividing the number of substituted hydroxyl groups by the total possible substitution sites.
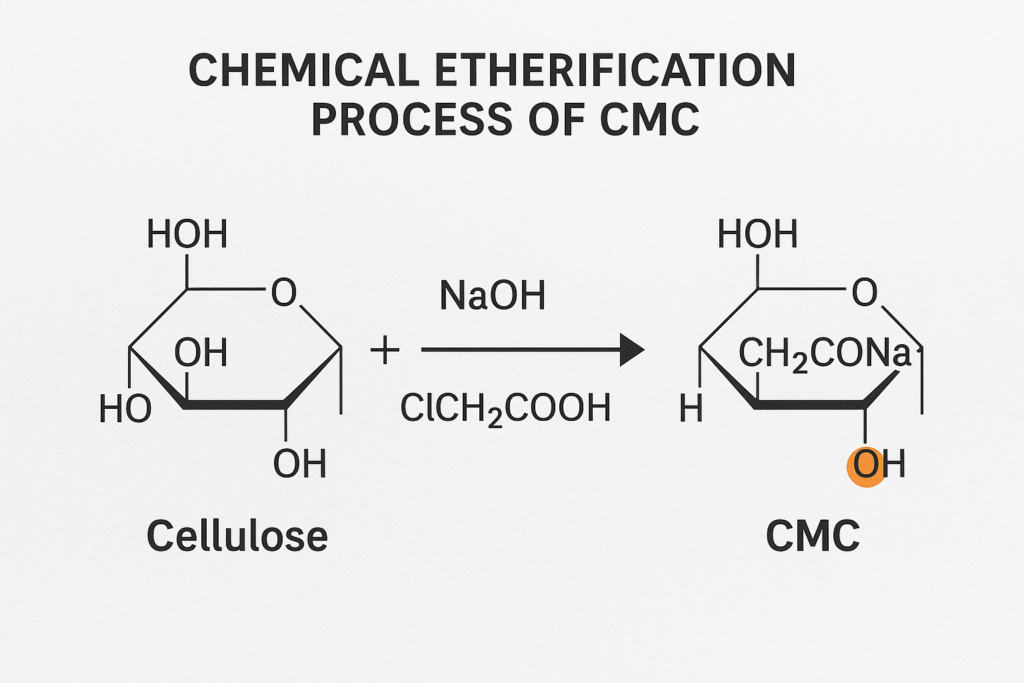
The chemistry behind DS measurement reveals why it matters so much in practical applications. When manufacturing CMC at our Kehao production lines, we carefully control the etherification reaction that transforms cellulose into CMC. This reaction involves treating alkali cellulose with sodium monochloroacetate under precisely controlled conditions.
Chemical Factors Affecting DS Values
| Factor | Effect on DS | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Alkali concentration | Higher concentration → Higher DS | Improved solubility but potentially lower viscosity |
| Reaction temperature | Higher temperature → Higher DS (to a point) | Better uniformity of substitution |
| Reaction time | Longer time → Higher DS (to equilibrium) | More complete reaction, more consistent properties |
| Solvent ratio | Optimized ratio → More uniform DS | Better product consistency |
The substitution pattern matters too - it's not just about how many hydroxyl groups are substituted but also which ones. Substitution at the C-2 position of the glucose unit provides better solubility than the same degree of substitution at C-6 positions. This is why two CMC products with identical DS values might still perform differently.
I remember visiting a client's mortar factory in Pakistan where they were experiencing settling issues despite using the "right" DS value. We discovered through specialized analysis that the distribution of substitution was uneven, leading to inconsistent performance. After switching to our more uniformly substituted CMC, their products achieved perfect stability.
What is the Degree of Substitution Analysis and How Is It Performed?
Concerned about getting what you pay for? Many buyers I consult with have received mislabeled CMC products because they didn't know how to verify DS claims.
Degree of substitution analysis is the laboratory process of determining how many hydroxyl groups in cellulose have been replaced with carboxymethyl groups. Standard methods include titration techniques, spectroscopic methods like FTIR, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy for more precise results.
At Kehao's quality control laboratory, we employ multiple methods to ensure accurate DS measurement. The titration method, based on ASTM D1439, is our routine approach for production quality control. This method involves converting the CMC to its acid form, neutralizing with standardized sodium hydroxide, and calculating DS from the amount of base consumed.
Comparison of DS Analysis Methods
| Method | Accuracy | Complexity | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acid-wash titration | ±0.03 DS units | Low | Routine QC |
| FTIR spectroscopy | ±0.05 DS units | Medium | Rapid screening |
| NMR spectroscopy | ±0.01 DS units | High | Research, dispute resolution |
| Elemental analysis | ±0.02 DS units | Medium | Verification |
For our clients who need to verify DS values in their own facilities, we recommend a simplified titration method. I've personally trained quality control personnel at several customer sites in UAE and Saudi Arabia to perform basic DS checks that help ensure they're receiving the correct material.
A reliable DS analysis is crucial because even small variations can impact performance. For example, in our testing, CMC with a DS of 0.75 vs. 0.85 showed a 30% difference in water retention capacity in cement-based tile adhesive formulations. This could mean the difference between a tile adhesive that performs perfectly and one that fails prematurely.
What are the Different Grades of CMC Based on Degree of Substitution?
Overwhelmed by too many options? I frequently see customers selecting inappropriate CMC grades because they don't understand how DS classifications relate to applications.
CMC grades are classified by several parameters, with DS being a primary factor. Commercial CMC typically falls into low DS (0.4-0.7), medium DS (0.7-1.0), and high DS (1.0-1.5) categories, each offering distinct benefits for specific applications in construction, food, pharmaceuticals, and other industries.
In my 15 years at Kehao, I've observed that the construction industry uses specific DS ranges for optimal performance. The following breakdown explains why certain DS values work better for specific applications:
CMC Grades for Construction Applications
| DS Range | Grade Classification | Ideal Applications | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4-0.6 | Low DS | Concrete admixtures, basic grouts | Limited water retention, economical |
| 0.7-0.9 | Medium DS | General-purpose mortars, rendering systems | Good balance of water retention and workability |
| 0.9-1.2 | High DS | Premium tile adhesives3, self-leveling compounds | Superior water retention, excellent workability |
| 1.2-1.4 | Ultra-high DS | Specialized applications, premium plasters | Exceptional stability in difficult conditions |
Beyond DS, we need to consider viscosity, purity, and particle size. For example, a client in Brazil was using a high DS CMC (1.1) in their exterior rendering mortar but experiencing application difficulties. Despite the high DS, the viscosity profile wasn't optimal for their application method. We developed a custom solution with a slightly lower DS (0.95) but a more suitable viscosity curve, solving their problem immediately.
Additionally, the manufacturing process affects uniformity of substitution. At Kehao, we use a proprietary slurry process that ensures more consistent substitution compared to the cheaper solvent methods used by some manufacturers. This results in more predictable performance even when the labeled DS values are similar.
I recently visited a client's site in Vietnam who was struggling with batch-to-batch consistency in their paint formulations. Their raw material specifications only mentioned DS, but not uniformity of substitution. After switching to our more uniformly substituted product, their production became much more consistent.
Conclusion
The degree of substitution1 in CMC directly impacts your product's performance. By selecting the right DS value for your specific application and ensuring consistent quality, you'll achieve superior results and avoid costly formulation problems.