Are you struggling with construction materials that crack, sag, or fail to perform? Poor material choice can lead to costly repairs and project delays. HPMC1 might be the solution you haven't considered.
HPMC1 (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose) is essential in construction materials as it works as a water retainer, thickener, and lubricant. It ensures cement hydrates properly, prevents sagging of mortars on vertical surfaces, and improves workability while maintaining strength and durability.

I've seen countless construction projects transformed by the simple addition of HPMC. This remarkable cellulose ether has become indispensable in modern building materials, turning unstable manual work into reliable industrial products. Let me show you why this invisible ingredient makes such a visible difference.
What is HPMC1 Used For in Construction?
Do you know why your mortar stays workable for hours yet sets perfectly? The secret lies in a powerful additive that works behind the scenes.
HPMC is used in construction as an additive for tile adhesives, renders, plasters, joint compounds, self-leveling floors2, and EIFS systems3. It improves water retention, consistency, open time, and adhesion4 while preventing material failure in various environmental conditions.

HPMC plays three vital roles in construction materials that make it irreplaceable. First, it acts as a "water reservoir," locking moisture inside the mixture to ensure complete cement or gypsum hydration. This prevents premature drying and resultant brittleness. Without proper water retention, cement doesn't develop its full strength potential.
Second, HPMC serves as a "structural framework" by increasing viscosity. This is why mortars don't slide down walls and tiles don't slip after placement. This thickening effect is particularly important in vertical applications where gravity works against us.
Third, it functions as a "lubricant" that gives workers a smooth, effortless application experience. This might sound minor, but the workability dramatically impacts installation quality and speed.
These three functions transform unpredictable site work into consistent, reliable industrial products. Here's how HPMC is used in common construction applications:
| Application | HPMC Function | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Tile Adhesives | Water retention, sag resistance | Extended open time, no tile slippage |
| Renders/Plasters | Viscosity control, water retention | Good workability, crack prevention |
| Self-leveling Compounds | Flow control, water retention | Smooth surface, proper curing |
| Joint Fillers | Workability, adhesion | Easy application, strong joints |
| EIFS Systems | Water resistance, bonding | Durable exterior insulation |
What are the Benefits of HPMC?
Have you ever wondered why modern construction materials perform so much better than those from just decades ago? The difference often comes down to one critical additive.
HPMC benefits construction materials by extending working time, preventing cracks, improving adhesion, increasing yield, enhancing freeze-thaw resistance, and ensuring consistent performance across varying conditions. These properties reduce waste, callbacks, and project delays.
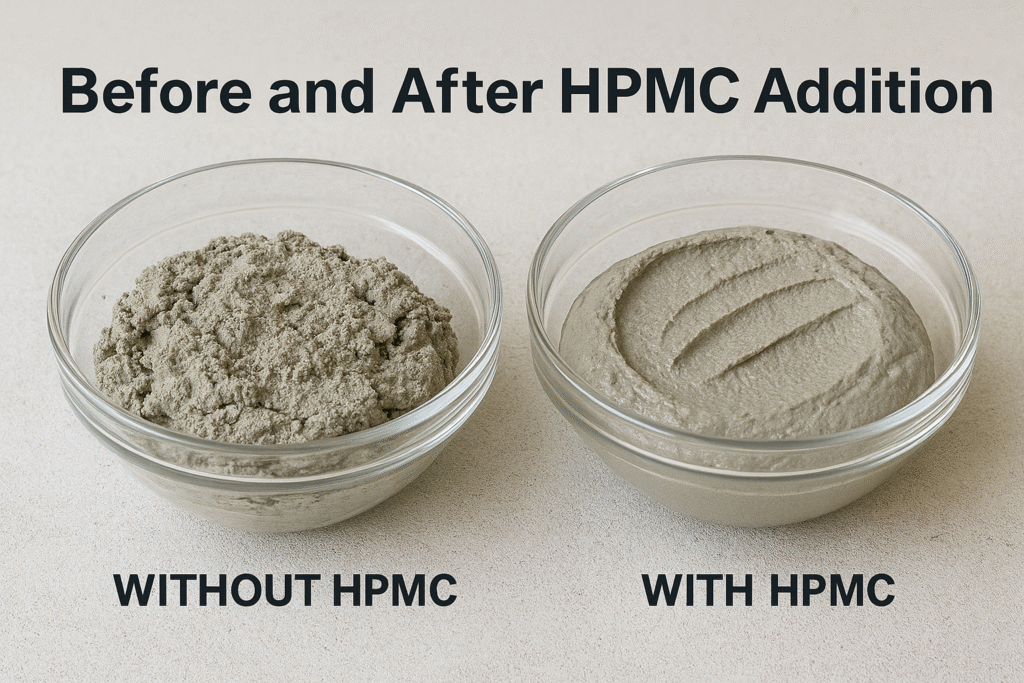
The benefits of HPMC extend far beyond its immediate technical functions. I've met many contractors who didn't understand why certain products performed better until they learned about HPMC's role. Let me break down these benefits from practical experience:
-
Quality Assurance: By controlling water retention and viscosity, HPMC transforms variable "craftsmanship" into reliable "engineered products." This standardization is crucial for modern construction where performance guarantees matter.
-
Problem Prevention: HPMC addresses the most common construction failures before they happen. Cracking, hollow spots behind tiles, and material detachment typically result from improper hydration or poor adhesion - precisely what HPMC1 prevents.
-
Labor Efficiency: The improved workability translates directly to faster installation and less worker fatigue. On large projects, this efficiency can save days or even weeks of labor time.
-
Material Economy: Though adding HPMC increases the base cost of materials, it reduces waste significantly. Better adhesion means thinner application layers, and extended working time means less discarded partially-set material.
-
Environmental Performance: HPMC-modified materials generally have better resistance to weather conditions, temperature fluctuations, and moisture changes. This environmental resilience extends building life and reduces maintenance.
The return on investment becomes clear when considering the cost of failure. A single callback to repair cracked or failing materials can erase the profit margin on an entire project. HPMC is effectively insurance against such costly scenarios.
What is the Use of HPMC1 in Cement?
Are your cement-based products drying too quickly or developing strength inconsistently? The problem might be water management during the critical hydration phase.
HPMC in cement mixtures primarily acts as a water retention agent, ensuring proper hydration of cement particles. It slows water evaporation, improves consistency, reduces bleeding and segregation, enhances bonding to substrates, and provides sag resistance for vertical applications.
Cement's transformation from powder to stone-like material depends entirely on its chemical reaction with water. This process, called hydration, determines the final strength, durability, and performance of cement-based products. HPMC plays a crucial role in optimizing this fundamental chemical reaction.
Without adequate water retention, cement hydration remains incomplete, resulting in reduced strength and increased vulnerability to future failures. HPMC creates a protective mechanism that holds water molecules within the cement matrix, releasing them gradually as needed for continued hydration.
I've observed remarkable differences in lab tests between standard cement mixtures and those modified with HPMC. The standard samples often show unpredictable strength development curves, while HPMC-modified samples demonstrate consistent, predictable strength gains. This predictability is invaluable for structural engineering calculations.
Beyond water retention, HPMC modifies cement rheology (flow behavior). It gives cement mixtures thixotropic properties – they flow when agitated but remain stable when left undisturbed. This characteristic explains why HPMC-modified mortars can be applied thickly to vertical surfaces without sagging.
HPMC also significantly reduces the bleeding effect (water rising to the surface) in fresh cement mixtures. This phenomenon typically weakens the surface layer of cement applications, making them dusty and prone to wear. By preventing bleeding, HPMC ensures uniform strength throughout the cement material.
Another important function is how HPMC modifies the interface between cement and substrates. The improved adhesion comes from both mechanical effects (better wetting of surfaces) and chemical interactions that create stronger bonds between dissimilar materials.
How Does HPMC Work as a Binder?
Have you noticed how modern construction adhesives seem to defy gravity, holding heavy materials in place without sliding? The secret lies in their unique binding mechanism5.
HPMC works as a binder by forming a three-dimensional network that interlocks with cement particles and aggregates. When mixed with water, it creates hydrogen bonds that increase cohesion while maintaining flexibility. This binding action improves adhesion to various substrates and prevents material separation during drying.
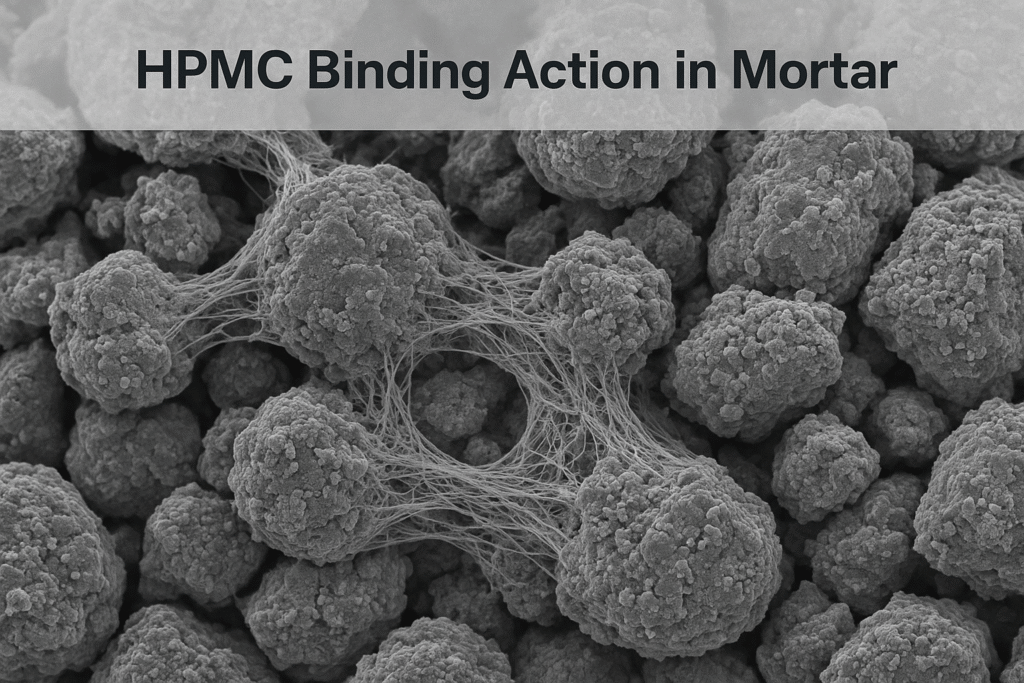
HPMC's binding capability represents one of the most fascinating aspects of polymer chemistry in construction. Unlike traditional cementitious binders that work through crystallization, HPMC creates flexible polymer chains that interlace throughout the material matrix.
I've conducted pull-off tests that clearly demonstrate how HPMC dramatically improves adhesive strength. When properly formulated, HPMC-modified mortars often exhibit substrate failure before adhesive failure – meaning the connection created is actually stronger than some of the materials being bonded.
This binding action works through several simultaneous mechanisms:
-
Hydrogen Bonding: HPMC forms numerous hydrogen bonds with water molecules, cement particles, and substrate materials. These relatively weak individual bonds collectively create significant adhesive strength through their sheer quantity.
-
Mechanical Interlocking: As the cellulose polymer chains extend throughout the material, they create a physical network that mechanically locks components together, similar to how rebar reinforces concrete.
-
Surface Tension Modification: HPMC changes the surface tension of water in the mixture, allowing better wetting of surfaces which leads to improved contact area and stronger adhesion.
-
Controlled Porosity: The polymer network creates optimized pore structures that balance strength and flexibility. This controlled porosity prevents the micro-cracking that often leads to adhesion failure.
-
Viscoelastic Properties: HPMC provides viscoelasticity to otherwise brittle cement systems, allowing slight movement without breaking bonds. This helps materials accommodate thermal expansion, minor substrate movement, and vibrations.
For construction professionals, understanding HPMC's binding mechanism explains why properly formulated mortars can successfully bond heavy materials like large-format tiles to vertical surfaces without slipping – a feat that would be impossible with traditional cement formulations.
Conclusion
HPMC1 transforms ordinary construction materials into high-performing solutions by controlling water, providing structure, and improving workability. Its ability to prevent failures while enhancing application makes it truly indispensable in modern construction technology.
-
Explore how HPMC enhances construction materials, ensuring durability and performance. ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩
-
Explore the advantages of self-leveling floors in modern construction practices. ↩
-
Learn about Exterior Insulation and Finish Systems and their role in energy efficiency. ↩
-
Discover the significance of adhesion in ensuring strong bonds in construction applications. ↩
-
Explore how HPMC's binding mechanism enhances adhesion and material strength. ↩







