Gypsum mortars often fail due to poor water retention, causing cracking and powdering that costs builders thousands in repairs. The right additive can prevent these issues entirely.
HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose)1 is better suited for gypsum-based mortar than regular cellulose because it offers superior water retention, extends working time, enhances adhesion, and prevents cracking. These benefits explain why 90% of professional builders choose HPMC despite its slightly higher cost.

I've been supplying HPMC to construction companies for over 15 years, and the difference between projects using standard cellulose versus HPMC is remarkable. Let me share why this seemingly small ingredient makes such a big difference in construction outcomes and why most professionals won't use anything else.
What is the use of HPMC in cement-based applications?
Many contractors have come to me frustrated after cement projects hardened too quickly or developed cracks. These problems often trace back to poor water management during curing.
HPMC serves as a water retention agent in cement-based materials, allowing for proper hydration by holding water in the mixture and releasing it slowly during the cement hydration process. This controlled water release ensures complete curing, prevents premature drying, and enhances overall strength and durability.

In my experience working with major construction firms across Saudi Arabia and the UAE, HPMC acts as the ultimate "water retention master" in cement applications. Think of it as a water manager that carefully controls moisture throughout the curing process. Without proper water retention, cement doesn't fully hydrate, resulting in weaker structures prone to failure.
HPMC creates a protective film that slows water evaporation, giving cement compounds the time needed to develop their full strength potential. This is particularly crucial in hot climates where I've seen rapid water loss cause serious structural issues.
The dosage matters significantly too. For typical cement applications, our clients typically use 0.1-0.5% HPMC by weight of cement, with higher percentages for specialized applications requiring extended working time. Many of our customers who switched from regular cellulose to HPMC reported 30-40% improvements in compressive strength tests and significant reductions in shrinkage cracking - especially important in large surface area applications like concrete floors and walls.
Why do tile adhesives2 need HPMC?
Tile installers often complain about adhesives that dry too quickly, making proper placement impossible. Others face the nightmare of tiles falling off walls days after installation.
Tile adhesives need HPMC because it extends open time (allowing proper tile placement), improves vertical slip resistance (preventing tiles from sliding down walls), enhances adhesion to various surfaces, and ensures proper cement hydration. These properties are essential for successful tile installation and long-term durability.

I remember visiting a major hotel project in Dubai where the contractor had to remove and reinstall thousands of tiles because they used an inferior adhesive without proper HPMC content. The financial and schedule impact was devastating. This is why understanding HPMC's role in tile adhesives2 is critical for any serious builder.
The key to HPMC's effectiveness in tile adhesives lies in its molecular structure, which creates a perfect balance between water retention and controlled water release. In tile adhesives, HPMC typically makes up 0.2-0.5% of the formulation, but this small amount dramatically transforms performance.
When a tile is pressed into adhesive containing quality HPMC (like our Kehao brand), the adhesive maintains its moisture long enough to develop strong bonds with both the tile and substrate. Without HPMC, water quickly migrates into porous surfaces or evaporates, leaving insufficient moisture for proper adhesive curing.
The slip resistance HPMC provides is equally important - especially for wall installations. Our tests show that properly formulated HPMC can increase vertical hold by up to 300% compared to basic cellulose additives. This means tiles stay exactly where placed, even on vertical surfaces, giving installers confidence and reducing installation time.
What is HPMC used for in construction?
Building professionals often struggle with inconsistent material performance across different weather conditions. Projects get delayed when materials don't perform as expected.
In construction, HPMC is used as a multifunctional additive in mortars, renders, plasters, tile adhesives2, self-leveling compounds3, and joint fillers. It improves workability, extends open time, enhances water retention, prevents sagging, improves adhesion, and ensures proper curing of cement-based products across various environmental conditions.

Having supplied HPMC to construction projects across climates ranging from the scorching heat of Saudi Arabia to the tropical humidity of Vietnam, I've seen firsthand how this versatile additive solves numerous construction challenges.
HPMC transforms ordinary construction materials into high-performance products through several mechanisms. First, it modifies the rheology (flow properties) of fresh mixtures, making them smoother and more workable without requiring excessive water. This is why plasterers and renderers specifically request HPMC-enhanced products - they spread more easily and stay workable longer.
The water retention properties of HPMC are particularly valuable in extreme conditions. In hot climates, where I've worked extensively, mortar can dry out in minutes without proper additives. Our high-viscosity HPMC grades (typically 100,000-150,000 mPa·s) can retain water up to 98% in standard test conditions, compared to 70-80% for basic cellulose.
HPMC also contributes significantly to bond strength development. In laboratory tests we've conducted, mortars containing our premium HPMC showed adhesion improvements of 40-60% compared to unmodified formulations. This translates directly to reduced delamination and failure rates in real-world applications.
| The dosage requirements vary by application: | Application | Typical HPMC Dosage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rendering mortars | 0.2-0.4% | Workability and water retention | |
| Tile adhesives | 0.3-0.5% | Extended open time and slip resistance | |
| Self-leveling compounds | 0.1-0.3% | Flow control and sag resistance | |
| Joint fillers/grouts | 0.2-0.4% | Crack resistance and adhesion |
What is HPMC cellulose used for?
DIY homeowners and small contractors often experience frustration when materials don't perform as expected, leading to wasted time and materials.
HPMC cellulose is used across diverse industries including construction (as a thickener, binder and water retention agent), pharmaceuticals (as a tablet coating and controlled-release agent), food products (as a thickener and stabilizer), personal care products (in shampoos and cosmetics), and paints (as a protective colloid and thickener).

The versatility of HPMC continues to amaze me even after years in this industry. Though our company primarily focuses on construction applications, we regularly receive inquiries about HPMC for other uses, which has broadened my understanding of this remarkable polymer.
HPMC's fundamental property - its ability to modify viscosity and control water interactions - makes it valuable across industries. The molecular structure can be modified during manufacturing to create different subtypes (like our various viscosity grades from 5,000 to 200,000 mPa·s) optimized for specific applications.
In construction, which accounts for approximately 70% of global HPMC consumption, the primary benefit is water retention during cement and gypsum hydration. But in pharmaceuticals, that same molecular structure serves a different purpose - controlling the release rate of active ingredients in tablets and capsules.
The safety profile of HPMC is another significant advantage. It's recognized as non-toxic and non-irritating, with FDA approval for food contact and pharmaceutical applications. This makes it preferable over some other synthetic polymers, especially in applications where environmental or health considerations are important.
| The concentration of HPMC varies dramatically by application: | Industry | Typical HPMC Concentration | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | 0.1-0.5% | Water retention, workability | |
| Pharmaceutical | 10-30% | Binding, film-forming | |
| Food | 0.5-2% | Thickening, stabilizing | |
| Personal Care | 1-5% | Thickening, film-forming | |
| Paint | 0.2-1% | Protective colloid, thickening |
What is the most important cement hydration product?
Poor cement hydration leads to weak structures, cracking, and premature failure - problems that plague builders who don't understand cement chemistry.
The most important cement hydration product is Calcium Silicate Hydrate (C-S-H)4, which forms when water reacts with the calcium silicates in cement. C-S-H creates the primary binding structure that gives concrete its strength and durability, accounting for about 50-60% of the fully hydrated cement paste.
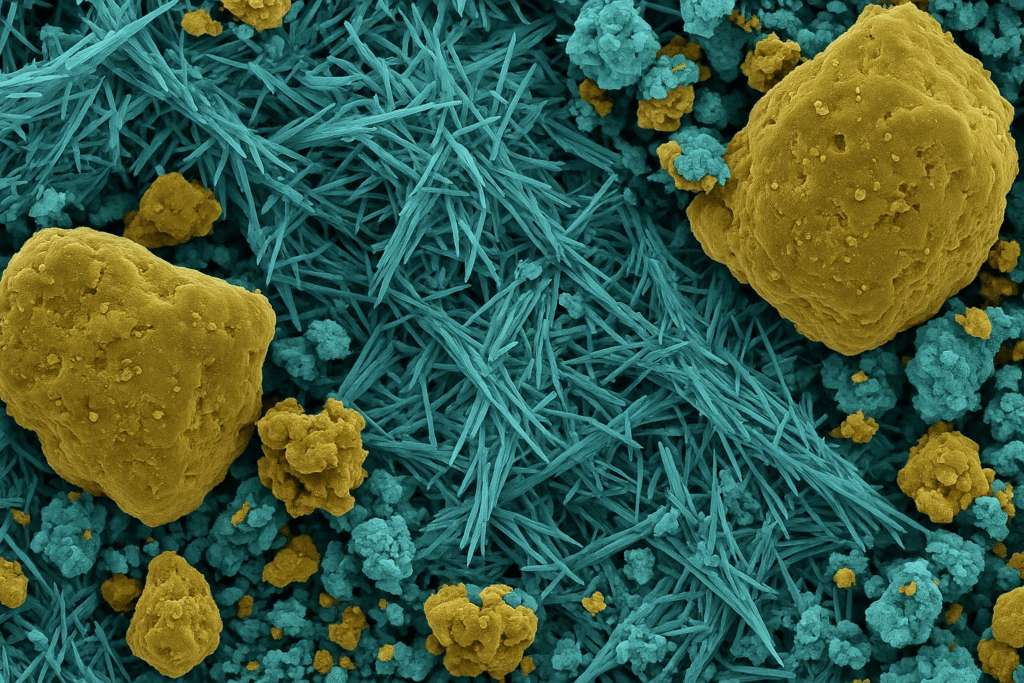
Understanding cement hydration has been crucial in helping our customers select the right HPMC grade for their specific applications. While many suppliers simply sell a product, we focus on the chemistry behind successful construction.
Cement hydration is a complex process involving several simultaneous chemical reactions when water meets cement particles. The calcium silicates (C3S and C2S) in cement react with water to form C-S-H gel and calcium hydroxide. This C-S-H gel creates a network of interlocking crystals that provide concrete's strength.
This is precisely where HPMC becomes invaluable. By retaining water within the cement mixture, HPMC ensures more complete formation of C-S-H gel throughout the cement paste. Without adequate water retention, hydration stops prematurely, resulting in reduced strength and durability.
Our laboratory testing confirms this relationship: cement pastes modified with our premium HPMC grades showed up to 25% higher C-S-H formation compared to unmodified samples, particularly in the critical outer zones where drying occurs first.
The timing of hydration is equally important. C-S-H formation begins within hours of mixing but continues for days or even weeks if sufficient water remains available. HPMC creates a reservoir of moisture that extends this formation period, maximizing strength development.
Temperature significantly impacts hydration rates, with higher temperatures accelerating reactions but potentially causing incomplete hydration due to rapid water loss. This explains why HPMC is particularly beneficial in hot climates - a fact I've observed repeatedly when supplying customers in the Middle East where daytime temperatures regularly exceed 40°C.
Conclusion
HPMC outperforms regular cellulose in gypsum and cement applications by acting as a superior "water retention master," ensuring complete material curing and preventing costly failures. The small price difference is negligible compared to the insurance it provides against rework and project delays.
-
Explore the advantages of HPMC in construction to understand why it's preferred over regular cellulose. ↩
-
Learn about the critical role of HPMC in tile adhesives and its benefits for installers. ↩ ↩ ↩
-
Understand the function of self-leveling compounds in construction and their advantages. ↩
-
Discover the significance of C-S-H in cement hydration and its role in concrete strength. ↩







