I face this question often from customers who need to improve their mortar formulations. Poor water retention causes cracking, weak bonds, and compromised durability in cement applications.
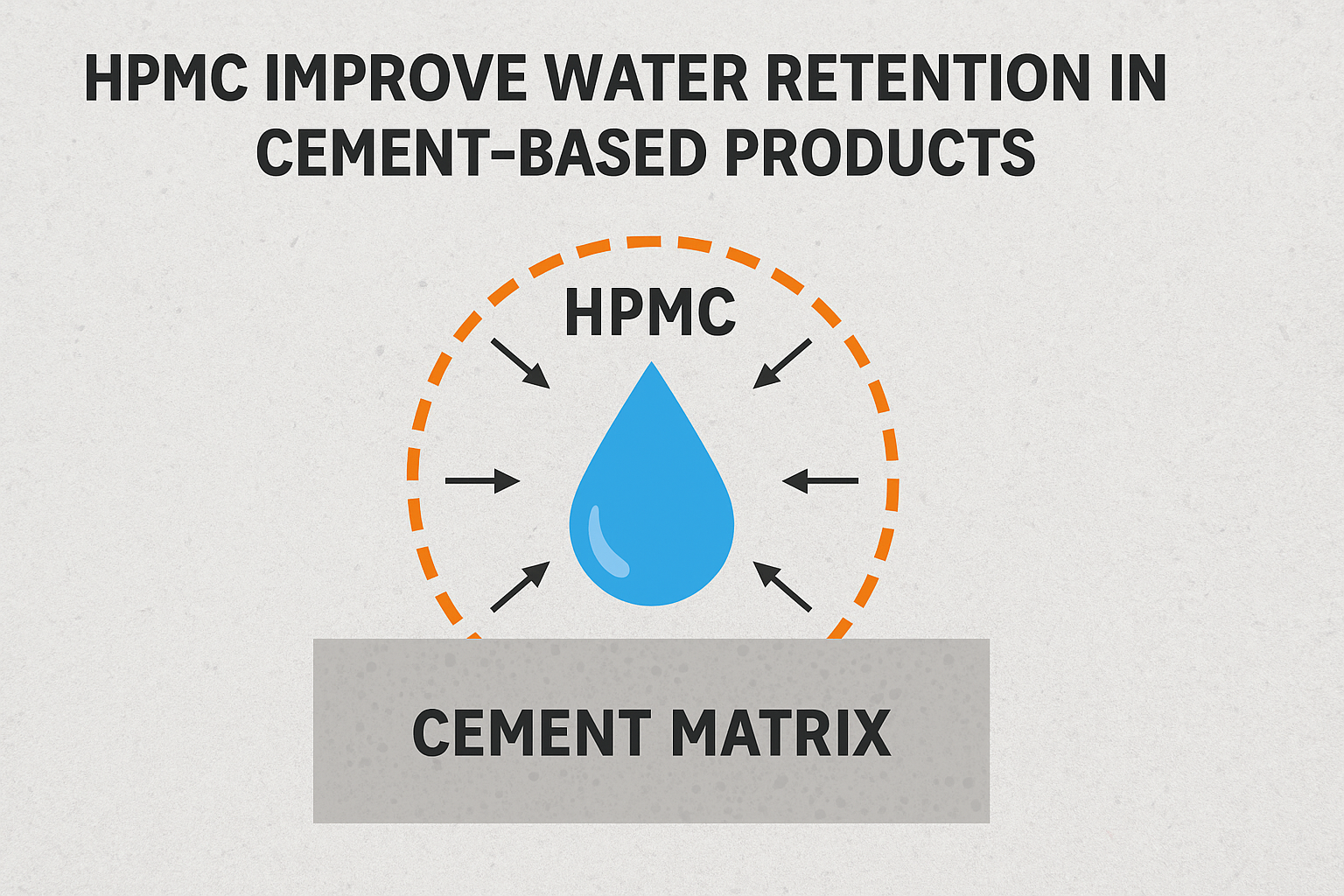
HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose)1 improves water retention in cement-based products by forming a three-dimensional molecular network that temporarily traps water molecules through hydrogen bonding. This controlled water release ensures proper cement hydration, prevents premature drying, and allows for complete curing.
When I first started supplying HPMC to construction material manufacturers2, many were skeptical about how a small percentage of this powder could so dramatically improve their products. Let me take you through exactly how HPMC transforms ordinary cement mixes into high-performance building materials.
What is the use of HPMC in cement?
Many customers come to me confused about why their mortars crack or fail to bond properly. These problems often trace back to poor water management during curing.
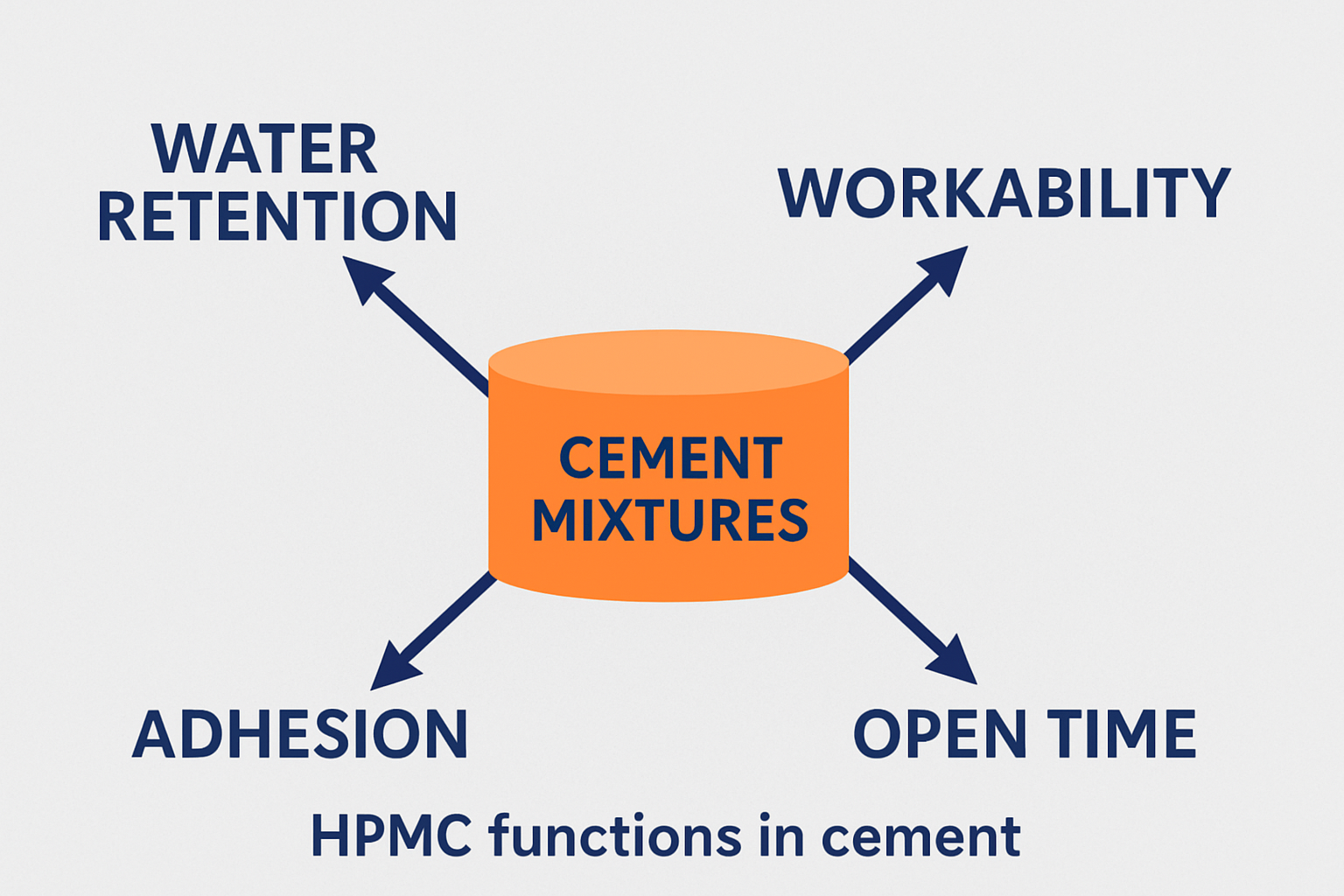
HPMC serves multiple critical functions in cement-based materials. It primarily acts as a water retention agent that forms a molecular "sponge" network throughout the mix. This network holds water molecules through hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl groups on the HPMC chain and water molecules. Additionally, HPMC improves workability, extends open time, enhances adhesion to substrates, and prevents sagging on vertical surfaces.
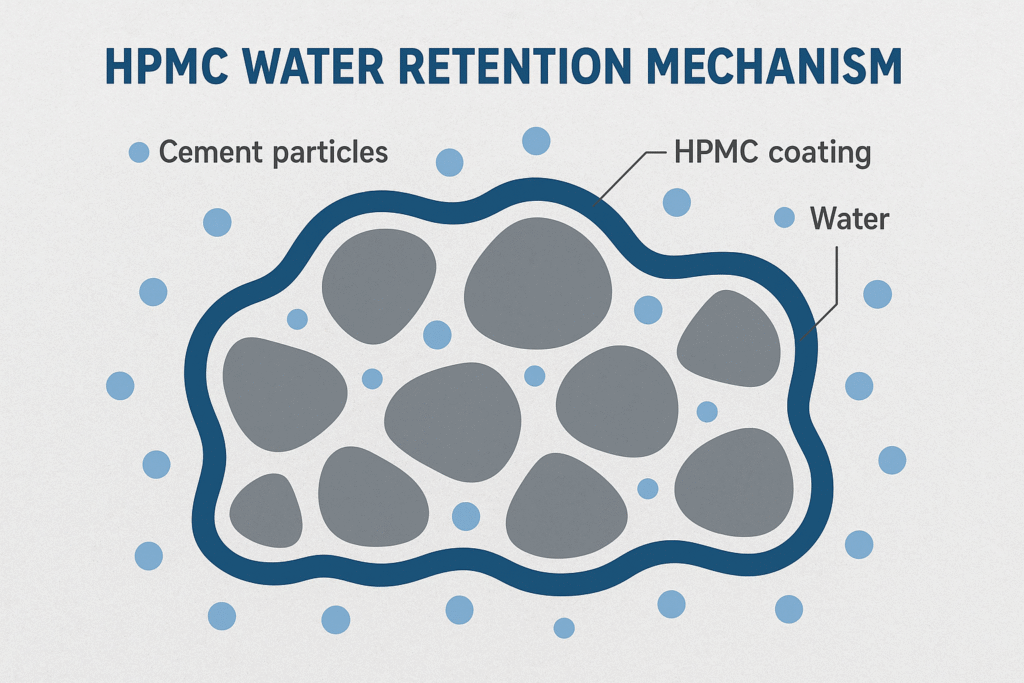
When I explain HPMC's role to customers, I use the analogy of a "temporary water reservoir." Imagine HPMC as a long molecular chain covered with tiny "hands" (hydroxyl groups) that grab onto water molecules. Once added to a cement mixture, these HPMC molecules unfold and create an invisible three-dimensional network throughout the material.
This network doesn't permanently trap the water - instead, it regulates its release in sync with the cement hydration process. The cement particles can gradually "drink" this stored water as needed. This regulated water supply ensures complete hydration of cement particles over time, which is crucial for developing maximum strength and durability.
In our laboratory tests, we've observed that adding just 0.2-0.5% HPMC to a cement formulation can increase water retention from around 60% to over 95%. This dramatic improvement prevents issues like premature drying, especially when applying mortar to highly absorbent substrates like dry brick or concrete.
Which additive improves the water retention capacity of mortar?
My clients often test various additives to solve water retention problems, wasting time and money on ineffective solutions.
HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose)1 is the most effective additive for improving water retention in mortars. Other cellulose ethers like HEMC (Hydroxyethyl Methylcellulose) and MC (Methylcellulose) also enhance water retention but with different performance characteristics. Starch derivatives and some synthetic polymers offer limited water retention but cannot match cellulose ethers' efficiency.
From my experience supplying additives to major construction material manufacturers across Saudi Arabia, UAE and other countries, I've seen firsthand how different water-retaining agents perform. While several options exist, cellulose ethers—particularly HPMC—consistently outperform other additives.
When comparing effectiveness, viscosity grade plays a crucial role. Higher viscosity HPMC (like 100,000 mPa·s) provides better water retention than lower viscosity grades (like 15,000 mPa·s). This is because higher viscosity grades form more extensive molecular networks with greater water-holding capacity.
The substitution pattern of HPMC also affects performance. Products with higher hydroxypropyl content often exhibit better water retention but may delay setting time slightly. Our factory can customize this balance based on your specific application needs.
Here's a comparison of common water retention additives based on our laboratory testing:
| Additive Type | Water Retention Capacity | Dosage Required | Cost Efficiency | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPMC | Excellent (95-98%) | 0.2-0.5% | High | Improves workability, adhesion |
| HEMC | Very Good (92-96%) | 0.2-0.6% | Medium-High | Better workability, less air entrainment |
| MC | Good (88-94%) | 0.3-0.7% | Medium | Economical option |
| Starch Derivatives | Moderate (70-85%) | 0.8-1.5% | Low-Medium | Economical but less effective |
| Synthetic Polymers | Variable (65-90%) | 0.5-1.2% | Low | May provide additional strength |
What are the benefits of HPMC?
Construction material manufacturers constantly struggle with product consistency and performance in different environmental conditions. Their products need to work reliably in both hot Saudi summers and cooler seasons.
HPMC provides multiple benefits including excellent water retention, improved workability, extended open time, enhanced adhesion, reduced sagging on vertical surfaces, and increased stability of air bubbles in the mix. It also improves freeze-thaw resistance and helps create consistent quality across different batches and environmental conditions.
I've worked with many large mortar factories facing production challenges, and HPMC has consistently solved multiple problems simultaneously. Beyond the primary water retention function, HPMC transforms construction materials in several important ways.
One significant advantage is workability improvement. HPMC adds lubrication between cement and aggregate particles, making the mixture more plastic and easier to apply. This reduces worker fatigue and increases productivity on construction sites. A customer in Pakistan reported that workers could cover 20-30% more area per day after they reformulated with our HPMC.
HPMC also extends open time—the period during which the mortar remains workable after mixing. This is particularly valuable in hot climates like Saudi Arabia or UAE where standard mortars can dry too quickly. Our high-performance HPMC grades can extend open time by 15-30 minutes even in temperatures exceeding 40°C.
The adhesion enhancement provided by HPMC is another critical benefit. By forming a film at the interface between mortar and substrate, HPMC increases bond strength by up to 40% in our laboratory tests. This translates to fewer callbacks for repairs and greater long-term durability of installations.
For vertical applications like wall tiling, HPMC's anti-sagging properties prevent tiles from sliding down before the adhesive sets. This is achieved through HPMC's ability to increase the yield stress of the mixture while maintaining good workability.
What is HPMC used for in construction?
Many new customers aren't aware of the full range of applications where HPMC can solve their formulation problems. They're missing opportunities to improve products across their entire line.
HPMC is widely used in tile adhesives3, self-leveling compounds4, renders, plasters, grouts, joint fillers, exterior insulation finishing systems (EIFS), gypsum-based products5, and cement-based waterproofing membranes. It's essential for dry-mix mortars, ensuring proper hydration and preventing cracking in various construction applications.
I've supplied HPMC to construction material manufacturers for over 15 years, and I'm continually impressed by how versatile this additive is. Each application leverages HPMC's properties in slightly different ways to solve specific challenges.
In tile adhesives, HPMC's water retention prevents premature drying when applying over porous substrates like concrete or brick. This ensures the cement has enough time to develop proper strength. Additionally, HPMC improves slip resistance, allowing heavier tiles to be fixed without sliding. Our customers typically use 0.3-0.5% HPMC in these formulations, with higher viscosity grade6s (60,000-100,000 mPa·s) for wall applications and medium viscosity grades (30,000-50,000 mPa·s) for floor applications.
Self-leveling compounds benefit from HPMC's ability to control rheology and water retention. The ideal HPMC for this application has carefully balanced water retention and set-retarding properties to allow air release while maintaining flowability. We recommend specific grades with modified particle size distribution that dissolve quickly without forming lumps.
For exterior rendering and plasters, HPMC prevents rapid water loss to the atmosphere, which is crucial for proper hydration and strength development. These applications typically require 0.1-0.3% HPMC with medium viscosity grades. Our factory has developed specialized HPMC varieties with enhanced resistance to alkaline degradation specifically for these high-pH environments.
EIFS (Exterior Insulation Finishing Systems)7 represent one of the most demanding applications. Here, HPMC must provide excellent water retention while also contributing to freeze-thaw resistance and long-term durability. Premium grades with optimized substitution patterns perform best in these systems.
Conclusion
HPMC transforms cement-based materials by creating a molecular water reservoir that ensures optimal hydration. This single additive improves water retention, workability, adhesion, and overall performance—making it essential for quality construction products.
-
Explore how HPMC enhances water retention and improves cement-based products for better durability. ↩ ↩
-
Understand the common challenges faced by manufacturers and how HPMC can help solve them. ↩
-
Find out what makes tile adhesives effective and how HPMC plays a role in their performance. ↩
-
Explore the properties and applications of self-leveling compounds in modern construction. ↩
-
Learn about the versatility of gypsum-based products and how HPMC enhances their performance. ↩
-
Understand the importance of viscosity in determining the effectiveness of HPMC in various applications. ↩
-
Discover the advantages of EIFS and how HPMC contributes to their effectiveness. ↩