Are you struggling to find a versatile construction additive that performs consistently? Many mortar and paint manufacturers face quality issues with substandard cellulose ethers1. HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose) might be the solution you need.
HPMC2 is a non-ionic cellulose ether widely used in construction materials, pharmaceuticals, and food products due to its excellent water retention, thickening, binding, film-forming, and adhesive properties. Its versatility makes it essential in tile adhesives, dry-mix mortars, gypsum plasters3, and various coating applications4.
I've spent over 15 years working with HPMC in our factory, testing countless formulations for clients worldwide. Our experience shows that understanding both the applications and properties of HPMC is crucial for selecting the right grade for your specific needs. Let's explore what makes this additive so valuable across different industries.
What Are the Key Applications of HPMC2 in Construction and Beyond?
Do you know why so many construction product manufacturers struggle with consistency? They're often using the wrong HPMC grade for their application. I see this mistake repeatedly when consulting with new clients.
HPMC serves as a critical additive in construction materials like cement mortars, gypsum-based products, and tile adhesives where it improves water retention, workability, adhesion strength, and sag resistance. Beyond construction, HPMC functions as a binder in pharmaceuticals, a thickener in food products, and a film-forming agent in personal care items.
When I visit client factories, I often find they're using generic HPMC grades across multiple product lines, which creates inconsistent results. HPMC applications vary significantly across industries, each requiring specific viscosity ranges and substitution levels. Let me break down the main application areas and what to look for:
Construction Applications
HPMC plays a crucial role in various construction materials, enhancing performance and workability:
| Application | HPMC Function | Recommended Viscosity | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cement-based mortars | Water retention agent | 100,000-200,000 mPa·s | Prevents premature dehydration, extends open time |
| Tile adhesives | Thickener and water retention | 15,000-30,000 mPa·s | Improves slip resistance, adhesion strength |
| Self-leveling compounds | Rheology modifier | 5,000-15,000 mPa·s | Controls flow properties, prevents segregation |
| Gypsum products | Binder and water retainer | 40,000-100,000 mPa·s | Extends working time, improves consistency |
| Exterior insulation systems | Thickener and adhesive | 20,000-50,000 mPa·s | Enhances cohesion, weather resistance |
In our factory, we've developed specialized HPMC grades for Middle Eastern markets where high temperatures demand exceptional water retention. For UAE and Saudi Arabian clients, we customize viscosity and particle size distribution to ensure optimal performance even in 45°C+ conditions.
What Are the Physical Properties of HPMC2 That Make It So Versatile?
Have you ever wondered why some batches of your products perform great while others fail? The physical properties of your HPMC might be inconsistent. This is a common issue I help clients solve.
HPMC exhibits distinctive physical properties including solubility in cold water but gel formation in hot water (thermal gelation), excellent film-forming capability, controlled viscosity5 (ranging from 5 to 200,000 mPa·s), and stability over a wide pH range (3-11). These properties make it versatile across numerous applications.
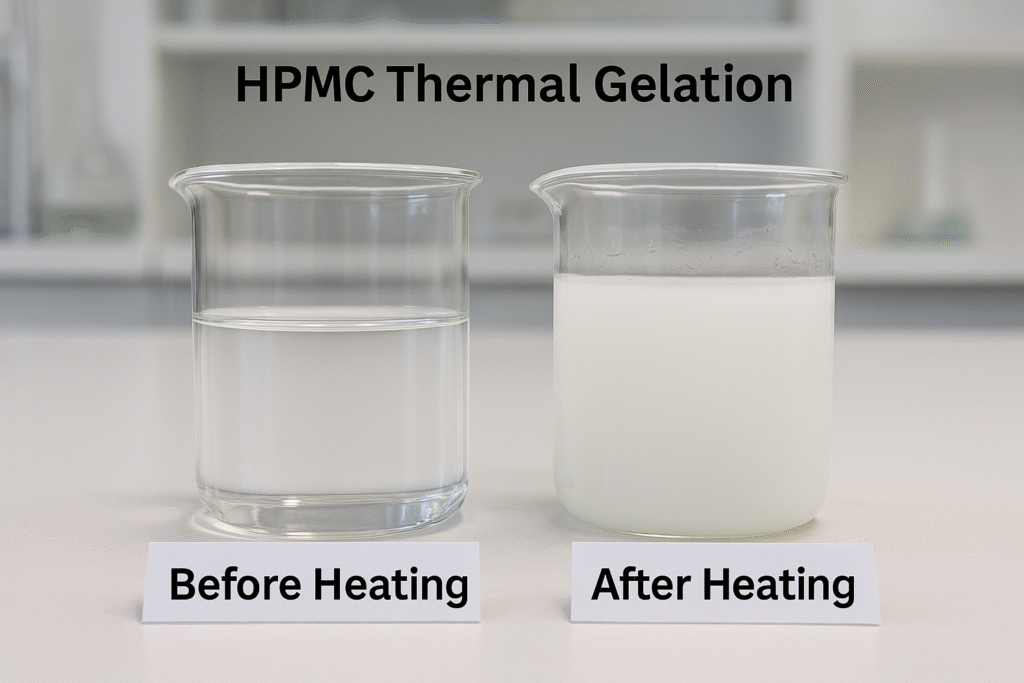
I remember testing HPMC samples from a client in Pakistan who was experiencing inconsistent setting times in their tile adhesive. Our analysis revealed significant variations in viscosity and particle size distribution from their supplier. The physical properties of HPMC directly impact final product performance, which is why understanding these characteristics is essential.
Critical Physical Properties of HPMC2
The performance of HPMC in any application depends on several key physical properties:
| Property | Description | Impact on Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | Resistance to flow, measured in mPa·s | Determines thickening efficiency and workability |
| Particle Size | Distribution of powder particles | Affects dissolution rate and incorporation into mixtures |
| Substitution Degree | Level of methoxyl and hydroxypropyl groups | Influences solubility, thermal gelation temperature |
| Surface Activity | Ability to reduce surface tension | Controls foam formation and stabilization |
| Thermal Gelation | Temperature at which HPMC forms a gel | Crucial for controlled release applications |
| Film Formation | Ability to create continuous films | Important for coating applications |
In our laboratory, we regularly measure these properties for quality control. For instance, we use advanced rheometers to test HPMC viscosity under various temperature conditions, simulating real-world application environments. This helps our clients in Vietnam and Philippines formulate products that perform consistently even during seasonal temperature changes.
What Are the Properties and Applications of Cellulose Acetate Compared to HPMC2?
Are your products requiring both water resistance and biodegradability? Many manufacturers confuse cellulose derivatives like HPMC and cellulose acetate, leading to formulation failures.
Cellulose acetate differs significantly from HPMC as it's water-insoluble but soluble in organic solvents, has excellent optical clarity, good dimensional stability, and biodegradability. It's primarily used in textiles, cigarette filters, film bases, eyeglass frames, and controlled release pharmaceutical coatings rather than construction applications.
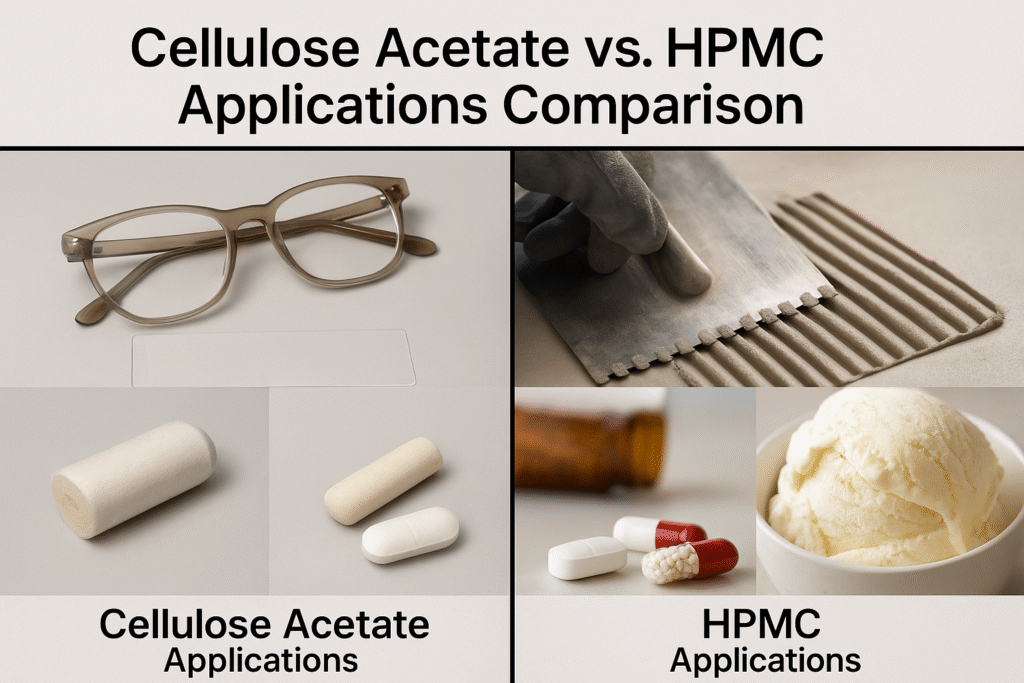
Last year, I consulted with a large Indian paint manufacturer who wanted to replace HPMC with cellulose acetate in their water-based formulations to improve water resistance. This was fundamentally misguided due to the different solubility profiles of these materials. Let me explain why these cellulose derivatives have complementary rather than interchangeable roles.
Comparing Cellulose Acetate and HPMC Properties and Applications
While both derived from cellulose, these materials have distinct properties that make them suitable for different applications:
| Property | Cellulose Acetate | HPMC |
|---|---|---|
| Water Solubility | Insoluble | Soluble in cold water |
| Organic Solvent Solubility | Soluble (acetone, etc.) | Generally insoluble |
| Biodegradability | Good | Excellent |
| Film Properties | Transparent, strong, rigid | Flexible, water-soluble |
| Main Applications | Textiles, filters, eyewear frames | Construction materials, pharmaceuticals, food |
| Processing Methods | Melt processing, solvent casting | Simple addition to water-based systems |
| Cost Comparison | Generally higher | Moderate |
In our product development work, we sometimes recommend hybrid systems where both cellulose derivatives are used—HPMC for initial setting and workability, and cellulose acetate-based coatings for water resistance in the final product. For our clients in Brazil and Mexico who manufacture exterior renders, this approach has provided excellent results in high-humidity conditions.
What Are the Essential Properties of Hypromellose That Matter for Your Applications?
Do you know if you're using the right grade of hypromellose for your specific application? Many of my clients initially select products based solely on price rather than performance specifications.
Hypromellose (pharmaceutical-grade HPMC6) features precisely controlled viscosity, substitution degree, particle size, and purity levels that make it suitable for pharmaceutical applications. Its key properties include controlled dissolution profiles, excellent film-forming capability, and compatibility with both aqueous and non-aqueous systems.

In my work with pharmaceutical excipient companies, I've noted that regulatory compliance is as important as physical properties. Hypromellose must meet specific pharmacopeia standards that construction-grade HPMC doesn't require. Understanding these distinctions helps manufacturers select the appropriate material for their application.
Key Properties and Specifications of Pharmaceutical-Grade Hypromellose
The pharmaceutical industry has strict requirements for hypromellose properties:
| Property | Specification | Importance in Pharmaceutical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity Precision | ±5% of labeled value | Critical for consistent manufacturing processes |
| Substitution Type | USP classification (2910, 2906, etc.) | Determines solubility and release characteristics |
| Heavy Metals Content | Typically <10 ppm | Essential for patient safety |
| Microbial Limits | <100 CFU/g | Prevents contamination risks |
| Residual Solvents | Meets ICH guidelines | Regulatory requirement for safety |
| Particle Size | Application-specific distribution | Affects dissolution and processing behavior |
Our specialized pharmaceutical-grade HPMC6 meets USP, EP, and JP specifications, making it suitable for regulated markets. For our clients in Singapore who manufacture tablets for export to multiple regions, we provide comprehensive documentation packages that facilitate regulatory submissions and ensure compliance with various pharmacopeias.
Conclusion
HPMC's versatile physical properties make it invaluable across construction, pharmaceuticals, and food industries. By selecting the right grade for your specific application, you can achieve consistent quality and avoid costly formulation failures.
-
Learn about cellulose ethers and how they impact the quality of construction materials. ↩
-
Explore the versatility of HPMC in construction materials and its critical role in enhancing performance. ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩ ↩
-
Find out why gypsum plasters are favored in construction and their advantages over other materials. ↩
-
Discover how HPMC enhances the performance of coatings in various industries. ↩
-
Understand the significance of viscosity in construction materials and its impact on formulation. ↩
-
Discover the specific applications and properties of pharmaceutical-grade HPMC in the industry. ↩ ↩







