Are you struggling to find the right thickening agent for your products? Poor viscosity control can ruin product performance and customer satisfaction. Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC)1 might be the solution you need.
Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC)1 is a non-ionic, water-soluble polymer derived from cellulose. It functions primarily as a thickener, stabilizer, and binder in various industries including construction, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and paints. HEC creates viscous solutions without changing product properties.

At Kehao, we've been manufacturing high-quality HEC for over a decade. Our customers often come to us confused about which cellulose derivative would work best for their specific applications. I'll explain everything you need to know about HEC, from its basic properties to its diverse applications across industries.
What is Hydroxyethyl Cellulose HEC Used For?
Pain points plague many manufacturers: unstable viscosity, poor water retention2, and formulation inconsistency. These issues can lead to product failure and wasted resources.
Hydroxyethyl cellulose is used primarily as a thickening agent, binder, stabilizer, and film-former in construction materials, paint, personal care products, pharmaceuticals, and oilfield applications. It provides consistent viscosity control, improved water retention, and enhanced product stability.
Construction Applications
HEC plays a crucial role in various construction materials. In my 15 years in the cellulose ether industry, I've seen how the right grade of HEC can dramatically improve mortar performance.
For cement-based products, HEC improves:
- Water retention (preventing too-rapid drying)
- Workability (making application easier)
- Adhesion (ensuring better bonding to surfaces)
- Sag resistance (allowing thicker application)
This is particularly important in hot, dry climates like Saudi Arabia and UAE, where many of our customers operate. In these environments, without proper water retention, mortars can dry before proper cement hydration, leading to weak structures and product failure.
The typical dosage ranges from 0.2% to 0.5% by weight, depending on the specific application:
| Application | Recommended HEC Dosage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Tile Adhesives | 0.2-0.3% | Water retention, extended open time |
| Joint Fillers | 0.3-0.4% | Sag resistance, smooth application |
| Renders/Plasters | 0.2-0.4% | Workability, crack reduction |
| Self-leveling Compounds | 0.1-0.2% | Flow control, defoaming |
What is the Use of HEC?
Are you frustrated with inconsistent product performance? Do your formulations lack stability or proper viscosity? These common problems can significantly impact your product quality.
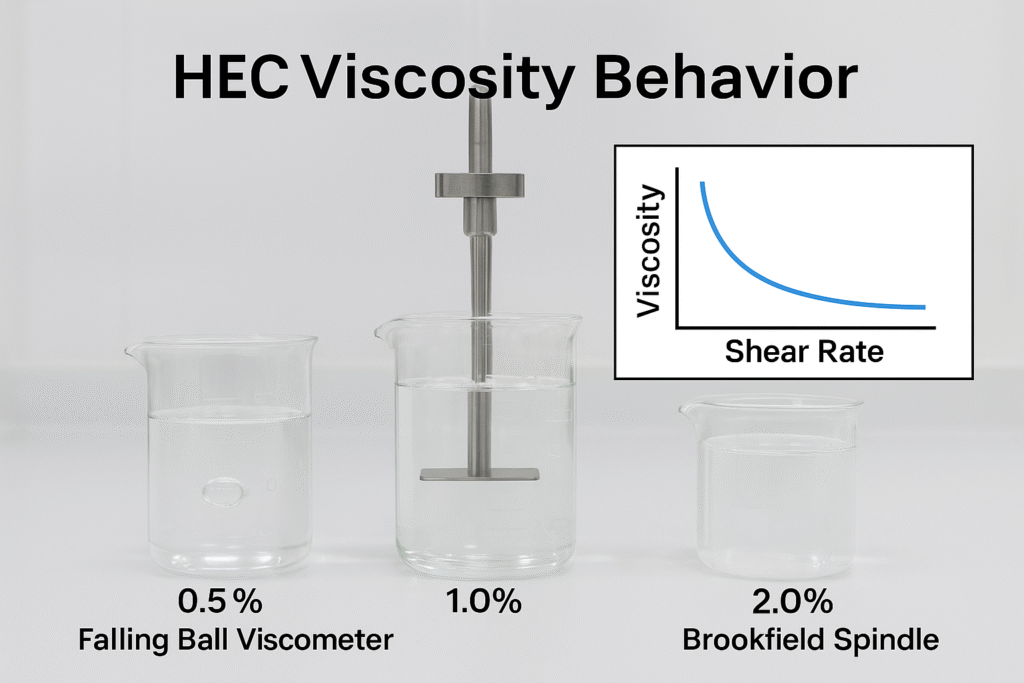
HEC functions as a versatile rheology modifier that enhances product stability, consistency, and performance. It creates pseudoplastic solutions that flow well during application but recover viscosity at rest. This property makes it valuable in paints, personal care products, and building materials.
Paint and Coating Applications
In my work with paint manufacturers across developing markets, I've observed how HEC transforms coating formulations. HEC serves multiple critical functions in water-based paints:
First, it provides the proper viscosity profile - allowing paints to flow smoothly during application but preventing drips and splatters. This is due to its pseudoplastic (shear-thinning) behavior, where viscosity decreases under stress but recovers when at rest.
Second, HEC acts as a protective colloid during storage, preventing pigment settling and separation. This extends shelf life and maintains color consistency - critical for maintaining brand reputation.
The molecular weight of HEC directly affects its performance in paint systems:
- Low molecular weight grades (30,000-90,000): Provide good leveling properties
- Medium grades (90,000-250,000): Offer balanced spatter resistance and application properties
- High molecular weight grades (250,000-720,000): Deliver maximum thickening and anti-sag properties
Many of our customers in India and Pakistan specifically request our HEC-H (high viscosity) grade for premium exterior paints that must withstand monsoon conditions. The enhanced water resistance and film strength prove invaluable in these challenging environments.
What is HEC in Skincare?
Does your skincare formulation feel sticky? Lack proper texture? Separate during storage? These issues not only affect customer experience but can also damage your brand reputation.
In skincare, HEC functions as a natural thickener and texture enhancer that creates smooth, gel-like consistencies without greasiness. It stabilizes emulsions3, improves product spreadability, and enhances the skin feel of lotions, creams, and gels while being gentle and non-irritating.

Personal Care and Cosmetic Applications
The personal care industry demands ingredients that perform consistently while meeting stringent safety requirements. HEC exceeds these expectations through its versatility and skin compatibility.
When formulating with HEC for cosmetic applications, manufacturers gain several advantages:
-
Texture control: HEC creates luxurious gel networks that provide structure without heaviness. The polymer chains form a three-dimensional matrix that holds water while maintaining a light skin feel - crucial for markets like Singapore and Vietnam where consumers prefer lightweight formulations.
-
Stability enhancement: By increasing the viscosity of the aqueous phase, HEC prevents coalescence in emulsions and inhibits phase separation. This ensures product integrity throughout the supply chain, particularly important when shipping to tropical climates.
-
Film-forming properties: Upon drying, HEC leaves a thin, flexible film on skin or hair that can deliver active ingredients while providing subtle conditioning effects.
-
Compatibility: Unlike some thickeners, HEC works effectively across a wide pH range (3-11) and remains stable in the presence of electrolytes, preservatives, and most active ingredients.
A pharmaceutical client in Brazil recently switched to our pharmaceutical-grade HEC for their topical gel formulations after experiencing batch inconsistencies with their previous supplier. By implementing proper dispersion techniques and selecting our precisely controlled viscosity grade, they achieved the ideal texture while reducing production time by 15%.
What is HEC Material?
Wondering about the exact nature of HEC? Confused by similar-sounding cellulose derivatives? Understanding the chemical composition helps you choose the right product for your needs.
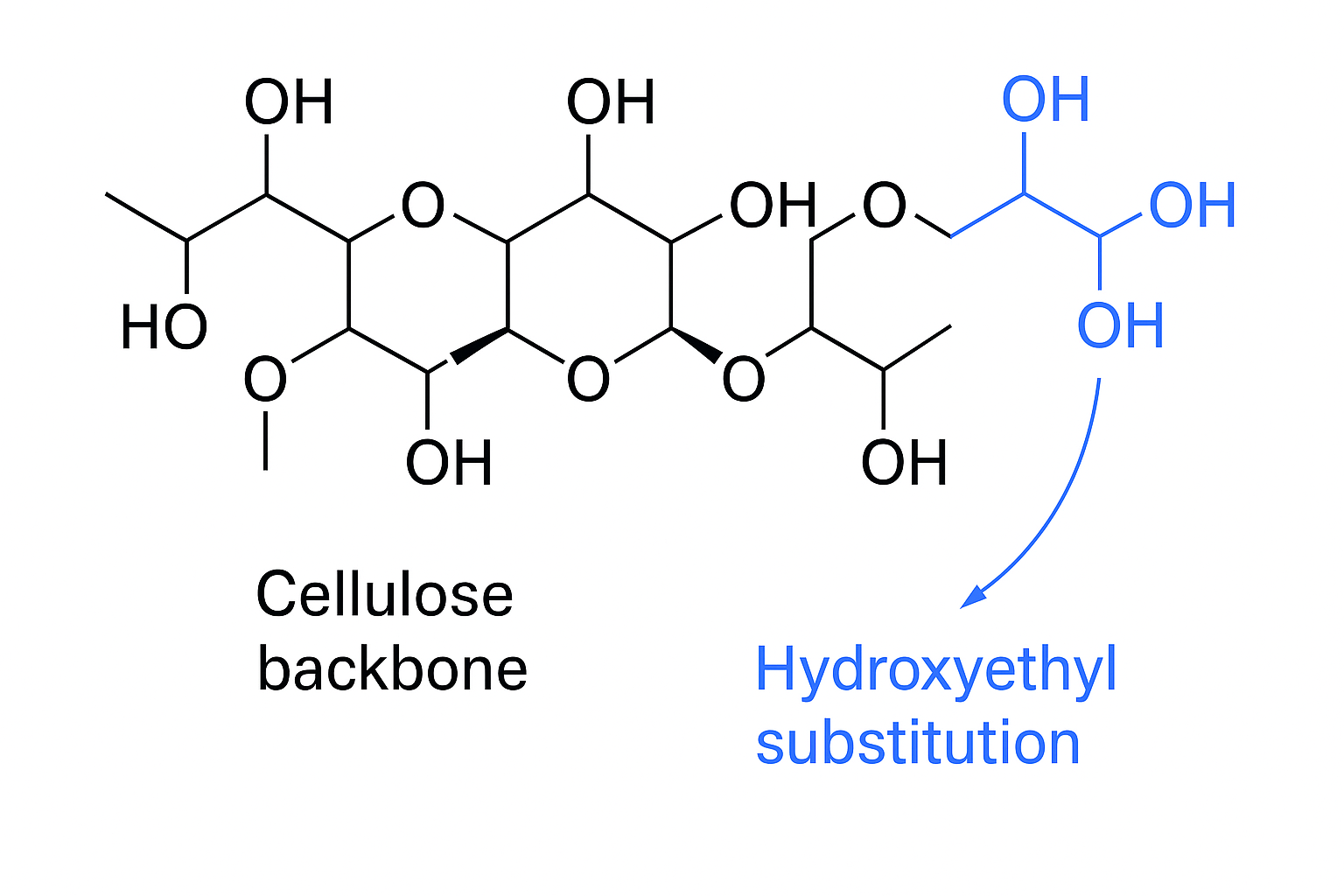
HEC material is a modified natural polymer created by reacting cellulose (from cotton or wood pulp) with ethylene oxide. This chemical modification adds hydroxyethyl groups to the cellulose backbone, making it water-soluble and providing thickening properties while maintaining its eco-friendly, biodegradable nature.
Manufacturing Process and Material Properties
At Kehao, we manufacture HEC through a carefully controlled process that determines its final properties and application suitability. Understanding this material science helps our customers select the optimal grade.
The production begins with high-purity cellulose, typically derived from sustainable wood pulp or cotton linters. This natural polymer undergoes alkaline treatment followed by reaction with ethylene oxide under precisely controlled conditions. The degree of substitution (DS) and molar substitution (MS) - technical terms that indicate how many hydroxyethyl groups are attached to each glucose unit - determine critical properties like solubility, viscosity stability, and salt tolerance.
Our quality control laboratory tests each batch for:
| Property | Test Method | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | Brookfield viscometer | Thickening efficiency |
| Moisture content | Infrared analysis | Storage stability |
| pH | Potentiometric | Compatibility with other ingredients |
| Particle size | Laser diffraction | Dissolution rate |
| Degree of substitution | Spectroscopic analysis | Chemical performance |
What makes HEC particularly valuable in modern formulations is its balance of performance and sustainability. Unlike synthetic thickeners derived from petroleum, HEC is biodegradable and has a favorable environmental profile. This aspect has become increasingly important to our customers in Mexico and Brazil, where regulatory requirements for eco-friendly materials continue to strengthen.
Several large mortar manufacturers in the Middle East have switched to our HEC for their tile adhesive formulations specifically because of its consistent quality batch-to-batch, which we achieve through rigorous process controls and standardized testing protocols.
Conclusion
Hydroxyethyl cellulose is a versatile, natural polymer that solves viscosity, stability, and performance issues across multiple industries. At Kehao, we provide customized HEC solutions with consistent quality to meet your specific application needs.







